| | ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
The 1913 Pittsburgh mayoral election was held on Tuesday, November 4, 1913, in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Joseph G. Armstrong was elected mayor of Pittsburgh over Stephen G. Porter in a nonpartisan election.
| | ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
| Elections in Pennsylvania |
|---|
 |
The 1913 Pittsburgh mayoral election was held on Tuesday, November 4, 1913, in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Joseph G. Armstrong was elected mayor of Pittsburgh over Stephen G. Porter in a nonpartisan election.
The election in 1913 was the first Pittsburgh mayoral contest to be conducted under a new nonpartisan ballot law that eliminated party labels from ballots and replaced the party primaries with a nonpartisan blanket primary. [1]
In the early stages of the campaign, support formed around two candidates, public works director Joseph G. Armstrong and U.S. Representative Stephen G. Porter. Incumbent mayor William A. Magee, who by law was ineligible to run for a consecutive term, gave his support to Porter, as did longtime political boss William Flinn. U.S. Senators George T. Oliver and Boies Penrose and local Republican leader Max G. Leslie backed Armstrong. [1] [2]
There were six official candidates in the primary. [1] Although the candidates were officially non-partisan, the press identified Armstrong and Porter as Republicans, [3] Frank I. Gosser as a Democrat, [4] William J. Van Essen as a Socialist, [5] and Robert S. Glass as a Prohibitionist. [5] Victor Breitenstein styled himself as "the workingmen's independent candidate" but rejected a socialist label. [6]
Porter was the top vote-getter, edging second-place Armstrong by 302 votes. [1] The rest of the candidates together captured less than 10 percent of the vote, but this was enough to keep either Porter or Armstrong from attaining a majority. [7]
| Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stephen G. Porter | 35,206 | 45.6 | |
| Joseph G. Armstrong | 34,904 | 45.2 | |
| Frank I. Gosser | 5,418 | 7.0 | |
| William J. Van Essen | 1,464 | 1.9 | |
| Robert S. Glass | 152 | 0.2 | |
| Victor Breitenstein | 96 | 0.1 | |
| M.W. Clair | 1 | 0.0 | |
| Total votes | 77,241 | 100.0 | |
As no candidate received a majority of votes in the primary, a runoff election was held between the top two finishers, Porter and Armstrong. [1] This time Armstrong came out ahead of Porter, by a margin of 2,440 votes. [8]
| Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Joseph G. Armstrong | 39,912 | 51.6 | |
| Stephen G. Porter | 37,472 | 48.4 | |
| Total votes | 77,384 | 100.0 | |

Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 3, 1908. Republican Party nominee William Howard Taft defeated threetime Democratic nominee William Jennings Bryan. Incumbent President Theodore Roosevelt honored his promise not to seek a third term, and persuaded his close friend, Taft, to become his successor. With Roosevelt's support, Taft won the presidential nomination at the 1908 Republican National Convention on the first ballot. The Democratic Party nominated Bryan, who had been defeated twice previously, in 1896 and 1900, by Republican William McKinley.
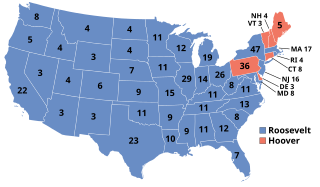
Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 8, 1932. Against the backdrop of the Great Depression, incumbent Republican President Herbert Hoover was defeated in a landslide by Democrat Franklin D. Roosevelt, the governor of New York and the vice presidential nominee of the 1920 presidential election. The election marked the effective end of the Fourth Party System, which had been dominated by Republicans, and it was the first time since 1916 that a Democrat was elected president.

The mayor of New York City is elected in early November every four years, in the year immediately following a United States presidential election year, and takes office at the beginning of the following year. The city, which elects the mayor as its chief executive, consists of the five boroughs, which consolidated to form "Greater" New York on January 1, 1898.

