Agis or AGIS may refer to:
This decade witnessed the continuing decline of the Achaemenid Empire, fierce warfare amongst the Greek city-states during the Peloponnesian War, the ongoing Warring States period in Zhou dynasty China, and the closing years of the Olmec civilization in modern-day Mexico.
Year 401 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Potitus, Cossus, Camillus, Ambustus, Mamercinus and Iullus. The denomination 401 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 243 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Fundulus and Galus. The denomination 243 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 413 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Cossus and Medullinus. The denomination 413 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 420 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. The denomination 420 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 418 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Fidenas, Axilla and Mugillanus. The denomination 418 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 417 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Tricipitinus, Lanatus, Crassus and Axilla. The denomination 417 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Asclepieia were healing temples in ancient Greece, dedicated to Asclepius, the first doctor-demigod in Greek mythology. Asclepius was said to have been such a skilled doctor that he could even raise people from the dead. So stemming from the myth of his great healing powers, pilgrims would flock to temples built in his honor in order to seek spiritual and physical healing.

Epidaurus was a small city (polis) in ancient Greece, on the Argolid Peninsula at the Saronic Gulf. Two modern towns bear the name Epidavros: Palaia Epidavros and Nea Epidavros. Since 2010 they belong to the new municipality of Epidaurus, part of the regional unit of Argolis. The seat of the municipality is the town Lygourio. The nearby sanctuary of Asclepius and ancient theatre were inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1988 because of their exemplary architecture and importance in the development and spread of healing sanctuaries and cults across the ancient Greek and Roman worlds.

Cleomenes III was one of the two kings of Sparta from 235 to 222 BC. He was a member of the Agiad dynasty and succeeded his father, Leonidas II. He is known for his attempts to reform the Spartan state.
The first Battle of Mantinea was fought in 418 BC during the Peloponnesian War. In this battle, Sparta and its Peloponnesian allies defeated an allied army of Argos, Athens, Mantinea and several others.
Agis II was the 18th Eurypontid king of Sparta, the eldest son of Archidamus II by his first wife, and half-brother of Agesilaus II. He ruled with his Agiad co-monarch Pausanias.
Agis III was the eldest son of Archidamus III, and the 21st Eurypontid king of Sparta between 338 and 331 BC. He tried to lead a revolt against Macedonian hegemony over Greece, but was defeated by Antipater—Alexander the Great's regent in Greece—at the Battle of Megalopolis in 331 BC, where he died.

Aratus of Sicyon was a politician and military commander of Hellenistic Greece. He was elected strategos of the Achaean League 17 times, leading the League through numerous military campaigns including the Cleomenean War and the Social War.

Larisa is the ancient and medieval acropolis of Argos, located on a high rocky hill, within the town's boundaries to the west. According to Strabo, it is named for a group of Pelasgians. The summit is occupied by the ruins of a Byzantine-Venetian castle, below it, roughly midway down the slope of the mountain, is Panagia Katakekrymeni-Portokalousa monastery, and opposite the castle entrance, the Monastery of Agia Marina, a nunnery. The site was fortified and in continuous use for nineteen centuries.

Carneia or Carnea (Κάρνεα) was one of the tribal traditional festivals of Sparta, the Peloponnese and Doric cities in Magna Grecia, held in honor of Apollo Karneios. Whether Carneus was originally an old Peloponnesian divinity subsequently identified with Apollo, or merely an "emanation" from him, is uncertain; but there seems no reason to doubt that Carneus means "the god of flocks and herds", in a wider sense, of the harvest and the vintage. The chief centre of his worship was Sparta, where the Carneia took place every year from the 7th to the 15th of the month Carneus. During this period all military operations were suspended.
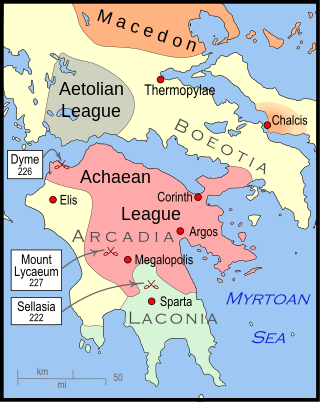
The Cleomenean War was fought between Sparta and the Achaean League for the control of the Peloponnese. Under the leadership of king Cleomenes III, Sparta initially had the upper hand, which forced the Achaean League to call for help the Macedonian king Antigonos Doson, who decisively defeated Cleomenes in the battle of Sellasia in 222.
The second Battle of Hysiae between the armies of Argos and Sparta took place in 417 BC during the Peloponnesian War, directly following Sparta's decisive defeat of the Argive/Athenian alliance in the Battle of Mantinea the year before.






