
A thermophile is an organism—a type of extremophile—that thrives at relatively high temperatures, between 41 and 122 °C. Many thermophiles are archaea, though some of them are bacteria and fungi. Thermophilic eubacteria are suggested to have been among the earliest bacteria.
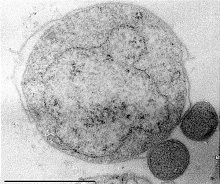
Nanoarchaeum equitans is a species of marine archaea that was discovered in 2002 in a hydrothermal vent off the coast of Iceland on the Kolbeinsey Ridge by Karl Stetter. It has been proposed as the first species in a new phylum, and is the only species within the genus Nanoarchaeum. Strains of this microbe were also found on the Sub-polar Mid Oceanic Ridge, and in the Obsidian Pool in Yellowstone National Park. Since it grows in temperatures approaching boiling, at about 80 °C (176 °F), it is considered to be a thermophile. It grows best in environments with a pH of 6, and a salinity concentration of 2%. Nanoarchaeum appears to be an obligate symbiont on the archaeon Ignicoccus; it must be in contact with the host organism to survive. Nanoarchaeum equitans cannot synthesize lipids but obtains them from its host. Its cells are only 400 nm in diameter, making it the smallest known living organism, and the smallest known archaeon.
A hyperthermophile is an organism that thrives in extremely hot environments—from 60 °C (140 °F) upwards. An optimal temperature for the existence of hyperthermophiles is often above 80 °C (176 °F). Hyperthermophiles are often within the domain Archaea, although some bacteria are also able to tolerate extreme temperatures. Some of these bacteria are able to live at temperatures greater than 100 °C, deep in the ocean where high pressures increase the boiling point of water. Many hyperthermophiles are also able to withstand other environmental extremes, such as high acidity or high radiation levels. Hyperthermophiles are a subset of extremophiles. Their existence may support the possibility of extraterrestrial life, showing that life can thrive in environmental extremes.

Sulfolobus is a genus of microorganism in the family Sulfolobaceae. It belongs to the archaea domain.
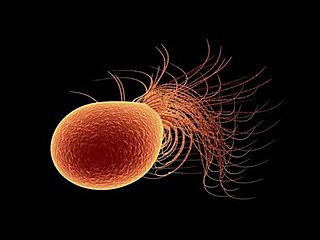
Pyrococcus furiosus is a heterotrophic, strictly anaerobic, extremophilic, model species of archaea. It is classified as a hyperthermophile because it thrives best under extremely high temperatures, and is notable for having an optimum growth temperature of 100 °C. P. furiosus belongs to the Pyrococcus genus, most commonly found in extreme environmental conditions of hydrothermal vents. It is one of the few prokaryotic organisms that has enzymes containing tungsten, an element rarely found in biological molecules.
Pyrobaculum is a genus of the Thermoproteaceae.
In taxonomy, Thermococcus is a genus of thermophilic Archaea in the family the Thermococcaceae.
Aeropyrum is a genus of archaea in the family Desulfurococcaceae.
In taxonomy, Staphylothermus is a genus of the Desulfurococcaceae.[1]
Caldococcus is a genus of Archaea in the order Desulfurococcales.
Guttaviridae is a family of viruses. Archaea serve as natural hosts. There are two genera in this family, containing one species each. The name is derived from the Latin gutta, meaning 'droplet'.
Thermococcus celer is a Gram-negative, spherical-shaped archaeon of the genus Thermococcus. The discovery of T. celer played an important role in rerooting the tree of life when T. celer was found to be more closely related to methanogenic Archaea than to other phenotypically similar thermophilic species. T. celer was the first archaeon discovered to house a circularized genome. Several type strains of T. celer have been identified: Vu13, ATCC 35543, and DSM 2476.

Clavaviridae is a family of double-stranded viruses that infect archaea. This family was first described by the team led by D. Prangishvili in 2010. There is one genus in this family (Clavavirus). Within this genus, a single species has been described to date: Aeropyrum pernix bacilliform virus 1 (APBV1).
Thermococcus kodakarensis is a species of thermophilic archaea. The type strain T. kodakarensis KOD1 is one of the best-studied members of the genus.
Geranylfarnesyl diphosphate synthase is an enzyme with systematic name geranylgeranyl-diphosphate:isopentenyl-diphosphate transtransferase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Thermoplasma volcanium is a moderate thermoacidophilic archaea isolated from acidic hydrothermal vents and solfatara fields. It contains no cell wall and is motile. It is a facultative anaerobic chemoorganoheterotroph. No previous phylogenetic classifications have been made for this organism. Thermoplasma volcanium reproduces asexually via binary fission and is nonpathogenic.
Sulfolobus metallicus is a coccoid shaped thermophilic archaeon. It is a strict chemolithoautotroph gaining energy by oxidation of sulphur and sulphidic ores into sulfuric acid. Its type strain is Kra 23. It has many uses that take advantage of its ability to grow on metal media under acidic and hot environments.
Saccharolobus solfataricus is a species of thermophilic archaeon. It was transferred from the genus Sulfolobus to the new genus Saccharolobus with the description of Saccharolobus caldissimus in 2018.
Spiraviridae is a family of incertae sedis viruses that replicate in hyperthermophilic archaea of the genus Aeropyrum, specifically Aeropyrum pernix. The family contains one genus, Alphaspiravirus, which contains one species, Aeropyrum coil-shaped virus. The virions of ACV are non-enveloped and in the shape of hollow cylinders that are formed by a coiling fiber that consists of two intertwining halves of the circular DNA strand inside a capsid. An appendage protrudes from each end of the cylindrical virion. The viral genome is ssDNA(+) and encodes for significantly more genes than other known ssDNA viruses. ACV is also unique in that it appears to lack its own enzymes to aid replication, instead likely using the host cell's replisomes. ACV has no known relation to any other archaea-infecting viruses, but it does share its coil-like morphology with some other archaeal viruses, suggesting that such viruses may be an ancient lineage that only infect archaea.
Acidilobus saccharovorans is a thermoacidophilic species of anaerobic archaea. The species was originally described in 2009 after being isolated from hot springs in Kamchatka.




