
Ascaris lumbricoides is the "large roundworm" of humans, growing to a length of up to 35 cm (14 in). It is one of several species of Ascaris. An ascarid nematode of the phylum Nematoda, it is the most common parasitic worm in humans. This organism is responsible for the disease ascariasis, a type of helminthiasis and one of the group of neglected tropical diseases. An estimated one-sixth of the human population is infected by A. lumbricoides or another roundworm. Ascariasis is prevalent worldwide, especially in tropical and subtropical countries.

Trichuriasis, also known as whipworm infection, is an infection by the parasitic worm Trichuris trichiura (whipworm). If infection is only with a few worms, there are often no symptoms. In those who are infected with many worms, there may be abdominal pain, tiredness and diarrhea. The diarrhea sometimes contains blood. Infections in children may cause poor intellectual and physical development. Low red blood cell levels may occur due to loss of blood.
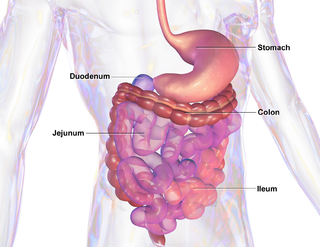
An intestinal parasite infection is a condition in which a parasite infects the gastro-intestinal tract of humans and other animals. Such parasites can live anywhere in the body, but most prefer the intestinal wall.
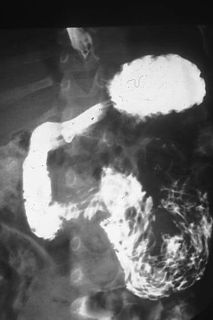
Ascariasis is a disease caused by the parasitic roundworm Ascaris lumbricoides. Infections have no symptoms in more than 85% of cases, especially if the number of worms is small. Symptoms increase with the number of worms present and may include shortness of breath and fever in the beginning of the disease. These may be followed by symptoms of abdominal swelling, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Children are most commonly affected, and in this age group the infection may also cause poor weight gain, malnutrition, and learning problems.

Praziquantel (PZQ), sold under the brandname Biltricide among others, is a medication used to treat a number of types of parasitic worm infections. Specifically it is used for schistosomiasis, clonorchiasis, opisthorchiasis, tapeworm infections, cysticercosis, hydatid disease, and other fluke infections. It should not be used for worm infections of the eye. It is taken by mouth.

Helminthiasis, also known as worm infection, is any macroparasitic disease of humans and other animals in which a part of the body is infected with parasitic worms, known as helminths. There are numerous species of these parasites, which are broadly classified into tapeworms, flukes, and roundworms. They often live in the gastrointestinal tract of their hosts, but they may also burrow into other organs, where they induce physiological damage.

Hookworm infection is an infection by a type of intestinal parasite known as a hookworm. Initially, itching and a rash may occur at the site of infection. Those only affected by a few worms may show no symptoms. Those infected by many worms may experience abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, and tiredness. The mental and physical development of children may be affected. Anemia may result.

Ascaris is a genus of parasitic nematode worms known as the "small intestinal roundworms", which is a type of parasitic worm. One species, Ascaris lumbricoides, affects humans and causes the disease ascariasis. Another species, Ascaris suum, typically infects pigs. Parascaris equorum, the equine roundworm, is also commonly called an "Ascarid".

Parasitic worms, also known as helminths, are large macroparasites, which as adults can generally be seen with the naked eye. Many are intestinal worms that are soil-transmitted and infect the gastrointestinal tract. Other parasitic worms such as schistosomes reside in blood vessels.

Helminthic therapy, an experimental type of immunotherapy, is the treatment of autoimmune diseases and immune disorders by means of deliberate infestation with a helminth or with the eggs of a helminth. Helminths are parasitic worms such as hookworms, whipworms, and threadworms that have evolved to live within a host organism on which they rely for nutrients. These worms are members of two phyla; nematodes, which are primarily used in human helminthic therapy, and flat worms (trematodes).
The soil-transmitted helminths are a group of intestinal parasites belonging to the phylum Nematoda that are transmitted primarily through contaminated soil. They are so called because they have a direct life cycle which requires no intermediate hosts or vectors, and the parasitic infection occurs through faecal contamination of soil, foodstuffs and water supplies. The adult forms are essentially parasites of humans, causing soil-transmitted helminthiasis (STH), but also infect domesticated mammals. The juveniles are the infective forms and they undergo tissue-migratory stages during which they invade vital organs such as lungs and liver. Thus the disease manifestations can be both local and systemic. The geohelminths together present an enormous infection burden on humanity, amounting to 135,000 deaths every year, and persistent infection of more than two billion people.

