
The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involuntary) functions, ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers, and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep–wake cycle.
Articles related to anatomy include:
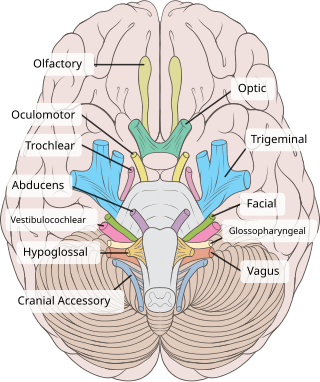
The vestibulocochlear nerve or auditory vestibular nerve, also known as the eighth cranial nerve, cranial nerve VIII, or simply CN VIII, is a cranial nerve that transmits sound and equilibrium (balance) information from the inner ear to the brain. Through olivocochlear fibers, it also transmits motor and modulatory information from the superior olivary complex in the brainstem to the cochlea.

The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing. It includes both the sensory organs and the auditory parts of the sensory system.

The lateral lemniscus is a tract of axons in the brainstem that carries information about sound from the cochlear nucleus to various brainstem nuclei and ultimately the contralateral inferior colliculus of the midbrain. Three distinct, primarily inhibitory, cellular groups are located interspersed within these fibers, and are thus named the nuclei of the lateral lemniscus.
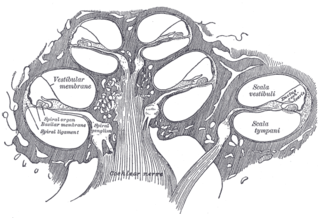
The cochlear nerve is one of two parts of the vestibulocochlear nerve, a cranial nerve present in amniotes, the other part being the vestibular nerve. The cochlear nerve carries auditory sensory information from the cochlea of the inner ear directly to the brain. The other portion of the vestibulocochlear nerve is the vestibular nerve, which carries spatial orientation information to the brain from the semicircular canals, also known as semicircular ducts.

A cranial nerve nucleus is a collection of neurons in the brain stem that is associated with one or more of the cranial nerves. Axons carrying information to and from the cranial nerves form a synapse first at these nuclei. Lesions occurring at these nuclei can lead to effects resembling those seen by the severing of nerve(s) they are associated with. All the nuclei except that of the trochlear nerve supply nerves of the same side of the body.

The anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) is one of three pairs of arteries that supplies blood to the cerebellum.

The internal auditory meatus is a canal within the petrous part of the temporal bone of the skull between the posterior cranial fossa and the inner ear.

The cochlear nuclear (CN) complex comprises two cranial nerve nuclei in the human brainstem, the ventral cochlear nucleus (VCN) and the dorsal cochlear nucleus (DCN). The ventral cochlear nucleus is unlayered whereas the dorsal cochlear nucleus is layered. Auditory nerve fibers, fibers that travel through the auditory nerve carry information from the inner ear, the cochlea, on the same side of the head, to the nerve root in the ventral cochlear nucleus. At the nerve root the fibers branch to innervate the ventral cochlear nucleus and the deep layer of the dorsal cochlear nucleus. All acoustic information thus enters the brain through the cochlear nuclei, where the processing of acoustic information begins. The outputs from the cochlear nuclei are received in higher regions of the auditory brainstem.

The dorsal cochlear nucleus is a cortex-like structure on the dorso-lateral surface of the brainstem. Along with the ventral cochlear nucleus (VCN), it forms the cochlear nucleus (CN), where all auditory nerve fibers from the cochlea form their first synapses.

The vestibular nuclei (VN) are the cranial nuclei for the vestibular nerve located in the brainstem.

The rhomboid fossa is a rhombus-shaped depression that is the anterior part of the fourth ventricle. Its anterior wall, formed by the back of the pons and the medulla oblongata, constitutes the floor of the fourth ventricle.
Binaural fusion or binaural integration is a cognitive process that involves the combination of different auditory information presented binaurally, or to each ear. In humans, this process is essential in understanding speech as one ear may pick up more information about the speech stimuli than the other.

The vestibule is the central part of the bony labyrinth in the inner ear, and is situated medial to the eardrum, behind the cochlea, and in front of the three semicircular canals.

The fascial compartments of arm refers to the specific anatomical term of the compartments within the upper segment of the upper limb of the body. The upper limb is divided into two segments, the arm and the forearm. Each of these segments is further divided into two compartments which are formed by deep fascia – tough connective tissue septa (walls). Each compartment encloses specific muscles and nerves.

The medial vestibular nucleus is one of the vestibular nuclei. It is located in the medulla oblongata.

In the ventral cochlear nucleus (VCN), auditory nerve fibers enter the brain via the nerve root in the VCN. The ventral cochlear nucleus is divided into the anterior ventral (anteroventral) cochlear nucleus (AVCN) and the posterior ventral (posteroventral) cochlear nucleus (PVCN). In the VCN, auditory nerve fibers bifurcate, the ascending branch innervates the AVCN and the descending branch innervates the PVCN and then continue to the dorsal cochlear nucleus. The orderly innervation by auditory nerve fibers gives the AVCN a tonotopic organization along the dorsoventral axis. Fibers that carry information from the apex of the cochlea that are tuned to low frequencies contact neurons in the ventral part of the AVCN; those that carry information from the base of the cochlea that are tuned to high frequencies contact neurons in the dorsal part of the AVCN. Several populations of neurons populate the AVCN. Bushy cells receive input from auditory nerve fibers through particularly large endings called end bulbs of Held. They contact stellate cells through more conventional boutons.

The salivatory nuclei are two parasympathetic general visceral efferent cranial nerve nuclei - the superior salivatory nucleus and the inferior salivatory nucleus - that innervate the salivary glands. Both are located in the pontine tegmentum of the brainstem.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:
















