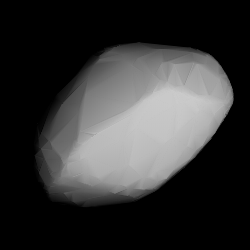
 Modelled shape of Malzovia from its lightcurve | |
| Discovery [1] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | S. Belyavskyj |
| Discovery site | Simeiz Obs. |
| Discovery date | 5 April 1913 |
| Designations | |
| (749) Malzovia | |
Named after | Nikolai Maltsov [2] (Russian amateur astronomer) |
| A913 GD ·1950 JO 1968 XA ·1913 RF | |
| Orbital characteristics [3] | |
| Epoch 31 May 2020 (JD 2459000.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 107.00 yr (39,080 d) |
| Aphelion | 2.6316 AU |
| Perihelion | 1.8558 AU |
| 2.2437 AU | |
| Eccentricity | 0.1729 |
| 3.36 yr (1,228 d) | |
| 289.14° | |
| 0° 17m 35.88s / day | |
| Inclination | 5.3946° |
| 109.76° | |
| 128.97° | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| 5.9274±0.0002 h [10] [a] | |
Pole ecliptic latitude | |
749 Malzovia ( prov. designation:A913 GDor1913 RF) is a stony background asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 11 kilometers (6.8 miles) in diameter. It was discovered on 5 April 1913, by Russian astronomer Sergey Belyavsky at the Simeiz Observatory on the Crimean peninsula. [1] The elongated S-type asteroid has a rotation period of 5.9 hours. It was named after Russian amateur astronomer Nikolai Maltsov (S. I. Maltsov) who founded the discovering Simeïs Observatory in 1900. [2]