
The dorsal column–medial lemniscus pathway (DCML) is a sensory pathway of the central nervous system that conveys sensations of fine touch, vibration, two-point discrimination, and proprioception (position) from the skin and joints. It transmits information from the body to the primary somatosensory cortex in the postcentral gyrus of the parietal lobe of the brain. The pathway receives information from sensory receptors throughout the body, and carries this in nerve tracts in the white matter of the dorsal columns of the spinal cord to the medulla, where it is continued in the medial lemniscus, on to the thalamus and relayed from there through the internal capsule and transmitted to the somatosensory cortex. The name dorsal-column medial lemniscus comes from the two structures that carry the sensory information: the dorsal columns of the spinal cord, and the medial lemniscus in the brainstem.

Oncidium, abbreviated as Onc. in the horticultural trade, is a genus that contains about 330 species of orchids from the subtribe Oncidiinae of the orchid family (Orchidaceae). As presently conceived, it is distributed across much of South America, Central America, Mexico and the West Indies, with one species (O. ensatum) extending into Florida. Common names for plants in this genus include dancing-lady orchid and golden shower orchid.

Nephelaphyllum is a genus with 12 species of orchids. Its genus is distributed in southern China, the Himalayas, Indochina, Indonesia, Malaysia and the Philippines.
Gracilis, a Latin adjective meaning slender, graceful or gracile, may refer to :

Prasophyllum, commonly known as leek orchids, is a genus of about 140 species of flowering plants in the orchid family, Orchidaceae and is found in Australia and New Zealand. The Australian species are found in all states but have not been recorded in the Northern Territory. The common name arises from their having a hollow, leek- or onion-like leaf. Some species only flower after summer fires and have flowers similar to those of Xanthorrhoea which flower at the same time, suggesting that they employ the same pollinating insects. Leek orchids are similar to those in the genus Genoplesium except that the free part of the leaf is cylindrical and the labellum has a solid connection to the column. They range in size from the little laughing leek orchid at about 15 cm (6 in) to the king leek orchid which grows up to 2 m (80 in) tall.
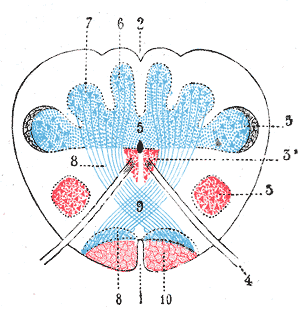
In neuroanatomy, the dorsal column nuclei are a pair of nuclei in the dorsal columns in the brainstem. The name refers collectively to the cuneate nucleus and gracile nucleus, which are present at the junction between the spinal cord and the medulla oblongata. Both nuclei contain second-order neurons of the dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway, which carries fine touch and proprioceptive information from the body to the brain. Each nucleus has an associated nerve tract, the gracile fasciculus and the cuneate fasciculus.

Homoeosaurus is an extinct genus of sphenodont reptile. It was found in limestone in Bavaria, Germany, as well as in France and the United Kingdom. It was related to the modern tuatara, though it was a considerably more gracile. There were several species varying greatly in size and morphology.

The Brazilian gracile opossum is a species of small opossum from Brazil.

Archidendron bigeminum is a tree species in the legume family (Fabaceae). It is found in India and Sri Lanka. It is known as "Kalitiya - කලටිය" in Sinhala people.

Aciagrion gracile is a species of damselfly in the family Coenagrionidae. It is found in Angola, Botswana, Ivory Coast, Gambia, Malawi, Mozambique, Nigeria, Tanzania, Uganda, Zambia, Zimbabwe, and possibly Kenya.

Herminium is a genus of plants in family Orchidaceae, widespread across much of Europe and Asia.

Dipodium, commonly known as hyacinth orchids, is a genus of about forty species of orchids native to tropical, subtropical and temperate regions of south-east Asia, New Guinea, the Pacific Islands and Australia. It includes both terrestrial and climbing species, some with leaves and some leafless, but all with large, often colourful flowers on tall flowering stems. It is the only genus of its alliance, Dipodium.

Mystacidium, abbreviated as Mycdm in horticultural trade, is a genus of the orchid family (Orchidaceae). It is native to eastern and southern Africa from Tanzania to South Africa.

Campylocentrum is a genus of rare orchids native to Mexico, the West Indies, Central America and South America. One species (C. pachyrrhizum) extends its range into Florida.

Rhynchostylis is a genus in the orchid family (Orchidaceae), closely allied to the genus Vanda and comprising four currently accepted species native to the Indian Subcontinent, China, Indochina, Malaysia, Indonesia and the Philippines. The name consists of a compound of two Greek elements : rhynchos 'beak' and stylis 'column' – in reference to the very broad, fleshy column of the flower. The flowers are borne in dense racemes and are noted for their intense, spicy fragrance. Although lacking in pseudobulbs, the plants have leathery leaves that are drought-resistant. These orchids grow naturally in warm, moist, shaded tropical areas and will thrive in cultivation if given consistent warmth, uniform moisture and bright, but indirect light. Hobbyists wanting to grow them will need a warm, humid growing environment with gentle air movement. They can be grown in pots, but are better grown in baskets, owing to the extreme fleshiness of their roots. Their unusually fragrant blooms often appear in the slightly cooler winter months.

Eriophorum gracile is a species of flowering plant in the sedge family, Cyperaceae. It is known by the common name slender cottongrass, or slender cottonsedge. Eriophorum gracile is a plant with circumboreal distribution, extending south into mountain ranges of the Northern Hemisphere. It grows in wet areas such as bogs.
Bulbophyllum gracile is a species of orchid in the genus Bulbophyllum.
Dipodium gracile is an orchid species that is native to Sulawesi in Indonesia. The species was formally described in 1911 by German botanist Rudolf Schlechter.
Ponerorchis gracilis is a species of plant in the family Orchidaceae. It is commonly known as delicate amitostigma. It is widespread across much of eastern Asia. It has been reported from Japan, Korea, Taiwan, and China.

Prasophyllum gracile, commonly known as the little laughing leek orchid, is a species of orchid endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is one of the most common and widespread orchids in the south-west and has a single smooth, tube-shaped leaf and up to forty or more, usually yellowish-green flowers.















