
A graphics card is a computer expansion card that generates a feed of graphics output to a display device such as a monitor. Graphics cards are sometimes called discrete or dedicated graphics cards to emphasize their distinction to an integrated graphics processor on the motherboard or the central processing unit (CPU). A graphics processing unit (GPU) that performs the necessary computations is the main component in a graphics card, but the acronym "GPU" is sometimes also used to erroneously refer to the graphics card as a whole.

A framebuffer is a portion of random-access memory (RAM) containing a bitmap that drives a video display. It is a memory buffer containing data representing all the pixels in a complete video frame. Modern video cards contain framebuffer circuitry in their cores. This circuitry converts an in-memory bitmap into a video signal that can be displayed on a computer monitor.

ATI Technologies Inc. was a Canadian semiconductor technology corporation based in Markham, Ontario, that specialized in the development of graphics processing units and chipsets. Founded in 1985, the company listed publicly in 1993 and was acquired by AMD in 2006. As a major fabless semiconductor company, ATI conducted research and development in-house and outsourced the manufacturing and assembly of its products. With the decline and eventual bankruptcy of 3dfx in 2000, ATI and its chief rival Nvidia emerged as the two dominant players in the graphics processors industry, eventually forcing other manufacturers into niche roles.

A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized electronic circuit initially designed for digital image processing and to accelerate computer graphics, being present either as a discrete video card or embedded on motherboards, mobile phones, personal computers, workstations, and game consoles. After their initial design, GPUs were found to be useful for non-graphic calculations involving embarrassingly parallel problems due to their parallel structure. Other non-graphical uses include the training of neural networks and cryptocurrency mining.

Radeon is a brand of computer products, including graphics processing units, random-access memory, RAM disk software, and solid-state drives, produced by Radeon Technologies Group, a division of AMD. The brand was launched in 2000 by ATI Technologies, which was acquired by AMD in 2006 for US$5.4 billion.
The R420 GPU, developed by ATI Technologies, was the company's basis for its 3rd-generation DirectX 9.0/OpenGL 2.0-capable graphics cards. Used first on the Radeon X800, the R420 was produced on a 0.13 micrometer low-K photolithography process and used GDDR-3 memory. The chip was designed for AGP graphics cards.

Scalable Link Interface (SLI) is the brand name for a now discontinued multi-GPU technology developed by Nvidia for linking two or more video cards together to produce a single output. SLI is a parallel processing algorithm for computer graphics, meant to increase the available processing power.

AMD CrossFire is a brand name for the multi-GPU technology by Advanced Micro Devices, originally developed by ATI Technologies. The technology allows up to four GPUs to be used in a single computer to improve graphics performance.

Graphics hardware is computer hardware that generates computer graphics and allows them to be shown on a display, usually using a graphics card in combination with a device driver to create the images on the screen.
The R520 is a graphics processing unit (GPU) developed by ATI Technologies and produced by TSMC. It was the first GPU produced using a 90 nm photolithography process.

The Radeon R100 is the first generation of Radeon graphics chips from ATI Technologies. The line features 3D acceleration based upon Direct3D 7.0 and OpenGL 1.3, and all but the entry-level versions offloading host geometry calculations to a hardware transform and lighting (T&L) engine, a major improvement in features and performance compared to the preceding Rage design. The processors also include 2D GUI acceleration, video acceleration, and multiple display outputs. "R100" refers to the development codename of the initially released GPU of the generation. It is the basis for a variety of other succeeding products.
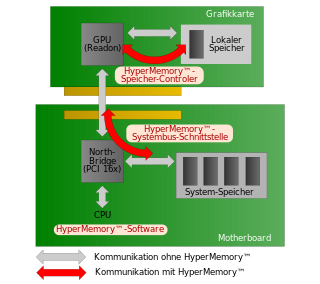
HyperMemory was a brand for ATI's method of using the motherboard's main system RAM as part of or all of the video card's framebuffer memory on their line of Radeon video cards and motherboard chipsets. It relies on new fast data transfer mechanisms within PCI Express.
The AMD 700 chipset series is a set of chipsets designed by ATI for AMD Phenom processors to be sold under the AMD brand. Several members were launched in the end of 2007 and the first half of 2008, others launched throughout the rest of 2008.
The Radeon R700 is the engineering codename for a graphics processing unit series developed by Advanced Micro Devices under the ATI brand name. The foundation chip, codenamed RV770, was announced and demonstrated on June 16, 2008 as part of the FireStream 9250 and Cinema 2.0 initiative launch media event, with official release of the Radeon HD 4800 series on June 25, 2008. Other variants include enthusiast-oriented RV790, mainstream product RV730, RV740 and entry-level RV710.
AMD FireStream was AMD's brand name for their Radeon-based product line targeting stream processing and/or GPGPU in supercomputers. Originally developed by ATI Technologies around the Radeon X1900 XTX in 2006, the product line was previously branded as both ATI FireSTREAM and AMD Stream Processor. The AMD FireStream can also be used as a floating-point co-processor for offloading CPU calculations, which is part of the Torrenza initiative. The FireStream line has been discontinued since 2012, when GPGPU workloads were entirely folded into the AMD FirePro line.

AMD Software is a device driver and utility software package for AMD's Radeon graphics cards and APUs. Its graphical user interface is built with Qt and is compatible with 64-bit Windows and Linux distributions.

AMD Hybrid Graphics technology, is a collective brand from AMD for its Radeon line of discrete and integrated GPU, promoting higher performance and productivity while saving energy consumption in GPUs.
The graphics processing unit (GPU) codenamed the Radeon R600 is the foundation of the Radeon HD 2000/3000 series and the FireGL 2007 series video cards developed by ATI Technologies.
The graphics processing unit (GPU) codenamed Radeon R600 is the foundation of the Radeon HD 2000 series and the FireGL 2007 series video cards developed by ATI Technologies. The HD 2000 cards competed with nVidia's GeForce 8 series.

The R300 GPU, introduced in August 2002 and developed by ATI Technologies, is its third generation of GPU used in Radeon graphics cards. This GPU features 3D acceleration based upon Direct3D 9.0 and OpenGL 2.0, a major improvement in features and performance compared to the preceding R200 design. R300 was the first fully Direct3D 9-capable consumer graphics chip. The processors also include 2D GUI acceleration, video acceleration, and multiple display outputs.












