
Tetraodontiformes, also known as the Plectognathi, is an order of ray-finned fishes which includes the pufferfishes and related taxa. This order has been classified as a suborder of the order Perciformes, although recent studies have found that it, as the Tetraodontoidei, is a sister taxon to the anglerfish order Lophiiformes, called Lophiodei, and have placed both taxa within the Acanthuriformes. The Tetraodontiformes are represented by 10 extant families and at around 430 species overall. The majority of the species within this order are marine but a few may be found in freshwater. They are found throughout the world.

Ceratiidae, the warty sea devils, caruncled seadevils or seadevils, are a family of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the suborder Ceratioidei, the deep-sea anglerfishes, in the anglerfish order Lophiiformes. The warty sea devils are sexually dimorphic with the small males being obligate sexual parasites of the much larger females. The fishes in this family are widely distributed from polar to tropical seas around the world.

Rhinopias is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes. The species in this genus are found in the Indian and Pacific oceans.

Pontinus is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes. The scorpionfishes in this genus are distributed in the tropical and warm temperate parts Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans.

Parascorpaena picta, the northern scorpionfish, painted scorpionfish or marbled rock cod is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes. This species is native to the Indian Ocean and the western Pacific Ocean. This species grows to a length of 16 centimetres (6.3 in) TL.

Aracanidae, the deep sea boxfishes or temperate boxfishes, are a family of marine ray-finned fishes belonong to the order Tetraodontiformes, which also includes the pufferfishes, triggerfishes and ocean sunfishes. The fishes in this family are found in the Indo-West Pacific region, particularly in the waters around Australia.

Rhycherus is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the subfamily Histiophryninae in the family Antennariidae, the frogfishes. The fishes in this genus are endemic to the waters off Australia. This genus is classified in the monogeneric family Rhycheridae, the Balrog frogfishes, by some authorities.
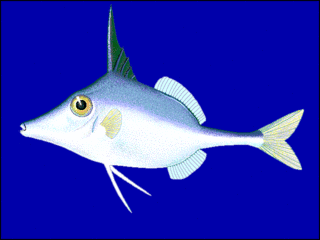
Triacanthus is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Triacanthidae, the triplespines or tripodfishes. The two species in this genus are found in the Indian Ocean and the western Pacific Ocean.

Tripodichthys is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Triacanthidae, the triplespines or tripodfishes. The three species in this genus are found in the Indian Ocean and the western Pacific Ocean in shallow water over soft substrates.

Hollardia is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Triacanthodidae, the spikefishes. These demersal fishes are found in the Western Atlantic Ocean with one species being found in the Pacific Ocean.
Pseudopataecus is a genus of marine ray-finned fish, velvetfishes belonging to the family Aploactinidae. This genus is endemic to the waters around Australia.

Triacanthus biaculeatus, also known as the short-nosed tripod fish, black-finned triple-spine, blacktail tripodfish, hollow-snouted tripodfish or silver tripodfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Triacanthidae, the triplespines or tripodfishes. This species is found in the Indo-West Pacific region.

Parascolopsis inermis, the unarmed dwarf monocle bream, banded monocle bream, redbelt monocle bream or yellow monocle bream, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Nemipteridae, the threadfin breams. This fish is found in the Indian and Western Pacific Oceans.

Lepadichthys frenatus, the bridled clingfish, is a species of clingfish from the family Gobiesocidae. It is found on shallow reefs in the western Pacific Ocean.

Lythrichthys, the red deepwater scorpionfishes, is a genus of marine ray-finned fish, belonging to the subfamily Setarchinae, the deep-sea bristly scorpionfishes, part of the family Scorpaenidae. They are native to the Pacific Ocean.

The Eastern fortescue, also known as the fortesque, Southern fortescue, fortie or Southern bullrout, is a species of ray-finned fish, a waspfish belonging to the subfamily Tetraroginae of the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and their relatives. It is found the coastal waters of eastern Australia.

Triacanthus nieuhofii, the silver tripodfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Triacanthidae, the triplespines or tripodfishes. This species is found in the Indo-West Pacific region.

Pterygotrigla polyommata, the latchet, butterfly gurnard, flying gurnard, lachet gurnard, pastry, sharpbeak gurnard, spiny gurnard or spinybeak gurnard, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Triglidae, the gurnards and sea robins. It is found in the southeastern Indian and southwestern Pacific Oceans.

Ostracioidea or Ostracioidei, the boxfishes, is a suborder of ray-finned fishes belonging to the order Tetraodontiformes, which also includes the pufferfishes, filefishes and triggerfishes. The fishes in this taxon are found in the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans.

The Western smooth boxfish, also known as the blue boxfish or robust boxfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Aracanidae, the deepwater boxfishes or tempereate boxfishes. This fish is endemic to the seas of southwestern Australia.






















