
The 1986 United States Senate elections were elections for the United States Senate. Held on November 4, in the middle of Ronald Reagan's second presidential term, the 34 seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections. The Republicans had to defend an unusually large number of freshman Senate incumbents who had been elected on President Ronald Reagan's coattails in 1980. Democrats won a net of eight seats, defeating seven freshman incumbents, picking up two Republican-held open seats, and regaining control of the Senate for the first time since January 1981. This remains the most recent midterm election cycle in which the sitting president's party suffered net losses while still flipping a Senate seat.

The 1984 United States Senate elections were held on November 6, with the 33 seats of Class 2 contested in regular elections. They coincided with the landslide re-election of President Ronald Reagan in the presidential election. In spite of the lopsided presidential race, Reagan's Republican Party suffered a net loss of two Senate seats to the Democrats, although it retained control of the Senate with a reduced 53–47 majority. Democrats defeated incumbents in Illinois and Iowa, and won an open seat in Tennessee, while Republicans defeated an incumbent in Kentucky.

The 1978 United States Senate elections were held on November 7, in the middle of Democratic President Jimmy Carter's term. The 33 seats of Class 2 were contested in regular elections. Special elections were also held to fill vacancies.

The 1976 United States Senate elections was an election for the United States Senate. Held on November 2, the 33 seats of Class 1 were contested in regular elections. They coincided with Democrat Jimmy Carter's presidential election and the United States Bicentennial celebration. Although almost half of the seats decided in this election changed parties, Carter's narrow victory did not provide coattails for the Democratic Party. Each party flipped seven Senate seats, although, one of the seats flipped by Democrats was previously held by a Conservative.

The 1972 United States Senate elections were held on November 7, with the 33 seats of Class 2 contested in regular elections. They coincided with the landslide re-election of Republican President Richard Nixon. Despite Nixon's landslide victory, Democrats increased their majority by two seats. The Democrats picked up open seats in Kentucky and South Dakota, and defeated four incumbent senators: Gordon Allott of Colorado, J. Caleb Boggs of Delaware, Jack Miller of Iowa, and Margaret Chase Smith of Maine. The Republicans picked up open seats in New Mexico, North Carolina, and Oklahoma, and defeated one incumbent, William B. Spong Jr. of Virginia.

The 1958 United States Senate elections were elections for the United States Senate which occurred in the middle of President Dwight D. Eisenhower's second term. Thirty-two seats of Class 1 were contested in regular elections, the new state of Alaska held its first Senate elections for its Class 2 and 3 seats, and two special elections were held to fill vacancies.

The 1950 United States Senate elections occurred in the middle of Harry S. Truman's second term as president. The 32 seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections, and four special elections were held to fill vacancies. As with most 20th-century second-term midterms, the party not holding the presidency made significant gains. The Republican opposition made a net gain of five seats, taking advantage of the Democratic administration's declining popularity during the Cold War and the aftermath of the Recession of 1949. The Democrats held a narrow 49-to-47-seat majority after the election. This was the first time since 1932 that the Senate majority leader lost his seat, and the only instance of the majority leader losing his seat while his party retained the majority.

Walter Stephan Baring Jr. was an American World War II veteran and politician who served ten terms as a United States representative from Nevada during the mid-20th century.

David Gilmer Towell was an American politician who served a single term as a U.S. Representative from Nevada, representing the state's at-large district. He was a Republican.
A Massachusetts general election was held on November 6, 1990 in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts.

The 1976 United States Senate election in New York was held on November 2, 1976. Incumbent Republican U.S. Senator James L. Buckley ran for re-election to a second term, but was defeated by Democratic diplomat Pat Moynihan. As of 2024, this is the last time an incumbent Senator from New York lost re-election to this seat.

The 1920 United States Senate election in Arizona took place on November 2, 1920. Incumbent Democratic U.S. Senator Marcus A. Smith ran for reelection to a third term, but was defeated by former Delegate to the U.S. House of Representatives from the Arizona Territory Ralph H. Cameron in the general election. Cameron would become the first Republican elected to the office of U.S. Senator from Arizona since the state joined the union in 1912. The same year, Republican Governor Thomas Edward Campbell was reelected to a second term.
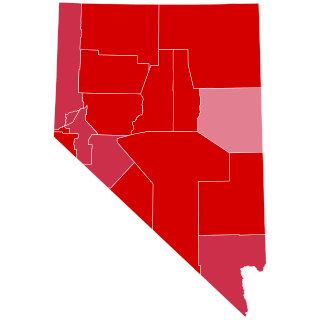
The 1984 United States presidential election in Nevada took place on November 6, 1984. All 50 states and the District of Columbia, were part of the 1984 United States presidential election. State voters chose four electors to the Electoral College, which selected the president and vice president of the United States.
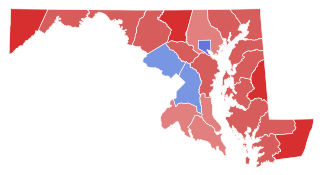
The 1970 United States Senate election in Maryland took place on November 3, 1970. Incumbent Democratic U.S. Senator Joseph Tydings ran for re-election to a second term, but was narrowly defeated by Republican U.S. Representative J. Glenn Beall Jr.

The 1968 United States House of Representatives election in Nevada was held on Tuesday November 5, 1968, to elect the state's at-large representative. This election occurred during the 1968 United States presidential election. Incumbent Democrat, Walter S. Baring Jr. won re-election to a ninth term in congress by a landslide margin of 44.29% winning every county in the state with over 60% of the vote.

The 1978 United States Senate election in Wyoming was held on November 7, 1978. Incumbent Republican Senator Clifford Hansen declined to seek a third term in office. Former State Representative Alan K. Simpson, the son of former Senator Milward Simpson, won a contested Republican primary and faced Raymond B. Whitaker, the 1960 Democratic nominee for the Senate, in the general election. Despite a favorable environment for Republicans nationwide, Simpson's performance decreased considerably from Hansen's 1972 landslide. Nonetheless, he easily defeated Whitaker, winning 62% of the vote to Whitaker's 38%.

The 1978 United States House of Representatives election in Nevada was held on Tuesday November 7, 1978, to elect the state's at-large representative. Primary elections were held on September 12, 1978.

The 1974 United States House of Representatives election in Nevada was held on Tuesday November 5, 1974, to elect the state's at-large representative. Primary elections were held on September 3, 1974.

The 1976 United States House of Representatives election in Nevada was held on Tuesday November 2, 1976, to elect the state's at-large representative. Primary elections were held on September 2, 1976.

The 1970 United States House of Representatives election in Nevada was held on Tuesday November 3, 1970, to elect the state's at-large representative. Primary elections were held on September 1, 1970.




















