
The 1982 United States Senate elections were held on November 2, 1982. They were elections for the United States Senate following Republican gains in 1980. The 33 Senate seats of Class 1 were up for election in 1982. A total of four seats changed hands between parties, with Democrats winning seats in New Jersey and New Mexico, and Republicans taking seats in Nevada and the seat of the lone independent, Senator Harry Byrd Jr., in Virginia. Democrats made a net gain of one seat bringing them to 46 seats, while Republicans stayed at 54 seats for a majority. However, the Democratic gain in New Jersey replaced a Republican that had been appointed earlier in the year.

The 1972 United States Senate elections were held on November 7, with the 33 seats of Class 2 contested in regular elections. They coincided with the landslide re-election of Republican President Richard Nixon. Despite Nixon's landslide victory, Democrats increased their majority by two seats. The Democrats picked up open seats in Kentucky and South Dakota, and defeated four incumbent senators: Gordon Allott of Colorado, J. Caleb Boggs of Delaware, Jack Miller of Iowa, and Margaret Chase Smith of Maine. The Republicans picked up open seats in New Mexico, North Carolina, and Oklahoma, and defeated one incumbent, William B. Spong Jr. of Virginia.
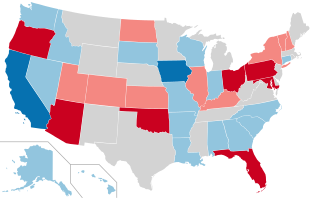
The 1968 United States Senate elections were elections for the United States Senate. Held on November 5, the 34 seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections. They coincided with the presidential election of the same year. The Republicans picked up five net seats in the Senate. This saw Republicans win a Senate seat in Florida for the first time since Reconstruction.

The 1966 United States Senate elections were elections on November 8, 1966, for the United States Senate which occurred midway through the second term of President Lyndon B. Johnson. The 33 seats of Class 2 were contested in regular elections. Special elections were also held to fill vacancies. With divisions in the Democratic base over the Vietnam War, and with the traditional mid-term advantage of the party not holding the presidency, the Republicans took three Democratic seats, thereby breaking Democrats' 2/3rds supermajority. Despite Republican gains, the balance remained overwhelmingly in favor of the Democrats, who retained a 64–36 majority. Democrats were further reduced to 63–37, following the death of Robert F. Kennedy in June 1968.

The 1964 United States Senate elections were held on November 3. The 33 seats of Class 1 were contested in regular elections. Special elections were also held to fill vacancies. They coincided with the election of President Lyndon B. Johnson by an overwhelming majority, to a full term. His Democratic Party picked up a net two seats from the Republicans. As of 2023, this was the last time either party has had a two-thirds majority in the Senate, which allowed the Senate Democrats to override a veto, propose constitutional amendments, or convict and expel certain officials without any votes from Senate Republicans. However, internal divisions would have prevented the Democrats from having done so. The Senate election cycle coincided with Democratic gains in the House in the same year.

The 1960 United States Senate elections coincided with the election of John F. Kennedy as president on November 8, 1960. The 33 seats of Class 2 were contested in regular elections. A special election was also held on June 28, 1960, for a mid-term vacancy in North Dakota where Democrats flipped a seat to expand their majority to 66–34. As Majority Leader Lyndon Johnson was elected Vice President, Mike Mansfield became the new majority leader.

The 1948 United States Senate elections were held concurrently with the election of Democratic President Harry S. Truman for a full term. The 32 seats of Class 2 were contested in regular elections, and one special election was held to fill a vacancy. Truman campaigned against an "obstructionist" Congress that had blocked many of his initiatives, and additionally, the U.S. economy recovered from the postwar recession of 1946–1947 by election day. Thus, Truman was rewarded with a Democratic gain of nine seats in the Senate, enough to give them control of the chamber. This was the last time until 2020 that Democrats flipped a chamber of Congress in a presidential election cycle.

The 1932 United States Senate elections coincided with Democrat Franklin D. Roosevelt's landslide victory over incumbent Herbert Hoover in the presidential election. The 32 seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections, and special elections were held to fill vacancies.

The 1930 United States Senate elections occurred in the middle of Republican President Herbert Hoover's term. The 32 seats of Class 2 were contested in regular elections, and special elections were held to fill vacancies. With the Great Depression beginning to take hold, Republican incumbents became unpopular, and Democrats picked up a net of eight seats, erasing the Republican gains from the previous election cycle, however, Republicans retained control of the chamber. This was the first of four consecutive Senate elections during the Depression in which Democrats made enormous gains, achieving a cumulative pick-up of 34 seats.

The 1912–13 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. They were the last U.S. Senate elections before the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, establishing direct elections for all Senate seats. Senators had been primarily chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1912 and 1913, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. Some states elected their senators directly even before passage of Seventeenth Amendment. Oregon pioneered direct election and experimented with different measures over several years until it succeeded in 1907. Soon after, Nebraska followed suit and laid the foundation for other states to adopt measures reflecting the people's will. By 1912, as many as 29 states elected senators either as nominees of their party's primary or in conjunction with a general election.
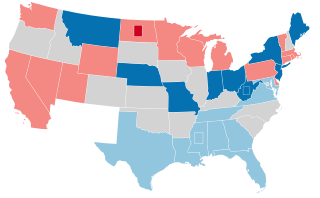
The 1910–11 United States Senate election were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were primarily chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1910 and 1911, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. However, some states had already begun direct elections during this time. Oregon pioneered direct election and experimented with different measures over several years until it succeeded in 1907. Soon after, Nebraska followed suit and laid the foundation for other states to adopt measures reflecting the people's will. By 1912, as many as 29 states elected senators either as nominees of their party's primary or in conjunction with a general election.

The North Carolina United States Senate election of 1978 was held on November 7, 1978 as part of the nationwide elections to the Senate. The general election was between the Republican incumbent Jesse Helms and the Democratic nominee John Ingram. Helms won re-election, by a slightly wider margin than in 1972. This was the first Senate election where Republicans were re-elected.

The 1876–77 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states, coinciding with Rutherford B. Hayes's narrow election as president. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1876 and 1877, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 2.

The 1944 United States Senate election in Pennsylvania was held on November 7, 1944. Incumbent Republican U.S. Senator James J. Davis sought re-election, but was defeated by Democratic nominee Francis J. Myers.

The 1930 United States Senate special election in Pennsylvania was held on November 4, 1930. Joseph R. Grundy, incumbent Republican appointed to fill the vacancy created by the unseating of William Scott Vare, was defeated for re-nomination. The Republican nominee, James J. Davis, defeated Democratic nominee Sedgwick Kistler to win the election.

The 1938 United States Senate election in Pennsylvania was held on November 8, 1938. Incumbent Republican U.S. Senator James J. Davis was re-elected to a second term in office over Democratic Governor George Howard Earle III.

The 1950 United States Senate election in Pennsylvania was held on November 7, 1950. Incumbent Democratic U.S. Senator Francis J. Myers sought re-election, but was defeated by Republican nominee James H. Duff. As of 2021, this is the last time that Lycoming County voted Democratic in a Senate election.

The 1916 United States Senate election in Missouri was held on November 7, 1916. Incumbent Democratic U.S. Senator James A. Reed was re-elected to a second term over Republican Walter S. Dickey.

Two United States Senate elections were held in Illinois on March 26, 1913. The two elections were interconnected through a compromise made to elect a Democrat in the regular election and a Republican in the special election.

The 1914 United States Senate election in Illinois took place on November 3, 1914.























