| ← 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 → Presidential election year | |
| Election day | November 7, 2000 |
|---|---|
| Incumbent president | Bill Clinton (Democratic) |
| Next Congress | 107th |
| Presidential election | |
| Partisan control | Republican gain |
| Popular vote margin | Democratic +0.5% |
| Electoral vote | |
| George W. Bush (R) | 271 |
| Al Gore (D) | 266 |
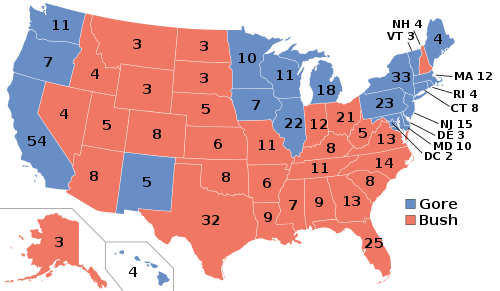 | |
| 2000 presidential election results. Red denotes states won by Bush, blue denotes states won by Gore. Numbers indicate the electoral votes won by each candidate. | |
| Senate elections | |
| Overall control | Republican hold [1] |
| Seats contested | 34 of 100 seats (33 Class I seats +1 special election) |
| Net seat change | Democratic +4 |
 | |
| 2000 Senate results Republican hold Republican gain Democratic hold Democratic gain | |
| House elections | |
| Overall control | Republican hold |
| Seats contested | All 435 voting members |
| Popular vote margin | Republican +0.5% |
| Net seat change | Democratic +1 |
 | |
| 2000 House of Representatives results (territorial delegate races not shown) Republican hold Republican gain Democratic hold Democratic gain Independent hold Independent gain | |
| Gubernatorial elections | |
| Seats contested | 14 (12 states, 2 territories) |
| Net seat change | Democratic +1 |
 | |
| 2000 gubernatorial election results Republican hold Democratic gain Democratic hold Popular Democratic gain Nonpartisan | |
Elections were held in the United States on November 7, 2000. Republican governor George W. Bush of Texas defeated Democratic Vice President Al Gore of Tennessee in the presidential election. Republicans retained control of both houses of Congress, giving the party unified control of Congress and the presidency for the first time since the 1954 elections.
Contents
- Federal elections
- President
- United States Senate
- United States House of Representatives
- State elections
- Gubernatorial elections
- State legislative elections
- Ballot Initiatives
- Local elections
- Mayoral elections
- References
- External links
With Democratic president Bill Clinton term-limited, Gore won his party's nomination by defeating Senator Bill Bradley in the Democratic primaries. Bush defeated Senator John McCain in the Republican primaries to win his party's presidential nomination. Bush took 271 of the 538 electoral votes, winning the decisive state of Florida by a margin of 537 votes after a recount was halted by the Supreme Court in the case of Bush v. Gore . Bush was the first winning presidential candidate to lose the popular vote since the 1888 presidential election. This marked the first time since 1988 where the winning presidential candidate's party failed to have any coattails in either house of Congress.
Democrats picked up a net of four seats in the Senate, tying Republicans, but Dick Cheney provided the tie-breaking vote as Vice President of the United States. Republicans maintained control of the chamber until June 6, 2001, when Senator Jim Jeffords left the Republican Party and began caucusing with the Democrats. Democrats also picked up a net of one seat in the House, but Republicans retained an overall narrow majority. In the gubernatorial elections, Democrats won a net gain of one seat.
