
The 1997 United Kingdom general election was held on Thursday, 1 May 1997. The governing Conservative Party led by Prime Minister John Major was defeated in a landslide by the opposition Labour Party led by Tony Blair, achieving a 179-seat majority and a total of 419 seats.

Álvaro Uribe Vélez is a Colombian who served as the 31st President of Colombia from 7 August 2002 to 7 August 2010.

Referendums in the United Kingdom are occasionally held at a national, regional or local level. Historically, national referendums are rare due to the long-standing principle of parliamentary sovereignty. Legally there is no constitutional requirement to hold a national referendum for any purpose or on any issue. However, the UK Parliament is free to legislate through an Act of Parliament for a referendum to be held on any question at any time.

Parliamentary elections were held in Yemen on 27 April 2003 to elect all 301 members of the House of Representatives for a six-year term. The elections had originally been scheduled to take place in 2001. The General People's Congress of President Ali Abdullah Saleh received 58% of the vote, increasing its majority in the parliament with 229 MPs.

A popular referendum, depending on jurisdiction also known as a citizens' veto, people's veto, veto referendum, citizen referendum, abrogative referendum, rejective referendum, suspensive referendum, and statute referendum, is a type of a referendum that provides a means by which a petition signed by a certain minimum number of registered voters can force a public vote (plebiscite) on an existing statute, constitutional amendment, charter amendment, or ordinance; in its minimal form, it simply obliges the executive or legislative bodies to consider the subject by submitting it to the order of the day. It is a form of direct democracy.

A constitutional referendum was held in Abkhazia on 3 October 1999, alongside presidential elections. Voters were asked whether they approved of the constitution that had been approved by the Supreme Soviet on 26 November 1994, together with an amendment abolishing the life term for appointed judges and replacing it with five year terms. It was approved by 97.7% of voters. However, ethnic Georgians (200,000–250,000) who had been expelled from Abkhazia during the conflict of 1992–93 did not participate in the referendum and the results were not recognised internationally.

A constitutional referendum was held in Armenia on 27 November 2005. The referendum was on a series of changes to the constitution of Armenia which were backed by the international community. The official results had a high turnout and overwhelming support for the changes. However the opposition and election monitors said that there were serious irregularities with the referendum.
A referendum on electing a Constitutional Assembly was held in Colombia on 27 May 1990 alongside presidential elections. The proposal was approved by 96% of voters. A Constitutional Assembly was later elected in December 1990 and produced the 1991 constitution.
Parliamentary elections were held in Colombia on 11 March 1990 alongside local elections and an unofficial referendum on electing a Constitutional Assembly.
Constitutional Assembly elections were held in Colombia on 9 December 1990 alongside a referendum on the Assembly itself. The Assembly sat from February to July 1991 and drew up the 1991 constitution.

This national electoral calendar for 2016 lists the national/federal elections held in 2016 in all sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referendums are included.

Presidential elections were held in Colombia on 27 May 2018. As no candidate received a majority of the vote, the second round of voting was held on 17 June. Incumbent president Juan Manuel Santos was ineligible to seek a third term. Iván Duque, a senator, defeated Gustavo Petro, former mayor of Bogotá, in the second round. Duque's victory made him one of the youngest individuals elected to the presidency, aged 42. His running mate, Marta Lucía Ramírez, was the first woman elected to the vice presidency in Colombian history.

An independence referendum was held on Anjouan, an island in the Comoros, on 26 October 1997. Over 99% of voters voted in favour of independence. However, the vote was not recognised and the island returned to the control of the Comorian government in 2001.

A constitutional referendum was held in Tajikistan on 22 May 2016. A total of 41 constitutional amendments were proposed. The changes included:

The Colombian peace agreement referendum was held on 2 October 2016, aiming to ratify the final agreement on the termination of the Colombian conflict between the Colombian government and the FARC guerillas. It failed, with 50.2% voting against it and 49.8% voting in favor. Approval of the referendum was taken for granted in Colombia prior to the vote based on opinion polls. However, the 'No' option ended up winning by a narrow margin.
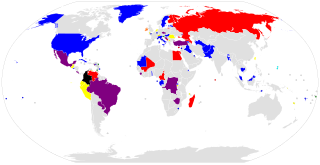
This national electoral calendar for 2018 lists the national/federal elections held in 2018 in all sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referendums are included.

The Commons, previously Common Alternative Revolutionary Force until 24 January 2021, is a communist political party in Colombia, established in 2017 as the political successor of the former rebel group the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC). The peace accords agreed upon by the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia and the Colombian government in 2016 provided for the FARC's participation in politics as a legal, registered political party following its successful disarmament.
A referendum on anti-corruption measures was held in Colombia on 26 August 2018. Voters were asked whether they approve of seven proposals aimed at reducing corruption: limiting the number of terms for politicians at all levels to three; requiring election candidates disclose their assets and those of their relatives; elected politicians being required to disclose their activities and private interests; a requirement for public hearings on budgets; a requirement for all public sector contracts to go out to tender; the removal of the right to parole for people convicted of corruption; and reducing the maximum salary of public officials and politicians from forty times the minimum wage to twenty-five times.
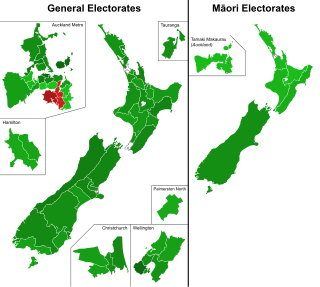
The 2020 New Zealand euthanasia referendum was a binding referendum held in New Zealand on 17 October 2020, on the question of whether to legalise euthanasia via the End of Life Choice Act 2019. The vote was held in conjunction with the 2020 general election, and official results were released on 6 November 2020. It was accepted by New Zealand voters, with 65.1% in support and 33.7% opposed.

1997 Eastern Slavonia integrity referendum was held on 6 April in short-lived Serb parallel entity of Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Syrmia which at the time was already governed by the United Nations Transitional Administration for Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Sirmium (UNTAES) as an UN governed territory. Voters were asked whether they supported the proposal for the region of Eastern Slavonia to remain a single territorial oblast within Croatia after the end of UNTAES mandate instead of division into Vukovar-Syrmia and Osijek-Baranja County. Reportedly 99.01% or 99.5% of voters voted for the integrity of the region within Croatia. 77,40% out of 100.275 registered voters participated in the referendum.
















