Related Research Articles

Domitian was Roman emperor from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Flavian dynasty. Described as "a ruthless but efficient autocrat", his authoritarian style of ruling put him at sharp odds with the Senate, whose powers he drastically curtailed.

Vespasian was Roman emperor from 69 to 79. The last emperor to reign in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty, which ruled the Empire for 27 years. His fiscal reforms and consolidation of the empire brought political stability and a vast building program.
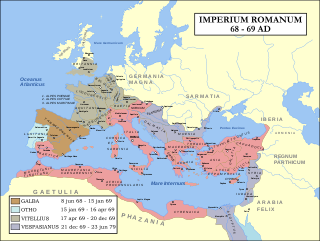
AD 69 (LXIX) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as the Year of the consulship of Galba and Vinius. The denomination AD 69 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

AD 79 (LXXIX) was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Titus and Vespasianus. The denomination AD 79 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The 60s decade ran from January 1, AD 60, to December 31, AD 69.

The 70s was a decade that ran from January 1, AD 70, to December 31, AD 79.
AD 70 (LXX) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Vespasian and Titus. The denomination AD 70 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
AD 71 (LXXI) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Vespasian and Nerva. The denomination AD 71 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
AD 72 (LXXII) was a leap year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Vespasian and Titus. The denomination AD 72 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

AD 73 (LXXIII) was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Domitian and Messalinus. The denomination AD 73 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
AD 75 (LXXV) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Augustus and Vespasianus. The denomination AD 75 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
AD 92 (XCII) was a leap year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Augustus and Saturninus. The denomination AD 92 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Gaius Plinius Secundus, known in English as Pliny the Elder, was a Roman author, naturalist, natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic Naturalis Historia, a comprehensive thirty-seven-volume work covering a vast array of topics on human knowledge and the natural world, which became an editorial model for encyclopedias. He spent most of his spare time studying, writing, and investigating natural and geographic phenomena in the field.

Titus Caesar Vespasianus was Roman emperor from 79 to 81. A member of the Flavian dynasty, Titus succeeded his father Vespasian upon his death, becoming the first Roman emperor ever to succeed his biological father.
A calendar era is the period of time elapsed since one epoch of a calendar and, if it exists, before the next one. For example, the current year is numbered 2025 in the Gregorian calendar, which numbers its years in the Western Christian era.

The Flavian dynasty, lasting from AD 69 to 96, was the second dynastic line of emperors to rule the Roman Empire following the Julio-Claudians, encompassing the reigns of Vespasian and his two sons, Titus and Domitian. The Flavians rose to power during the civil war of AD 69, known as the Year of the Four Emperors; after Galba and Otho died in quick succession, Vitellius became emperor in mid 69. His claim to the throne was quickly challenged by legions stationed in the eastern provinces, who declared their commander Vespasian emperor in his place. The Second Battle of Bedriacum tilted the balance decisively in favor of the Flavian forces, who entered Rome on 20 December, and the following day, the Roman Senate officially declared Vespasian emperor, thus commencing the Flavian dynasty. Although the dynasty proved to be short-lived, several significant historic, economic and military events took place during their reign.

The siege of Jerusalem of 70 CE was the decisive event of the First Jewish–Roman War, in which the Roman army led by future emperor Titus besieged Jerusalem, the center of Jewish rebel resistance in the Roman province of Judaea. Following a five-month siege, the Romans destroyed the city, including the Second Temple.

The Canon of Kings was a dated list of kings used by ancient astronomers as a convenient means to date astronomical phenomena, such as eclipses. For a period, the Canon was preserved by the astronomer Claudius Ptolemy, and is thus known sometimes as Ptolemy's Canon. It is one of the most important bases for our knowledge of ancient chronology.

De vita Caesarum, commonly known as The Twelve Caesars or The Lives of the Twelve Caesars, is a set of twelve biographies of Julius Caesar and the first 11 emperors of the Roman Empire written by Gaius Suetonius Tranquillus. The subjects consist of: Julius Caesar, Augustus, Tiberius, Caligula, Claudius, Nero, Galba, Otho, Vitellius, Vespasian, Titus, Domitian.

The Chronograph, Chronography, or Calendar of 354 is a compilation of chronological and calendrical texts produced in 354 AD for a wealthy Roman Christian named Valentinus by the calligrapher and illustrator Furius Dionysius Filocalus. The original illustrated manuscript is lost, but several copies have survived. It is the earliest known codex to have had full page illustrations. The name Calendar of Filocalus or Filocalian Calendar is sometimes used to describe the whole collection, and sometimes just the sixth part, which is the Calendar itself. Other versions of the names are occasionally used. The text and illustrations are available online. It has had a variety of other names over the years; the historian Theodor Mommsen titled it "Chronica urbis Romae".
References
- ↑ "The Chronography of 354 AD. Part 8: Consular feasts from the fall of the kings to AD 354".
- ↑ Westenholz, Aage (December 18, 2007). "The Graeco-Babyloniaca Once Again". Zeitschrift für Assyriologie und Vorderasiatische Archäologie. 97 (2): 294. doi:10.1515/ZA.2007.014. S2CID 161908528.
The latest datable cuneiform tablet that we have today concerns astronomical events of 75 AD and comes from Babylon. It provides a terminus post quem, at least for Babylon.