Related Research Articles
This article concerns the period 229 BC – 220 BC.

This article concerns the 200 BC decade, that lasted from 209 BC to 200 BC.
This article concerns the period 159 BC – 150 BC.
This article concerns the period 239 BC – 230 BC.
This article concerns the period 179 BC – 170 BC.
This article concerns the period 189 BC – 180 BC.
This article concerns the period 199 BC – 190 BC.
Year 150 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Flamininus and Balbus. The denomination 150 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 200 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Maximus and Cotta. The denomination 200 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 205 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Scipio and Dives. The denomination 205 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 196 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Purpureo and Marcellus. The denomination 196 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 193 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Merula and Thermus. The denomination 193 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming a year.
Year 154 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Opimius and Albinus/Glabrio. The denomination 154 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 230 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Barbula and Pera. The denomination 230 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Philip V was king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon from 221 to 179 BC. Philip's reign was principally marked by the Social War in Greece and a struggle with the emerging power of the Roman Republic. He would lead Macedon against Rome in the First and Second Macedonian Wars. While he lost the latter, Philip later allied with Rome against Antiochus III in the Roman-Seleucid War. He died in 179 BC from illness after efforts to recover the military and economic condition of Macedonia and passed the throne onto his elder son, Perseus of Macedon.
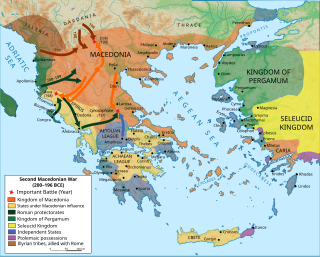
The Second Macedonian War was fought between Macedon, led by Philip V of Macedon, and Rome, allied with Pergamon and Rhodes. Philip was defeated and was forced to abandon all possessions in southern Greece, Thrace and Asia Minor. During their intervention, although the Romans declared the "freedom of the Greeks" against the rule from the Macedonian kingdom, the war marked a significant stage in increasing Roman intervention in the affairs of the eastern Mediterranean, which would eventually lead to Rome's conquest of the entire region.

Hellenistic Greece is the historical period of the country following Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the annexation of the classical Greek Achaean League heartlands by the Roman Republic. This culminated at the Battle of Corinth in 146 BC, a crushing Roman victory in the Peloponnese that led to the destruction of Corinth and ushered in the period of Roman Greece. Hellenistic Greece's definitive end was with the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, when the future emperor Augustus defeated Greek Ptolemaic queen Cleopatra VII and Mark Antony, the next year taking over Alexandria, the last great center of Hellenistic Greece.

Eumenes II Soter was a ruler of Pergamon, and a son of Attalus I Soter and queen Apollonis and a member of the Attalid dynasty of Pergamon.

Attalus I, surnamed Soter was the ruler of the Ionian Greek polis of Pergamon and the larger Pergamene Kingdom from 241 BC to 197 BC. He was the adopted son of King Eumenes I, whom he succeeded, and was the first of the Attalid dynasty to assume the title of king, sometime around 240 to 235 BC. He was the son of Attalus and his wife Antiochis.