
Raymond Philip Shafer was an American attorney and politician who served as the 39th governor of Pennsylvania from 1967 to 1971. Prior to that, he served as the 23rd lieutenant governor of Pennsylvania from 1963 to 1967 and as a Pennsylvania state senator from 1959 to 1962. He was a national leader of the moderate wing of the Republican Party in the late 1960s.

William Warren Scranton was an American Republican Party politician and diplomat. Scranton served as the 38th governor of Pennsylvania from 1963 to 1967, and as United States Ambassador to the United Nations from 1976 to 1977. "Many who serve as governor today are still measured against Bill Scranton's leadership - some 50 years later," said former state Republican National Committeewoman Elsie Hillman when she learned of Scranton's death in 2013.

Richardson K. Dilworth was an American Democratic Party politician who served as the 91st mayor of Philadelphia from 1956 to 1962. He twice ran as the Democratic nominee for governor of Pennsylvania, in 1950 and in 1962. He is to date the last White Anglo-Saxon Protestant mayor of Philadelphia.

The 2006 Pennsylvania gubernatorial election was held on November 7, 2006 and included the races for the Governor of Pennsylvania and Lieutenant Governor of Pennsylvania. Incumbent Democratic Governor Ed Rendell successfully ran for re-election. Pennsylvania's first female lieutenant governor, Catherine Baker Knoll, was also running for re-election.

William H. Milliken Jr. was an American politician from Pennsylvania who served as a Republican member of the U.S. House of Representatives for Pennsylvania's 7th congressional district from 1959 to 1965. He served in the Pennsylvania House of Representatives for Delaware County from 1943 to 1946 and from 1949 to 1950.

The 2002 Pennsylvania gubernatorial election was held on November 5, 2002, to elect the Governor and Lieutenant Governor of Pennsylvania. Incumbent Republican governor Mark Schweiker, who took office in 2001 when Tom Ridge resigned to become Homeland Security Advisor, was eligible to run for a full term, but did not do so. Democrat Ed Rendell, the former mayor of Philadelphia and Chairman of the Democratic National Committee, emerged from a competitive primary to win the general election against Republican Pennsylvania Attorney General Mike Fisher.

The 1994 Pennsylvania gubernatorial election was held on November 8, 1994. The incumbent governor, Bob Casey, Sr. (Democrat), was barred from seeking a third term by the state constitution. The Republican Party nominated Congressman Tom Ridge, while the Democrats nominated Mark Singel, Casey's lieutenant governor. Ridge went on to win the race with 45% of the vote. Singel finished with 39%, and Constitution Party candidate Peg Luksik finished third, garnering 12% of the vote.

The 1990 Pennsylvania gubernatorial election was held on November 6, 1990. Incumbent Democratic governor Robert P. Casey easily defeated Republican Barbara Hafer. Governor Casey defeated Hafer by a margin of 35.29%, and carried 66 out of 67 Pennsylvania counties.

The 1986 Pennsylvania gubernatorial election was held on November 4, 1986. Democrat Bob Casey narrowly defeated Republican Bill Scranton III, in a race that featured two very high-profile candidates. As of 2022, this is the most recent Pennsylvania gubernatorial race to have a margin within five points for either party.

The 1982 Pennsylvania gubernatorial election was held on November 2, 1982, between incumbent Republican Dick Thornburgh and Democratic U.S. Congressman Allen E. Ertel. Thornburgh was a popular incumbent, who largely was the favorite throughout the race. However, owing to a nationwide recession which hit the state particularly hard, and a backlash to Reaganomics, the final result ended up becoming much closer than what was initially anticipated.

The 1978 Pennsylvania gubernatorial election was held on November 7, 1978. Incumbent Governor Milton Shapp was constitutionally ineligible to run for a third consecutive term in office. Republican Dick Thornburgh defeated Democrat Pete Flaherty in the general election.

The 1970 Pennsylvania gubernatorial election was held on November 3. Democrat Milton Shapp challenged incumbent Republican Lieutenant Governor Ray Broderick.

