The Julian calendar, proposed by Julius Caesar in AUC 708, was a reform of the Roman calendar. It took effect on 1 January AUC 709 , by edict. It was designed with the aid of Greek mathematicians and Greek astronomers such as Sosigenes of Alexandria.
The 6th century BC started the first day of 600 BC and ended the last day of 501 BC.
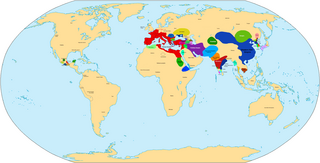
AD 1 (I), 1 AD or 1 CE is the epoch year for the Anno Domini calendar era. It was the first year of the Common Era (CE), of the 1st millennium and of the 1st century. It was a common year starting on Saturday or Sunday, a common year starting on Saturday by the proleptic Julian calendar, and a common year starting on Monday by the proleptic Gregorian calendar. In its time, year 1 was known as the Year of the Consulship of Caesar and Paullus, named after Roman consuls Gaius Caesar and Lucius Aemilius Paullus, and less frequently, as year 754 AUC within the Roman Empire. The denomination "AD 1" for this year has been in consistent use since the mid-medieval period when the anno Domini (AD) calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. It was the beginning of the Christian/Common era. The preceding year is 1 BC; there is no year 0 in this numbering scheme. The Anno Domini dating system was devised in AD 525 by Dionysius Exiguus.

AD 50 (L) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. At the time it was known in Europe as the Year of the Consulship of Vetus and Nerullinus. The denomination AD 50 for this year has been used since the Early Middle Ages, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 100 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Marius and Flaccus. The denomination 100 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The year 500 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. In the Roman Empire it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Camerinus and Longus. The denomination 500 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 480 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Vibulanus and Cincinnatus. The denomination 480 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 200 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Maximus and Cotta. The denomination 200 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 190 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Asiaticus and Laelius. The denomination 190 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 160 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Gallus and Cethegus and the Fourth Year of Houyuan. The denomination 160 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 350 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Laenas and Scipio. The denomination 350 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 470 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Potitus and Mamercus. The denomination 470 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The year 560 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as year 194 Ab urbe condita. The denomination 560 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 430 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Crassus and Iullus. The denomination 430 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The year 546 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as year 208 Ab urbe condita. The denomination 546 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The year 600 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as year 154 Ab urbe condita. The denomination 600 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The year 535 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as year 219 Ab urbe condita. The denomination 535 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The year 530 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as year 224 Ab urbe condita. The denomination 600 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The year 610 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as year 144 Ab urbe condita. The denomination 610 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The year 624 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as year 130 Ab urbe condita. The denomination 624 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.





