The thalamus is a large mass of gray matter on the lateral walls of the third ventricle forming the dorsal part of the diencephalon. Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all directions, known as the thalamocortical radiations, allowing hub-like exchanges of information. It has several functions, such as the relaying of sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex and the regulation of consciousness, sleep, and alertness.

The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involuntary) functions, ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers, and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep–wake cycle. "Medulla" is from Latin, ‘pith or marrow’. And "oblongata" is from Latin, ‘lengthened or longish or elongated'.

The pons is part of the brainstem that in humans and other mammals, lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum.

The brainstem is the stalk-like part of the brain that connects the forebrain with the spinal cord. In the human brain, the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is continuous with the thalamus of the diencephalon through the tentorial notch.

Brodmann area 23 (BA23) is a region in the brain that lies inside the posterior cingulate cortex. It lies between Brodmann area 30 and Brodmann area 31 and is located on the medial wall of the cingulate gyrus between the callosal sulcus and the cingulate sulcus.

The hypoglossal nucleus is a cranial nerve nucleus, found within the medulla. Being a motor nucleus, it is close to the midline. In the open medulla, it is visible as what is known as the hypoglossal trigone, a raised area protruding slightly into the fourth ventricle.

The fibers of the oculomotor nerve arise from a nucleus in the midbrain, which lies in the gray substance of the floor of the cerebral aqueduct and extends in front of the aqueduct for a short distance into the floor of the third ventricle. From this nucleus the fibers pass forward through the tegmentum, the red nucleus, and the medial part of the substantia nigra, forming a series of curves with a lateral convexity, and emerge from the oculomotor sulcus on the medial side of the cerebral peduncle.

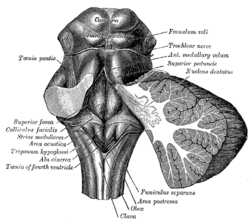
The fourth ventricle is one of the four connected fluid-filled cavities within the human brain. These cavities, known collectively as the ventricular system, consist of the left and right lateral ventricles, the third ventricle, and the fourth ventricle. The fourth ventricle extends from the cerebral aqueduct to the obex, and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).

The inferior colliculus (IC) is the principal midbrain nucleus of the auditory pathway and receives input from several peripheral brainstem nuclei in the auditory pathway, as well as inputs from the auditory cortex. The inferior colliculus has three subdivisions: the central nucleus, a dorsal cortex by which it is surrounded, and an external cortex which is located laterally. Its bimodal neurons are implicated in auditory-somatosensory interaction, receiving projections from somatosensory nuclei. This multisensory integration may underlie a filtering of self-effected sounds from vocalization, chewing, or respiration activities.

The corticobulbartract is a two-neuron white matter motor pathway connecting the motor cortex in the cerebral cortex to the medullary pyramids, which are part of the brainstem's medulla oblongata region, and are primarily involved in carrying the motor function of the non-oculomotor cranial nerves. The corticobulbar tract is one of the pyramidal tracts, the other being the corticospinal tract.

The olivary bodies or simply olives are a pair of prominent oval structures on either side of the medullary pyramids in the medulla, the lower portion of the brainstem. They contain the olivary nuclei.

The precentral gyrus is a prominent gyrus on the surface of the posterior frontal lobe of the brain. It is the site of the primary motor cortex that in humans is cytoarchitecturally defined as Brodmann area 4.

The subthalamus or prethalamus is a part of the diencephalon. Its most prominent structure is the subthalamic nucleus. The subthalamus connects to the globus pallidus, a basal nucleus of the telencephalon.

A cranial nerve nucleus is a collection of neurons in the brain stem that is associated with one or more of the cranial nerves. Axons carrying information to and from the cranial nerves form a synapse first at these nuclei. Lesions occurring at these nuclei can lead to effects resembling those seen by the severing of nerve(s) they are associated with. All the nuclei except that of the trochlear nerve supply nerves of the same side of the body.

The rhomboid fossa is a rhombus-shaped depression that is the anterior part of the fourth ventricle. Its anterior wall, formed by the back of the pons and the medulla oblongata, constitutes the floor of the fourth ventricle.
Basal plate may refer to:

In the developing nervous system, the basal plate is the region of the neural tube ventral to the sulcus limitans. It extends from the rostral mesencephalon to the end of the spinal cord and contains primarily motor neurons, whereas neurons found in the alar plate are primarily associated with sensory functions. The cell types of the basal plate include lower motor neurons and four types of interneuron.

In the human brain, the rhomboid fossa is divided into symmetrical halves by a median sulcus which reaches from the upper to the lower angles of the fossa and is deeper below than above. On either side of this sulcus is an elevation, the medial eminence, bounded laterally by a sulcus, the sulcus limitans.
The substantia ferruginea is an underlying patch of deeply pigmented nerve cells located in the floor of the superior part of the sulcus limitans.
A shallow, longitudinal groove separating the developing gray matter into a basal and alar plates along the length of the neural tube. The sulcus limitans extends the length of the spinal cord and through the mesencephalon.