Related Research Articles
A reduced instruction set computer, or RISC, is a computer with a small, highly optimized set of instructions, rather than the more specialized set often found in other types of architecture, such as in a complex instruction set computer (CISC). The main distinguishing feature of RISC architecture is that the instruction set is optimized with a large number of registers and a highly regular instruction pipeline, allowing a low number of clock cycles per instruction (CPI). Another common RISC feature is the load/store architecture, in which memory is accessed through specific instructions rather than as a part of most instructions in the set.
ARM is a family of reduced instruction set computing (RISC) architectures for computer processors, configured for various environments. Arm Holdings develops the architecture and licenses it to other companies, who design their own products that implement one of those architectures—including systems-on-chips (SoC) and systems-on-modules (SoM) that incorporate memory, interfaces, radios, etc. It also designs cores that implement this instruction set and licenses these designs to a number of companies that incorporate those core designs into their own products.
SuperH is a 32-bit reduced instruction set computing (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) developed by Hitachi and currently produced by Renesas. It is implemented by microcontrollers and microprocessors for embedded systems.
OpenRISC is a project to develop a series of open-source hardware based central processing units (CPUs) on established reduced instruction set computer (RISC) principles. It includes an instruction set architecture (ISA) using an open-source license. It is the original flagship project of the OpenCores community.
The DLX is a RISC processor architecture designed by John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, the principal designers of the Stanford MIPS and the Berkeley RISC designs (respectively), the two benchmark examples of RISC design.
LEON is a radiation-tolerant 32-bit CPU microprocessor core that implements the SPARC V8 instruction set architecture (ISA) developed by Sun Microsystems. It was originally designed by the European Space Research and Technology Centre (ESTEC), part of the European Space Agency (ESA), and after a short lifespan at Gaisler Research. It is described in synthesizable VHDL. LEON has a dual license model: An LGPL/GPL FLOSS license that can be used without licensing fee, or a proprietary license that can be purchased for integration in a proprietary product. The core is configurable through VHDL generics, and is used in system-on-a-chip (SOC) designs both in research and commercial settings.
QEMU is a free and open-source emulator and virtualizer that can perform hardware virtualization.
Nios II is a 32-bit embedded-processor architecture designed specifically for the Altera family of field-programmable gate array (FPGA) integrated circuits. Nios II incorporates many enhancements over the original Nios architecture, making it more suitable for a wider range of embedded computing applications, from digital signal processing (DSP) to system-control.
The MicroBlaze is a soft microprocessor core designed for Xilinx field-programmable gate arrays (FPGA). As a soft-core processor, MicroBlaze is implemented entirely in the general-purpose memory and logic fabric of Xilinx FPGAs.
PicoBlaze is the designation of a series of three free soft processor cores from Xilinx for use in their FPGA and CPLD products. They are based on an 8-bit RISC architecture and can reach speeds up to 100 MIPS on the Virtex 4 FPGA's family. The processors have an 8-bit address and data port for access to a wide range of peripherals. The license of the cores allows their free use, albeit only on Xilinx devices, and they come with development tools. Third party tools are available from Mediatronix and others. Also PacoBlaze, a behavioral and device independent implementation of the cores exists and is released under the BSD License. The PauloBlaze is an open source VHDL implementation under the Apache License.

The AVR32 is a 32-bit RISC microcontroller architecture produced by Atmel. The microcontroller architecture was designed by a handful of people educated at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology, including lead designer Øyvind Strøm and CPU architect Erik Renno in Atmel's Norwegian design center.
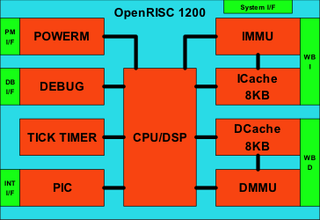
The OpenRISC 1200 (OR1200) is an implementation of the open source OpenRISC 1000 RISC architecture.

The ARM Cortex-A8 is a 32-bit processor core licensed by ARM Holdings implementing the ARMv7-A architecture.

The ARM Cortex-M is a group of 32-bit RISC ARM processor cores licensed by Arm Holdings. These cores are optimized for low-cost and energy-efficient microcontrollers, which have been embedded in tens of billions of consumer devices. The cores consist of the Cortex-M0, Cortex-M0+, Cortex-M1, Cortex-M3, Cortex-M4, Cortex-M7, Cortex-M23, Cortex-M33, Cortex-M35P, Cortex-M55. The Cortex-M4 / M7 / M33 / M35P / M55 cores have an FPU silicon option, and when included in the silicon these cores are sometimes known as "Cortex-Mx with FPU" or "Cortex-MxF", where 'x' is the core number.
OVPsim is a multiprocessor platform emulator used to run unchanged production binaries of the target hardware. It has public APIs allowing users to create their own processor, peripheral and platform models. Various models are available as open source. OVPsim is a key component of the Open Virtual Platforms initiative (OVP), an organization created to promote the use of open virtual platforms for embedded software development. OVPSim requires OVP registration to download.
RISC-V is an open standard instruction set architecture (ISA) based on established reduced instruction set computer (RISC) principles. Unlike most other ISA designs, the RISC-V ISA is provided under open source licenses that do not require fees to use. A number of companies are offering or have announced RISC-V hardware, open source operating systems with RISC-V support are available and the instruction set is supported in several popular software toolchains.
The ZPU is a microprocessor stack machine designed by Norwegian company Zylin AS to run supervisory code in electronic systems that include a field-programmable gate array (FPGA).
The Microwatt is an open source soft processor core originally written by Anton Blanchard at IBM, announced at the OpenPOWER Summit NA 2019 and published on GitHub in August 2019. It adheres to the Power ISA 3.0 instruction set and can be run on FPGA boards, booting Linux, MicroPython and Zephyr.
References
- ↑ Spooner, John G. (January 2, 2002). "Open-source credo moves to chip design". Tech Industry. CNET . Retrieved 2018-05-15.
- ↑ "Amber RISC Core". Soft Processor. 32bit micro. Archived from the original on 2015-02-02.
- ↑ van Someren, Alex; van Someren, Nic (February 1989). Archimedes Operating System: A Dabhand Guide (PDF). Dabs Press. ISBN 1-870336-48-8 . Retrieved 2018-05-15..
- ↑ VLSI Technology (1990). Acorn RISC Machine (ARM) Data Manual (PDF). Prentice Hall. ISBN 0-13-781618-9 . Retrieved 2018-05-15..