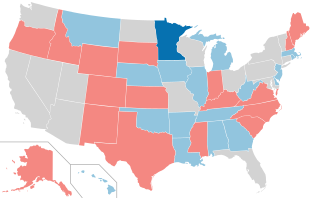
The 1990 United States Senate elections were held on Tuesday, November 6, 1990, with the 33 seats of Class 2 contested in regular elections. Special elections were also held to fill vacancies. The Democratic Party increased its majority with a net gain of one seat from the Republican Party. The election cycle took place in the middle of President George H. W. Bush's term, and as with most other midterm elections, the party not holding the presidency gained seats in Congress. This was the first time since 1980 that any party successfully defended all their own seats, and the first time Democrats did so since 1958.

The 1988 United States Senate elections were elections for the United States Senate. Held on November 8, 1988, the 33 seats of Class 1 were contested in regular elections. In spite of the Republican victory by George H. W. Bush in the presidential election, the Democrats gained a net of 1 seat in the Senate. 7 seats changed parties, with 4 incumbents being defeated. The Democratic majority in the Senate increased by one to 55–45.

The 1986 United States Senate elections were elections for the United States Senate. Held on November 4, in the middle of Ronald Reagan's second presidential term, the 34 seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections. The Republicans had to defend an unusually large number of freshman Senate incumbents who had been elected on President Ronald Reagan's coattails in 1980. Democrats won a net of eight seats, defeating seven freshman incumbents, picking up two Republican-held open seats, and regaining control of the Senate for the first time since January 1981. This remains the most recent midterm election cycle in which the sitting president's party suffered net losses while still flipping a Senate seat.

The 1984 United States Senate elections were held on November 6, with the 33 seats of Class 2 contested in regular elections. They coincided with the landslide re-election of President Ronald Reagan in the presidential election. In spite of the lopsided presidential race, Reagan's Republican Party suffered a net loss of two Senate seats to the Democrats, although it retained control of the Senate with a reduced 53–47 majority.

The 1980 United States Senate elections were held on November 4, coinciding with Ronald Reagan's victory in the presidential election. The 34 Senate seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections. Reagan's large margin of victory over incumbent Jimmy Carter gave a huge boost to Republican Senate candidates, allowing them to flip 12 Democratic seats and win control of the chamber for the first time since the end of the 83rd Congress in January 1955. This was the first time since 1966 that any party successfully defended all their own seats.

The 1978 United States Senate elections were held on November 7, in the middle of Democratic President Jimmy Carter's term. The 33 seats of Class 2 were contested in regular elections. Special elections were also held to fill vacancies.

The 1972 United States Senate elections were held on November 7, with the 33 seats of Class 2 contested in regular elections. They coincided with the landslide re-election of Republican President Richard Nixon. Despite Nixon's landslide victory, Democrats increased their majority by two seats. The Democrats picked up open seats in Kentucky and South Dakota, and defeated four incumbent senators: Gordon Allott of Colorado, J. Caleb Boggs of Delaware, Jack Miller of Iowa, and Margaret Chase Smith of Maine. The Republicans picked up open seats in New Mexico, North Carolina, and Oklahoma, and defeated one incumbent, William B. Spong Jr. of Virginia.

The 1958 United States Senate elections were elections for the United States Senate which occurred in the middle of President Dwight D. Eisenhower's second term. Thirty-two seats of Class 1 were contested in regular elections, the new state of Alaska held its first Senate elections for its Class 2 and 3 seats, and two special elections were held to fill vacancies.

The 1952 United States Senate elections was an election for the United States Senate which coincided with the election of Dwight D. Eisenhower to the presidency by a large margin. The 32 Senate seats of Class 1 were contested in regular elections, and three special elections were held to fill vacancies. The Republicans took control of the Senate by managing to make a net gain of two seats. However, Wayne Morse (R-OR) became an independent forcing Republicans to rely on Vice President Richard Nixon's tie-breaking vote, although Republicans maintained a 48–47–1 plurality. Wayne Morse would caucus with the Republicans at the start of Congress’ second session on January 6, 1954 to allow the GOP to remain in control of the Senate. This was the third time, as well as second consecutive, in which a sitting Senate leader lost his seat.

The 1932 United States House of Representatives elections were elections for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 73rd United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 8, 1932, while Maine held theirs on September 12. They coincided with the landslide election of President Franklin D. Roosevelt.

1914 United States House of Representatives elections were elections for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 64th United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 3, 1914, while Maine held theirs on September 14. They were held in the middle of President Woodrow Wilson's first term.

The 1888 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 6, 1888, with three states holding theirs early between June and September. They occurred at the same time as the election of President Benjamin Harrison. Elections were initially held for 325 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 38 states, to serve in the 51st United States Congress. Six new states would later join the union and increase the House to 332 seats. Special elections were also held throughout the year.
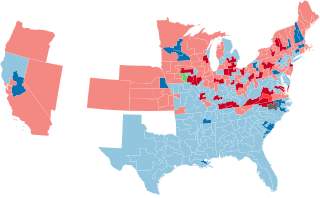
The 1886 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 2, 1886, with three states holding theirs early between June and September. They occurred in the middle of President Grover Cleveland's first term. Elections were held for 325 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 38 states, to serve in the 50th United States Congress. Special elections were also held throughout the year.

The 1882 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 7, 1882, with five states holding theirs early between June and October. They occurred during President Chester A. Arthur's term. Elections were held for 325 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 38 states, to serve in the 48th United States Congress. They were the first elections after reapportionment following the 1880 United States census, increasing the size of the House. Special elections were also held throughout the year.

The 1834–35 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 7, 1834, and November 5, 1835. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 24th United States Congress convened on December 7, 1835. They were held during President Andrew Jackson's second term. Elections were held for 240 seats that represented 24 states, as well as the at-large-district seat for the pending new state of Michigan.

The 1824–25 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 7, 1824, and August 30, 1825. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 19th United States Congress convened on December 5, 1825. Elections were held for all 213 seats, representing 24 states.

Michael F. Brennan is an American politician who formerly served as the 87th Mayor of Portland, Maine. Brennan, a Democrat, served as State Senator from 2002 to 2006 and Senate Majority Leader and a 2008 Democratic candidate for Maine's 1st congressional district. On May 15, 2011 Brennan announced his candidacy in the Portland, Maine mayoral election. On November 9, Brennan won the 15-candidate contest and became the first directly-elected mayor of Portland since 1923.
A Massachusetts general election was held on November 6, 1990 in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts.

The 1978 United States Senate election in Delaware was held on November 7, 1978. Incumbent Democratic senator Joe Biden won re-election to a second term, defeating Republican challenger James H. Baxter Jr. in a landslide victory. This is the first of five elections in which Biden won all counties.

The 1879 Maine gubernatorial election was held on September 8, 1879. Republican nominee Daniel F. Davis defeated Greenback nominee Joseph L. Smith and incumbent Governor Alonzo Garcelon. This election saw the continued rise of the newly popular Greenback party, it was an American political party with an anti-monopoly ideology which was active between 1874 and 1889.




















