This article may be too technical for most readers to understand.(May 2025) |
| Facial colliculus | |
|---|---|
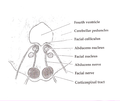
 Rhomboid fossa. (Colliculus facialis labeled at center left.) | |
 Human caudal brainstem posterior view (Colliculus facialis is #3) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | colliculus facialis |
| NeuroNames | 624 |
| TA98 | A14.1.05.705 |
| FMA | 78480 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The facial colliculus is an elevated area located in the pontine tegmentum (dorsal pons),[ citation needed ] within the floor of the fourth ventricle (i.e. the rhomboid fossa). It is formed by fibres from the facial motor nucleus looping over the abducens nucleus. The facial colliculus is an essential landmark of the rhomboid fossa. [1]