The 1966 Pennsylvania gubernatorial election was held on November 8. Republican Ray Shafer, the state's incumbent Lieutenant Governor, was elected to the state's highest office after holding off a charge from future governor Milton Shapp.

The 1954 Pennsylvania gubernatorial election was held on November 2. In what is considered a crucial realigning election for the state, Democratic State Senator George M. Leader defeated Republican incumbent Lieutenant Governor Lloyd Wood by a large margin, becoming the first Democrat to be elected governor since 1934.
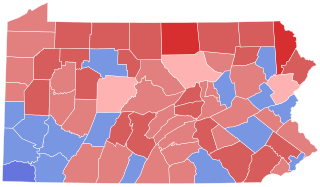
The 1950 Pennsylvania gubernatorial election was held on November 7. For the twenty-second time in twenty-five elections, the Republican candidate was victorious, but by a much smaller than usual margin. Superior Court Judge John S. Fine defeated Democrat Richardson Dilworth, the City Controller of Philadelphia. This election marked the last time until 2022 that a political party would win three consecutive gubernatorial elections in Pennsylvania.

The 1951 Philadelphia municipal election, held on Tuesday, November 6, was the first election under the city's new charter, which had been approved by the voters in April, and the first Democratic victory in the city in more than a half-century. The positions contested were those of mayor and district attorney, and all seventeen city council seats. There was also a referendum on whether to consolidate the city and county governments. Citywide, the Democrats took majorities of over 100,000 votes, breaking a 67-year Republican hold on city government. Joseph S. Clark Jr. and Richardson Dilworth, two of the main movers for the charter reform, were elected mayor and district attorney, respectively. Led by local party chairman James A. Finnegan, the Democrats also took fourteen of seventeen city council seats, and all of the citywide offices on the ballot. A referendum on city-county consolidation passed by a wide margin. The election marked the beginning of Democratic dominance of Philadelphia city politics, which continues today.

The 1955 Philadelphia municipal election, held on Tuesday, November 8, involved contests for mayor, district attorney, all seventeen city council seats, among other offices. Citywide, the Democrats took majorities of over 130,000 votes, continuing their success from the elections four years earlier. Richardson Dilworth, who had been elected district attorney in 1951, was elected mayor. Victor H. Blanc, a city councilman, was elected district attorney. The Democrats also kept fourteen of seventeen city council seats, losing one district seat while gaining another, and kept control of the other citywide offices. The election represented a further consolidation of control by the Democrats after their citywide victories of four years earlier.

1959 Philadelphia's municipal election, held on November 3, involved contests for mayor, all seventeen city council seats, and several other executive and judicial offices. Citywide, the Democrats took majorities of over 200,000 votes, continuing their success from the elections four years earlier. Richardson Dilworth, who had been elected mayor in 1955, was re-elected over Republican nominee Harold Stassen. The Democrats also took fifteen of seventeen city council seats, the most seats allowed to any one party under the 1951 city charter. They further kept control of the other citywide offices. The election represented a continued consolidation of control by the Democrats after their citywide victories of the previous eight years.

Philadelphia's municipal election of November 7, 1961, involved the election of the district attorney, city controller, and several judgeships. Democrats swept all of the city races but saw their vote totals much reduced from those of four years earlier, owing to a growing graft scandal in city government. District Attorney James C. Crumlish, Jr. and City Controller Alexander Hemphill, both incumbents, were returned to office. Several ballot questions were also approved, including one permitting limited sales of alcohol on Sundays.

The 1963 Philadelphia's municipal election, held on November 5, involved contests for mayor, all seventeen city council seats, and several other executive and judicial offices. The Democrats lost vote share citywide and the Republicans gained one seat in City Council, but the Democratic acting mayor, James Tate, was elected to a full term and his party maintained their hold on the city government. The election was the first decline in the Democrats' share of the vote since they took control of the city government in the 1951 elections, and showed the growing tension between the reformers and ward bosses within their party.

















