The September 2007 Sumatra earthquakes were a series of megathrust earthquakes that struck the Sunda Trench off the coast of Sumatra, Indonesia, with three of magnitude 7 or greater. A series of tsunami bulletins was issued for the area. The most powerful of the series had a magnitude of 8.4, which makes it in the top 20 of the largest earthquakes ever recorded on a seismograph.

The 2007 Gisborne earthquake occurred under the Pacific Ocean about 50 kilometres (31 mi) off the eastern coast of New Zealand's North Island at 8:55 pm NZDT on 20 December. With a moment magnitude of 6.7 and maximum Mercalli intensity of VII, the tremor affected the city of Gisborne and was felt widely throughout the country, from Auckland in the north to Dunedin in the south.
The 1975 Morris earthquake occurred in western Minnesota on July 9 at 14:54:15 UTC, or 9:54 a.m. local time. The strongest instrumentally recorded rupture in the history of the state, it registered at magnitude 4.6 Mn and had a maximum Mercalli intensity of VI (Strong). It was the first earthquake to be recorded on any seismic instrument in the state since 1917. Tremors were felt over much of Minnesota, northern Iowa, and the eastern Dakotas.

The 1968 Illinois earthquake was the largest recorded earthquake in the U.S. Midwestern state of Illinois. Striking at 11:02 a.m. on November 9, it measured 5.3 on the Richter scale. Although no fatalities occurred, the event caused considerable structural damage to buildings, including the toppling of chimneys and shaking in Chicago, the region's largest city. The earthquake was one of the most widely felt in U.S. history, largely affecting 23 states over an area of 580,000 sq mi (1,500,000 km2). In studying its cause, scientists discovered the Cottage Grove Fault in the Southern Illinois Basin.
Earthquakes have occurred in Western Australia (WA) on a regular basis throughout its geological history.
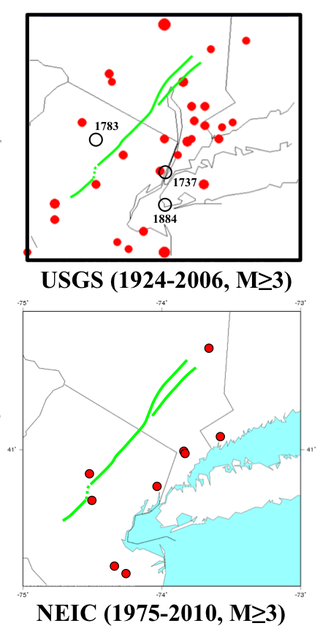
Seismicity of the New York City area is relatively low. New York is less seismically active than California because it is far from any plate boundaries. Large and damaging intraplate earthquakes are relatively rare. When they do occur in the Northeastern United States, the areas affected by them are much larger than for earthquakes of similar magnitude on the West Coast of the United States. The largest known earthquake in the greater New York City area occurred in 1884, probably somewhere between Brooklyn and Sandy Hook, and had a magnitude of approximately 5. The New York quakes in 2023 and 2024 were shallow quakes.

The 2011 Lorca earthquake was a moderate 5.1 earthquake that occurred 6:47 p.m. CEST on 11 May 2011, near the town of Lorca, causing significant localized damage in the Region of Murcia, Spain, and panic among locals, and displacing many from their homes. The quake was preceded by a magnitude 4.4 foreshock at 17:05, that inflicted substantial damage to many older structures in the area, including the historical Espolón Tower of Lorca Castle, the Hermitage of San Clemente and the Convent of Virgen de Las Huertas. Three people were killed by a falling cornice. A total of nine deaths have been confirmed, while dozens are reported injured. The earthquake was the worst to hit the region since a 5.0 Mw tremor struck west of Albolote, Granada in 1956.

The June 2011 Christchurch earthquake was a shallow magnitude 6.0 earthquake that occurred on 13 June 2011 at 14:20 NZST. It was centred at a depth of 7 km (4.3 mi), about 5 km (3 mi) south-east of Christchurch, which had previously been devastated by a magnitude 6.2 MW earthquake in February 2011. The June quake was preceded by a magnitude 5.9 ML tremor that struck the region at a slightly deeper 8.9 km (5.5 mi). The United States Geological Survey reported a magnitude of 6.0 Mw and a depth of 9 km (5.6 mi).
The 1954 Adelaide earthquake had its epicentre at Darlington, a suburb of the city of Adelaide in South Australia, some 12 km (7.5 mi) to the south of the Adelaide city centre. The quake took place at 3:40 am in the early morning of 1 March 1954 and had a reported magnitude of 5.6. An area of more than 700 km2 sustained an intensity greater than V on the Mercalli intensity scale.

