| ← 1930 1931 1932 1933 1934 → Presidential election year | |
| Election day | November 8 |
|---|---|
| Incumbent president | Herbert Hoover (Republican) |
| Next Congress | 73rd |
| Presidential election | |
| Partisan control | Democratic gain |
| Popular vote margin | Democratic +17.8% |
| Electoral vote | |
| Franklin D. Roosevelt (D) | 472 |
| Herbert Hoover (R) | 59 |
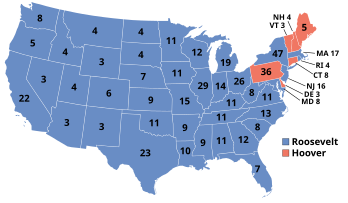 | |
| 1932 presidential election results. Red denotes states won by Hoover, blue denotes states won by Roosevelt. Numbers indicate the electoral votes won by each candidate. | |
| Senate elections | |
| Overall control | Democratic gain |
| Seats contested | 34 of 96 seats (32 Class 3 seats + 5 special elections) [1] |
| Net seat change | Democratic +12 |
 | |
| 1932 Senate results Democratic gain Democratic hold | |
| House elections | |
| Overall control | Democratic hold |
| Seats contested | All 435 voting members |
| Net seat change | Democratic +97 |
 | |
| 1932 House of Representatives results Democratic gain Democratic hold | |
| Gubernatorial elections | |
| Seats contested | 35 |
| Net seat change | Democratic +11 |
 | |
| 1932 gubernatorial election results Democratic gain Democratic hold | |
Elections were held on November 8, 1932, during the Great Depression. The presidential election coincided with U.S. Senate, U.S. House, and gubernatorial elections in several states. [2] [3] The election marked the end of the Fourth Party System and the start of the Fifth Party System. The election is widely considered to be a realigning election, and the newly established Democratic New Deal coalition experienced much more success than their predecessors had in the Fourth Party System. [4] The Democratic Party swept control of the White House and both chambers of Congress, ending 72 years of Republican dominance of the country that lasted since 1860 and Lincoln's presidency.
Democratic New York Governor Franklin D. Roosevelt defeated Republican incumbent president Herbert Hoover in a landslide, with Hoover winning only six Northeastern states. Roosevelt's victory was the first by a Democratic candidate since Woodrow Wilson won re-election in 1916. Roosevelt took his party's nomination on the fourth ballot, defeating 1928 nominee Al Smith and Speaker of the House John Nance Garner.
In addition to Hoover's defeat, the Republicans also suffered crushing defeats in both congressional chambers: they lost 101 seats in the House of Representatives, with the Democrats expanding their House majority to a supermajority, and also lost twelve seats in the Senate, [3] with Democrats winning control of the chamber for the first time since 1918. [5] This would be the last time that an incumbent president lost re-election and his party lost control of both chambers of Congress in a single term until 2020. [6] [7]
The election took place after the 1930 United States census and the subsequent congressional re-apportionment. The Reapportionment Act of 1929 provided a permanent method of apportioning 435 House seats; previously, Congress had had to pass apportionment legislation after each census.