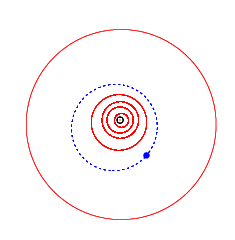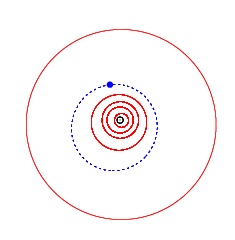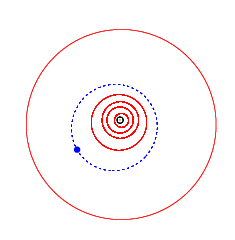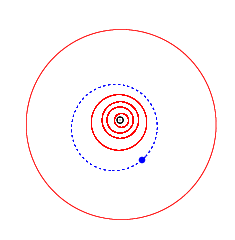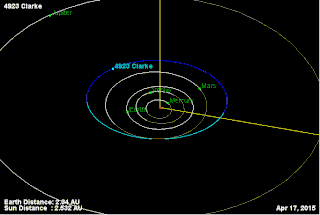
4923 Clarke, provisional designation 1981 EO27, is a stony background asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 3.5 kilometers (2.2 miles) in diameter. It was discovered on 2 March 1981, by American astronomer Schelte Bus at the Siding Spring Observatory in Australia. The spheroidal S-type asteroid has a rotation period of 3.14 hours. It was named after British science fiction writer Arthur C. Clarke. On the same night, Schelte Bus also discovered 5020 Asimov.

7166 Kennedy, provisional designation 1985 TR, is a stony Nysian asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 5 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 15 October 1985, by American astronomer Edward Bowell at Lowell's Anderson Mesa Station near Flagstaff, Arizona, in the United States. The asteroid was named after Malcolm Kennedy of the Astronomical Society of Glasgow.
6398 Timhunter, provisional designation 1991 CD1, is a stony Phocaea asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 5.5 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 10 February 1991, by American astronomer couple Carolyn and Eugene Shoemaker, in collaboration with Canadian astronomer David H. Levy at Palomar Observatory in California, United States. It was named for American amateur astronomer Tim Hunter.
4899 Candace, provisional designation 1988 JU, is a background asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 7 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 9 May 1988, by astronomer couple Carolyn and Eugene Shoemaker at the Palomar Observatory in California, United States. The asteroid was named after American chemist Candace Kohl.
12848 Agostino, provisional designation 1997 NK10, is a stony Eunomia asteroid from the central region of the asteroid belt, approximately 5 kilometers in diameter.
7385 Aktsynovia, provisional designation 1981 UQ11, is a background asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately between 4 and 9 kilometers in diameter, depending on its assumed spectral type. It was discovered on 22 October 1981, by Soviet–Russian astronomer Nikolai Chernykh at the Crimean Astrophysical Observatory in Nauchnyj on the Crimean peninsula.
19982 Barbaradoore is an eccentric, stony Phocaea asteroid and a recent Mars-crosser from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 5 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 22 January 1990, by American astronomer Eleanor Helin at the Palomar Observatory in California, United States. The asteroid was named after Barbara Doore, a cousin of the discoverer.
6084 Bascom, provisional designation 1985 CT, is a binary Phocaea asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 6.3 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 12 February 1985, by American astronomer couple Carolyn and Eugene Shoemaker at Palomar Observatory in California. It is named after American geologist Florence Bascom. Its satellite measures approximately 2.3 kilometers and has an orbital period of 43.51 hours.
4340 Dence, provisional designation 1986 JZ, is a background or Phocaea asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 8 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 4 May 1986, by American astronomer Carolyn Shoemaker at the Palomar Observatory in California. The S-type asteroid has a rotation period of 7.5 hours. It was named after Canadian geologist Michael R. Dence.
7225 Huntress, provisional designation 1983 BH, is a binary Florian asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 6 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 22 January 1983, by American astronomer Edward Bowell at Lowell's Anderson Mesa Station in Flagstaff, Arizona, United States. It is named after astrochemist Wesley Huntress.
21795 Masi (provisional designation 1999 SN9) is a Nysian asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 3 kilometers (2 miles) in diameter. It was discovered on 29 September 1999, by Italian amateur astronomer Franco Mallia at the Campo Catino Astronomical Observatory in Lazio, Italy. The likely S-type asteroid has a rotation period of 13.86 hours. It was named for Italian astronomer Gianluca Masi.
15350 Naganuma, provisional designation 1994 VB2, is a stony background asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 4.3 kilometers (2.7 miles) in diameter. It was discovered on 3 November 1994, by Japanese astronomers Yoshio Kushida and Osamu Muramatsu at the Yatsugatake South Base Observatory. The likely S-type asteroid has a rotation period of 2.5 hours. It was named for the town of Naganuma in northern Japan.
13154 Petermrva, provisional designation 1995 RC, is a stony Flora asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 4.2 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 7 September 1995, by Slovak astronomers Adrián Galád and Alexander Pravda at the Modra Observatory in the Bratislava Region of Slovakia. The asteroid was named after Slovak amateur astronomer Peter Mrva.
1979 Sakharov, provisionally designated 2006 P-L, is a stony Vestian asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 4.5 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered during the Palomar–Leiden survey in 1960, and named after Russian physicist Andrei Sakharov.
6376 Schamp, provisional designation 1987 KD1, is a stony background asteroid from the central regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 8 kilometers (5 miles) in diameter. It was discovered on 29 May 1987, by American astronomer couple Carolyn and Eugene Shoemaker at the Palomar Observatory in California. The S-type asteroid has a rotation period of 6.6 hours. It was named after Larry and Becky Schamp who took care of the Shoemaker family after Eugene's fatal car accident in Australia.
1405 Sibelius, provisional designation 1936 RE, is a stony Florian asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 8 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 12 September 1936, by Finnish astronomer Yrjö Väisälä at Turku Observatory in Southwest Finland. The asteroid was named after composer Jean Sibelius.
2391 Tomita, provisional designation 1957 AA, is a Nysian asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 15 kilometers in diameter. The asteroid was discovered on 9 January 1957, by German astronomer Karl Reinmuth at Heidelberg Observatory in southern Germany. It was named after Japanese astronomer Kōichirō Tomita.
4760 Jia-xiang, provisional designation 1981 GN1, is a background asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 5 kilometers (3 miles) in diameter. It was discovered on 1 April 1981, by astronomers at Harvard University's Oak Ridge Observatory in Massachusetts, United States. The presumed stony S-type asteroid was named after Chinese astronomer Zhang Jiaxiang. It has a rotation period of 14.96 hours.
2195 Tengström, provisional designation 1941 SP1, is a stony Florian asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 8 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 27 September 1941, by Finnish astronomer Liisi Oterma at Turku Observatory in Southwest Finland, and named for Swedish geodesist Erik Tengström.
(6265) 1985 TW3 (provisional designation 1985 TW3) is a background asteroid and binary system from the inner regions of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 11 October 1985, by astronomer by T. F. Fric and Richard Gilbrech at the Palomar Observatory in California. It is the only minor-planet discovery for these two astronomers. The stony L-type asteroid measures approximately 5 kilometers (3.1 miles) in diameter and has a rotation period of 2.7 hours. Its 1.2-kilometer sized minor-planet moon was discovered in July 2007 and announced the following month.