The 2011 Oklahoma earthquake was a 5.7 magnitude intraplate earthquake which occurred near Prague, Oklahoma on November 5 at 10:53 p.m. CDT in the U.S. state of Oklahoma. The epicenter of the earthquake was in the vicinity of several active wastewater injection wells. According to the United States Geological Survey (USGS), it was the most powerful earthquake ever recorded in Oklahoma until the 2016 Oklahoma earthquake. The previous record was a 5.5 magnitude earthquake that struck near the town of El Reno in 1952. The quake's epicenter was approximately 44 miles (71 km) east-northeast of Oklahoma City, near the town of Sparks and was felt in the neighboring states of Texas, Arkansas, Kansas and Missouri and even as far away as Tennessee and Wisconsin. The quake followed several minor quakes earlier in the day, including a 4.7 magnitude foreshock. The quake had a maximum perceived intensity of VIII (Severe) on the Mercalli intensity scale in the area closest to the epicenter. Numerous aftershocks were detected after the main quake, with a few registering at 4.0 magnitude.
A magnitude 5.2 earthquake struck Gippsland near Moe at 8.55 pm on 19 June 2012, at a shallow depth of 10.0 km. It was the strongest recorded in Victoria in at least three decades, with some sources suggesting it was the strongest in over a century. It was felt across much of Victoria and parts of New South Wales, with strong shaking reported across the state capital, Melbourne. Some minor building damage was reported in the Latrobe Valley close to the epicentre, and in the eastern suburbs of Melbourne. Around 30 requests for help were made to the SES, mainly due to cracked walls and ceilings, and a number of local businesses lost some stock. Power outages occurred in some homes, but no significant reports of gas leaks were reported. Approximately 60 aftershocks were recorded the following day, but most of these were not felt.

The 1839 Ava earthquake, also known as the Amarapura earthquake or Inwa earthquake, was a disastrous seismic event that struck present-day central Myanmar on March 23. This earthquake with an estimated moment magnitude as high as 8.3, was one of the largest in the country, since 1762. It was assigned a maximum of XI (Extreme) on the Modified Mercalli intensity scale, and was felt in Rangoon and Bhamo. Damage was enormous in Ava, resulting in the death of hundreds.
On the morning of January 5, 1699, a violent earthquake rocked the then Dutch East Indies city of Batavia on the island of Java, now known as the Indonesian capital city of Jakarta. Dutch accounts of the event described the earthquake as being "so heavy and strong" and beyond comparable to other known earthquakes. This event was so large that it was felt throughout west Java, and southern Sumatra.
An earthquake struck approximately 53 kilometres SSE of the town of Mansfield, in the Victorian Alps of Australia on 22 September 2021, at 09:15 local time. The earthquake measured 5.9 on the moment magnitude scale. The earthquake caused minor structural damage in parts of Melbourne and left one person injured. The earthquake was also felt in New South Wales, Australian Capital Territory, South Australia and Tasmania. The earthquake was substantially stronger than the 1989 Newcastle earthquake that measured 5.6 and killed 13 people.
The 2021 Lasithi earthquake was a magnitude 6.4 earthquake with a maximum intensity of VIII (Severe) on the Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale which occurred on 12 October 2021, 12:24 (UTC+3:30) off the island of Crete. The quake was also felt at low intensity as far as Cairo and Istanbul.
The 1870 Charlevoix earthquake occurred on 20 October in the Canadian province of Quebec. It had a moment magnitude of 6.6 Mw and a Modified Mercalli intensity rating of X (Extreme). The town of Baie-Saint-Paul was seriously damaged by the event, with the loss of six lives. Effects from the earthquake were felt as far as Virginia and along the New England coast of the United States.
A magnitude 7.1 earthquake struck 38.3 km (23.8 mi) east-southeast of Ambunti in East Sepik Province, Papua New Guinea on 3 April 2023.