The 1912–13 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. They were the last U.S. Senate elections before the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, establishing direct elections for all Senate seats. Senators had been primarily chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1912 and 1913, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. Some states elected their senators directly even before passage of Seventeenth Amendment. Oregon pioneered direct election and experimented with different measures over several years until it succeeded in 1907. Soon after, Nebraska followed suit and laid the foundation for other states to adopt measures reflecting the people's will. By 1912, as many as 29 states elected senators either as nominees of their party's primary or in conjunction with a general election.

The 1914 New York state election was held on November 3, 1914, to elect the governor, the lieutenant governor, the Secretary of State, the state comptroller, the attorney general, the state treasurer, the state engineer, a U.S. Senator and a judge of the New York Court of Appeals, as well as all members of the New York State Assembly and the New York State Senate, and delegates-at-large to the New York State Constitutional Convention of 1915.

The 1918 California gubernatorial election was held on November 5, 1918. William Stephens had defeated James Rolph for the Republican nomination and won the general election in a landslide after Rolph was denied the Democratic Party's nomination. Stephens was the first governor elected with an absolute majority of the vote since Henry Gage in 1898 and won the highest share of the vote since Frederick Low in 1863.
In American politics, cross-filing occurs when a candidate runs in the primary election of not only their own party, but also that of one or more other parties, generally in the hope of reducing or eliminating their competition at the general election. It was in effect in California from 1913 to 1959, when it was abolished, and has been used in other states, most significantly in New York and New Hampshire, where it is still in effect.

The Mayoral election of 1933 in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania was held on Tuesday, November 6, 1933. In a realigning election, Democrats regained control of the mayor's office for the first time in twenty-eight years; they have not relinquished this position since.

The 1862–63 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states, occurring during the American Civil War. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1862 and 1863, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 1.
A Massachusetts general election was held on November 3, 1964, in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts.

The 1929 Los Angeles mayoral election took place on June 9, 1929. Incumbent George E. Cryer chose not contest the election and retire from office, making it the first open seat since 1911. The race was won by John Clinton Porter, who defeated Councilman William G. Bonelli, John R. Quinn, and 11 other candidates.

The 2017 United States elections were held, in large part, on Tuesday, November 7, 2017. This off-year election featured gubernatorial elections in Virginia and New Jersey, as well as state legislative elections in both houses of the New Jersey Legislature and in the Virginia House of Delegates. Numerous citizen initiatives, mayoral races, and a variety of other local elections also occurred. Special elections were also held for one seat of the U.S. Senate, representing Alabama, and six seats of the U.S. House of Representatives. The Democrats picked up the governorship in New Jersey and the Alabama Senate seat that was up for a special election. The governorship in Virginia and the six House seats that were up for special elections did not change party hands.

One justice of the seven-member North Carolina Supreme Court and five judges of the 15-member North Carolina Court of Appeals were elected by North Carolina voters on November 8, 2016, concurrently with other state elections. Terms for seats on each court are eight years.

The 1930 Massachusetts gubernatorial election was held on November 4, 1930.

The 1926 Massachusetts gubernatorial election was held on November 2, 1926.

The 2020 Alaska Senate elections took place as part of the biennial 2020 United States elections. Voters in Alaska elected state senators in 11 of the state's 20 senate districts – the usual ten plus one special election. State senators serve four-year terms in the Alaska Senate, with half seats up for election every two years. Primary elections on August 18, 2020, determined which candidates appeared on the general election ballot on November 3, 2020.

The 2020 Fresno mayoral election was held on March 3, 2020, to elect the mayor of Fresno, California. Republican Jerry Dyer was elected after winning a majority in the primary.

The 1921 Pittsburgh mayoral election was held on Tuesday, November 8, 1921. Republican nominee William A. Magee was elected by a large margin over Democratic candidate William N. McNair.

The 1917 Pittsburgh mayoral election was held on Tuesday, November 6, 1917. Edward V. Babcock was elected over William A. Magee in a nonpartisan election.

Beginning shortly after the city's incorporation as a city in 1846, elections have been held in the mayor of Manchester, New Hampshire. The following article provides information on the elections for mayor in the city during the 20th century.
| Preceded by 1909 | Pittsburgh mayoral election 1913 | Succeeded by 1917 |