Fenbendazole is a broad spectrum benzimidazole anthelmintic used against gastrointestinal parasites including: giardia, roundworms, hookworms, whipworms, the tapeworm genus Taenia, pinworms, aelurostrongylus, paragonimiasis, strongyles and strongyloides and can be administered to sheep, cattle, horses, fish, dogs, cats, rabbits and seals. Drug interactions may occur if salicylanilides like dibromsalan and niclosamide are co-administered. Abortions in cattle and death in sheep have been reported after using these medications together.
Antiparasitics are a class of medications which are indicated for the treatment of parasitic diseases, such as those caused by helminths, amoeba, ectoparasites, parasitic fungi, and protozoa, among others. Antiparasitics target the parasitic agents of the infections by destroying them or inhibiting their growth; they are usually effective against a limited number of parasites within a particular class. Antiparasitics are one of the antimicrobial drugs which include antibiotics that target bacteria, and antifungals that target fungi. They may be administered orally, intravenously or topically.

Nitazoxanide is a broad-spectrum antiparasitic and broad-spectrum antiviral drug that is used in medicine for the treatment of various helminthic, protozoal, and viral infections. It is indicated for the treatment of infection by Cryptosporidium parvum and Giardia lamblia in immunocompetent individuals and has been repurposed for the treatment of influenza. Nitazoxanide has also been shown to have in vitro antiparasitic activity and clinical treatment efficacy for infections caused by other protozoa and helminths; emerging evidence suggests that it possesses efficacy in treating a number of viral infections as well.

Deworming is the giving of an anthelmintic drug to a human or animal to rid them of helminths parasites, such as roundworm, flukes and tapeworm. Purge dewormers for use in livestock can be formulated as a feed supplement that is eaten, a paste or gel that is deposited at the back of the animal's mouth, a liquid drench given orally, an injectable, or as a pour-on which can be applied to the animal's topline. In dogs and cats, purge dewormers come in many forms including a granular form to be added to food, pill form, chew tablets, and liquid suspensions.
Ascaricides are drugs to treat ascariasis that is caused by infections with parasitic nematodes (roundworms) of the genus Ascaris. The large roundworm of pigs typically infects pigs while Ascaris lumbricoides affects human populations, typically in sub-tropical and tropical areas with poor sanitation. Ascaricides belong to the group of drugs collectively called anthelmintics which expel parasitic worms (helminths) and other internal parasites from the body by either stunning or killing them and without causing significant damage to the host.

Soil-transmitted helminthiasis is a type of helminth infection (helminthiasis) caused by different species of roundworms. It is caused specifically by those worms which are transmitted through soil contaminated with faecal matter and are therefore called soil-transmitted helminths. Three types of soil-transmitted helminthiasis can be distinguished: ascariasis, hookworm infection and whipworm infection. These three types of infection are therefore caused by the large roundworm A. lumbricoides, the hookworms Necator americanus or Ancylostoma duodenale and by the whipworm Trichuris trichiura.
Children Without Worms (CWW) is a program of the Task Force for Global Health and envisions a world in which all at-risk people are healthy and free of intestinal worms so they can develop to their full potential. To accomplish the vision of a worm-free world, CWW works closely with the World Health Organization, national Ministries of Health, nongovernmental organizations and private-public coalitions such as Uniting to Combat NTDs.
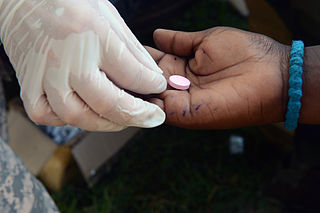
Mass deworming, also called preventive chemotherapy, is the process of treating large numbers of people, particularly children, for helminthiasis and schistosomiasis in areas with a high prevalence of these conditions. It involves treating everyone – often all children who attend schools, using existing infrastructure to save money – rather than testing first and then only treating selectively. Serious side effects have not been reported when administering the medication to those without worms, and testing for the infection is many times more expensive than treating it. So for the same amount of money, mass deworming can treat more people more cost-effectively than selective deworming. Mass deworming is one example of mass drug administration.















