Births
| | This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (December 2021) |
| Millennium: | 1st millennium BC |
|---|---|
| Centuries: | |
| Decades: | |
| Years: |
| 421 BC by topic |
| Politics |
|---|
| Categories |
| Gregorian calendar | 421 BC CDXX BC |
| Ab urbe condita | 333 |
| Ancient Egypt era | XXVII dynasty, 105 |
| - Pharaoh | Darius II of Persia, 3 |
| Ancient Greek era | 89th Olympiad, year 4 |
| Assyrian calendar | 4330 |
| Balinese saka calendar | N/A |
| Bengali calendar | −1013 |
| Berber calendar | 530 |
| Buddhist calendar | 124 |
| Burmese calendar | −1058 |
| Byzantine calendar | 5088–5089 |
| Chinese calendar | 己未年 (Earth Goat) 2276 or 2216 — to — 庚申年 (Metal Monkey) 2277 or 2217 |
| Coptic calendar | −704 – −703 |
| Discordian calendar | 746 |
| Ethiopian calendar | −428 – −427 |
| Hebrew calendar | 3340–3341 |
| Hindu calendars | |
| - Vikram Samvat | −364 – −363 |
| - Shaka Samvat | N/A |
| - Kali Yuga | 2680–2681 |
| Holocene calendar | 9580 |
| Iranian calendar | 1042 BP – 1041 BP |
| Islamic calendar | 1074 BH – 1073 BH |
| Javanese calendar | N/A |
| Julian calendar | N/A |
| Korean calendar | 1913 |
| Minguo calendar | 2332 before ROC 民前2332年 |
| Nanakshahi calendar | −1888 |
| Thai solar calendar | 122–123 |
| Tibetan calendar | 阴土羊年 (female Earth-Goat) −294 or −675 or −1447 — to — 阳金猴年 (male Iron-Monkey) −293 or −674 or −1446 |
Year 421 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known in Rome as the Year of the Consulship of Vibulanus and Barbatus (or, less frequently, year 333 Ab urbe condita ). The denomination 421 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
| | This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (December 2021) |

The Peloponnesian War was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world. The war remained undecided for a long time, until the decisive intervention of the Persian Empire in support of Sparta. Led by Lysander, the Spartan fleet, built with Persian subsidies, finally defeated Athens and started a period of Spartan hegemony over Greece.
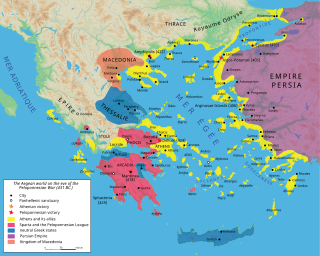
The Peloponnesian League was an alliance of ancient Greek city-states, dominated by Sparta and centred on the Peloponnese, which lasted from c.550 to 366 BC. It is known mainly for being one of the two rivals in the Peloponnesian War, against the Delian League, which was dominated by Athens.

The 5th century BC started the first day of 500 BC and ended the last day of 401 BC.
This article concerns the period 429 BC – 420 BC.
This decade witnessed the continuing decline of the Achaemenid Empire, fierce warfare amongst the Greek city-states during the Peloponnesian War, the ongoing Warring States period in Zhou dynasty China, and the closing years of the Olmec civilization in modern-day Mexico.
Year 424 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Crassus, Fidenas, Rutilus and Iullus. The denomination 424 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 425 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Atratinus, Medullinus, Cincinnatus and Barbatus. The denomination 425 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 423 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Atratinus and Ambustus. The denomination 423 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The Peace of Nicias was a peace treaty signed between the Greek city-states of Athens and Sparta in March 421 BC that ended the first half of the Peloponnesian War.

Nicias was an Athenian politician and general during the period of the Peloponnesian War. Nicias was a member of the Athenian aristocracy and had inherited a large fortune from his father, which was invested in the silver mines around Attica's Mt. Laurium. Following the death of Pericles in 429 BC, he became the principal rival of Cleon and the democrats in the struggle for the political leadership of the Athenian state. He was a moderate in his political views and opposed the aggressive imperialism of the democrats. His principal aim was to conclude a peace with Sparta as soon as it could be obtained on terms favourable to Athens.
Cleon was an Athenian general during the Peloponnesian War. He was an early representative of the commercial class in Athenian politics; which during the early Peloponnesian war was coming into prominence - although he was an aristocrat himself. He strongly advocated for an offensive war strategy and is remembered for being ruthless in carrying out his policies. He was often depicted in a negative way, predominantly by Thucydides and the comedic playwright Aristophanes, who both represent him as an unscrupulous, warmongering demagogue.

The Sicilian Expedition was an Athenian military expedition to Sicily, which took place from 415–413 BC during the Peloponnesian War between Athens on one side and Sparta, Syracuse and Corinth on the other. The expedition ended in a devastating defeat for the Athenian forces, severely impacting Athens.
Pleistoanax, also spelled Plistoanax, was Agiad king of Sparta from 458 to 409 BC. He was the leader of the peace party in Sparta at a time of violent confrontations against Athens for the hegemony over Greece.

Demosthenes, son of Alcisthenes, was an Athenian general during the Peloponnesian War.
Laches was an Athenian aristocrat and general during the Peloponnesian War.

Classical Greece was a period of around 200 years in Ancient Greece, marked by much of the eastern Aegean and northern regions of Greek culture gaining increased autonomy from the Persian Empire; the peak flourishing of democratic Athens; the First and Second Peloponnesian Wars; the Spartan and then Theban hegemonies; and the expansion of Macedonia under Philip II. Much of the early defining politics, artistic thought, scientific thought, theatre, literature and philosophy of Western civilization derives from this period of Greek history, which had a powerful influence on the later Roman Empire. Part of the broader era of classical antiquity, the classical Greek era ended after Philip II's unification of most of the Greek world against the common enemy of the Persian Empire, which was conquered within 13 years during the wars of Alexander the Great, Philip's son.
The period of the 5th century BC in classical Greece is generally considered as beginning in 500 BC and ending in 404 BC, though this is debated. This century is essentially studied from the Athenian viewpoint, since Athens has left more narratives, plays and other written works than the other Greek states. If one looks at Athens, our principal source, one might consider that this century begins in 510 BC, with the fall of the Athenian tyrant and Cleisthenes's reforms. If one looks at the whole Greek world, however, we might place its beginning at the Ionian Revolt in 500 BC, that provoked the first Persian invasion of 492 BC. The Persians were finally defeated in 490 BC. A second Persian attempt failed in 480–479 BC. The Delian League then formed, under Athenian hegemony and as Athens' instrument. Athens' excesses caused several revolts among the allied cities, which were all put down by force, but Athenian dynamism finally awoke Sparta and brought about the Peloponnesian War in 431 BC. After both sides were exhausted, a brief peace occurred, and then the war resumed to Sparta's advantage. Athens was definitively defeated in 404 BC, and some internal Athenian agitations ended the 5th century in Greece.

The Chalcidian League, also referred to as the Olynthians or the Chalcidians in Thrace to distinguish them from the Chalcidians in Euboea, was a federal state that existed on the Chalcidice peninsula, on the shores of the northwest Aegean Sea, from around 430 BCE until it was destroyed by Philip II of Macedon in 348 BCE.

Pausanias was the Agiad King of Sparta; the son of Pleistoanax. He ruled Sparta from 445 BC to 427 BC and again from 409 BC to 395 BC. He was the leader of the faction in Sparta that opposed the imperialist policy conducted by Lysander.
The Elean or Eleian War was a conflict between the Greek city-states of Sparta and Elis.