
Herring are various species of forage fish, mostly belonging to the family of Clupeidae.

Atlantic herring is a herring in the family Clupeidae. It is one of the most abundant fish species in the world. Atlantic herrings can be found on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean, congregating in large schools. They can grow up to 45 centimetres (18 in) in length and weigh up to 1.1 kilograms (2.4 lb). They feed on copepods, krill and small fish, while their natural predators are seals, whales, cod and other larger fish.

Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life or, more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place. Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farms, both in freshwater waterbodies and the oceans. About 500 million people worldwide are economically dependent on fisheries. 171 million tonnes of fish were produced in 2016, but overfishing is an increasing problem, causing declines in some populations.
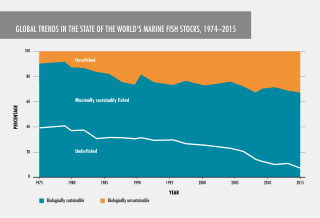
Fish stocks are subpopulations of a particular species of fish, for which intrinsic parameters are traditionally regarded as the significant factors determining the stock's population dynamics, while extrinsic factors are traditionally ignored. Stocks fished within biologically sustainable levels decreased from 90% in 1974 to 62.3% in 2021.

The skipjack tuna is a perciform fish in the tuna family, Scombridae, and is the only member of the genus Katsuwonus. It is also known as katsuo, arctic bonito, mushmouth, oceanic bonito, striped tuna or victor fish. It grows up to 1 m (3 ft) in length. It is a cosmopolitan pelagic fish found in tropical and warm-temperate waters. It is a very important species for fisheries. It is also the namesake of the USS Skipjack.

The Atlantic horse mackerel, also known as the European horse mackerel or common scad, is a species of jack mackerel in the family Carangidae, which includes the jacks, pompanos and trevallies. It is found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean off Europe and Africa and into the south-eastern Indian Ocean. It is an important species in commercial fisheries and is listed as a Vulnerable species on The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.

The European sprat, also known as brisling, brisling sardine, bristling, garvie, garvock, Russian sardine, russlet, skipper or whitebait, is a species of small marine fish in the herring family Clupeidae. Found in European, West Asian and North African waters, it has silver grey scales and white-grey flesh. Specific seas in which the species occurs include the Irish Sea, Black Sea, Baltic Sea and Sea of the Hebrides. The fish is the subject of fisheries, particularly in Scandinavia, and is made into fish meal, as well as being used for human consumption. When used for food it can be canned, salted, breaded, fried, boiled, grilled, baked, deep fried, marinated, broiled, and smoked.

The European seabass, also known as the branzino, European bass, sea bass, common bass, white bass, capemouth, white salmon, sea perch, white mullet, sea dace or loup de mer, is a primarily ocean-going fish native to the waters off Europe's western and southern and Africa's northern coasts, though it can also be found in shallow coastal waters and river mouths during the summer months and late autumn. It is one of only six species in its family, Moronidae, collectively called the temperate basses.
The Argentine anchoita or Argentine anchovy is an anchovy of the genus Engraulis, found in and around waters of Argentina, Uruguay and southern Brazil.

Epigonus telescopus, the black cardinal fish, is a species of deepwater cardinalfish found in most temperate oceans worldwide, at depths of between 75 and 1,200 metres though mostly between 300 and 800 metres. It can reach a length of 75 centimetres (30 in) TL though most specimens do not exceed 55 centimetres (22 in) TL. It has been reported that this species can reach an age of 104 years.

The Australasian snapper or silver seabream is a species of porgie found in coastal waters of Australia, Philippines, Indonesia, mainland China, Taiwan, Japan and New Zealand. Its distribution areas in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres are disjunct. Although it is almost universally known in Australia and New Zealand as snapper, it does not belong to the Lutjanidae snapper family. It is highly prized as an edible fish, with a sweet sea taste and a firm texture.

The Japanese flying squid, Japanese common squid or Pacific flying squid, scientific name Todarodes pacificus, is a squid of the family Ommastrephidae. This animal lives in the northern Pacific Ocean, in the area surrounding Japan, along the entire coast of China up to Russia, then spreading across the Bering Strait east towards the southern coast of Alaska and Canada. They tend to cluster around the central region of Vietnam.

The round sardinella is a species of ray-finned fish in the genus Sardinella found in both sides of the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea.

Sardinella maderensis is a species of small ray-finned fish in the genus Sardinella which is found in the Eastern Atlantic and Southeastern Mediterranean. it is a silvery fish similar to the round sardinella, but can be distinguished from that species by having gray caudal fins with black tips. It feeds on phytoplankton and fish larvae and is a pelagic, oceanodromous species that forms schools in coastal waters, often mixed with S. aurita. The International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated this fish's conservation status as "vulnerable".

The areolate grouper, also known as the yellowspotted rockcod, areolate rockcod, green-spotted rock-cod, squaretail grouper or squaretail rock-cod, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a grouper from the subfamily Epinephelinae which is part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the anthias and sea basses. It inhabits coral reefs in the Indo-Pacific region. They are produced through aquaculture and commercially fished. They currently face no threats to their survival.

Ilisha is a genus of ray-finned fishes in the family Pristigasteridae. The genus contains 16 species. It is similar to Pellona but lacks a toothed hypo-maxilla. The genus has a worldwide distribution in tropical and subtropical coastal waters and estuaries. Some species also enter rivers, and I. amazonica and I. novacula are largely–if not entirely–restricted to tropical rivers.

The Chilean jack mackerel, sometimes called the Jurel, Inca scad or Peruvian jack mackerel, is a species of jack mackerel in the genus Trachurus of the family Carangidae. Since the 1970s, it has become one of the world's more important commercial fish species. High volumes have been harvested, but the fishery may now be in danger of collapsing.

The Japanese Spanish mackerel, also known as the Japanese seer fish, is a species of true mackerel in the scombrid family (Scombridae). Their maximum reported length is 100 cm, and the maximum reported weight is 10.57 kg.

The elongate ilisha, also known as the Chinese herring or slender shad, is a species of longfin herring native to the coastal waters and estuaries of North Indian Ocean and Northwest Pacific. It is a relatively large species, up to 45–60 centimetres (18–24 in) in total length. It is an important fishery species.

Lift nets, also called lever nets, are a method of fishing using nets that are submerged to a certain depth and then lifted out of the water vertically. The nets can be flat or shaped like a bag, a rectangle, a pyramid, or a cone. Lift nets can be hand-operated, boat-operated, or shore-operated. They typically use bait or a light-source as a fish-attractor. Lift nets are also sometimes called "dip nets", though that term applies more accurately to hand nets.






















