December 14 is the 348th day of the year in the Gregorian calendar; 17 days remain until the end of the year.
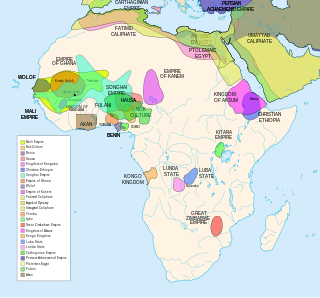
The history of Africa begins with the emergence of hominids, archaic humans and - around 300-250,000 years ago—anatomically modern humans, in East Africa, and continues unbroken into the present as a patchwork of diverse and politically developing nation states. The earliest known recorded history arose in Ancient Egypt, and later in Nubia, the Sahel, the Maghreb and the Horn of Africa.

Paris is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km², making it the 34th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, fashion, gastronomy, science, and arts, and has sometimes been referred to as the capital of the world. The City of Paris is the centre and seat of government of the region and province of Île-de-France, or Paris Region, with an estimated population of 12,997,058 in 2020, or about 18% of the population of France, making it in 2020 the second largest metropolitan area in the OECD, and 14th largest in the world in 2015. The Paris Region had a GDP of €709 billion in 2017. According to the Economist Intelligence Unit Worldwide Cost of Living Survey, in 2021 Paris was the city with the second-highest cost of living in the world, tied with Singapore, and after Tel Aviv.

The demographics of Benin include population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.

The Ewe people are a Gbe ethnic group. The largest population of Ewe people is in Ghana, and the second largest population in Togo. They speak the Ewe language which belongs to the Gbe family of languages. They are related to other speakers of Gbe languages such as the Fon, Gen, Phla Phera, and the Aja people of Togo and Benin.

St. James' Church is a former Collegiate church in Antwerp, Belgium. The church is built on the site of a hostel for pilgrims to Santiago de Compostela. The present building is the work of the Waghemakere family and Rombout Keldermans, in Brabantine Gothic style. The church contains the grave of Peter Paul Rubens in the eastern chapel.

The departments of Benin are subdivided into 77 communes, which in turn are divided into arrondissements and finally into villages or city districts. Prior to 1999 provinces were broken down into 84 districts, titled either urban or rural. Before independence, the six provinces were subdivided into Cercles, cantons, préfectures and villages or towns.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Benin:

Second Empire style, also known as the Napoleon III style, was a highly eclectic style of architecture and decorative arts, which used elements of many different historical styles, and also made innovative use of modern materials, such as iron frameworks and glass skylights. It flourished during the reign of Emperor Napoleon III in France (1852–1871) and had an important influence on architecture and decoration in the rest of Europe and North America. Major examples of the style include the Opéra Garnier (1862–1871) in Paris by Charles Garnier, the Bibliothèque nationale de France, the Church of Saint Augustine (1860–1871), and the Philadelphia City Hall. The architectural style was closely connected with Haussmann's renovation of Paris carried out during the Second Empire; the new buildings, such as the Opéra, were intended as the focal points of the new boulevards.

The Yoruba people are a West African ethnic group that mainly inhabits parts of Nigeria, Benin and Togo that constitute Yorubaland. The Yorubas constitute more than 43 million people in Africa, are a few hundred thousand outside the continent, and bear further representation among members of the African diaspora. The vast majority of the Yoruba population is today within the country of Nigeria, where they make up 15.5% of the country's population according to CIA estimations, making them one of the largest ethnic groups in Africa. Most Yoruba people speak the Yoruba language, which is the Niger-Congo language with the largest number of native or L1 speakers.

One of the oldest countries in Africa, the Ethiopian civilization emergence dates back over thousands of years. Due to migration and imperial expansion, it grew to include many other primarily Afro-Asiatic-speaking communities, including Amhara, Oromos, Somalis, Tigray, Afars, Sidama, Gurage, Agaw and Harari, among others.
Benin, officially the Republic of Benin, is a country in Western Africa. It borders Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east and Burkina Faso and Niger to the north; its short coastline to the south leads to the Bight of Benin. Its size is just over 110000 km2 with a population of almost 8500000. Its capital is the Yoruba founded city of Porto Novo, but the seat of government is the Fon city of Cotonou. About half the population live below the international poverty line of US$1.25 per day.

The Monastery of the mother of God at the Spring or simply Zoödochos Pege is an Eastern Orthodox sanctuary in Istanbul, Turkey. The present church, built in 1835, bears the same dedication as the shrine erected in this place between the end of the fifth and the beginning of the sixth century. After several renovations, this building was destroyed in the first half of the fifteenth century by the Ottomans. The complex got its name from a nearby holy spring, reputed to have healing properties. For almost fifteen hundred years, this sanctuary has been one of the most important pilgrimage sites of Greek Orthodoxy.

Fez or Fes is a city in northern inland Morocco and the capital of the Fès-Meknès administrative region. It is the third largest city in Morocco, with a population of 1.15 million according to the 2014 census. Located to the north west of the Atlas Mountains, Fez is linked to several important cities of different regions; it is 206 km (128 mi) from Tangier to the northwest, 246 km (153 mi) from Casablanca, 189 km (117 mi) from Rabat to the west. The Trans-Saharan trade route may be accessed via Marrakesh, 387 km (240 mi) to the southwest of Fez. It is surrounded by hills and the old city is centered around the Fez River flowing from west to east.

The city of Paris has notable examples of architecture of every period, from the Middle Ages to the 21st century. It was the birthplace of the Gothic style, and has important monuments of the French Renaissance, Classical revival, the Flamboyant style of the reign of Napoleon III, the Belle Époque, and the Art Nouveau style. The great Exposition Universelle (1889) and 1900 added Paris landmarks, including the Eiffel Tower and Grand Palais. In the 20th century, the Art Deco style of architecture first appeared in Paris, and Paris architects also influenced the postmodern architecture of the second half of the century.

Paris in the Belle Époque was a period in the history of the city between the years 1871 to 1914, from the beginning of the Third French Republic until the First World War. It saw the construction of the Eiffel Tower, the Paris Métro, the completion of the Paris Opera, and the beginning of the Basilica of Sacré-Cœur on Montmartre. Three lavish "universal expositions" in 1878, 1889, and 1900 brought millions of visitors to Paris to sample the latest innovations in commerce, art, and technology. Paris was the scene of the first public projection of a motion picture, and the birthplace of the Ballets Russes, Impressionism, and Modern Art.

Beninese nationality law is regulated by the Constitution of Benin, as amended; the Beninese Nationality Code, and its revisions; the Family Code; and various international agreements to which the country is a signatory. These laws determine who is, or is eligible to be, a national of Benin. The legal means to acquire nationality, formal legal membership in a nation, differ from the domestic relationship of rights and obligations between a national and the nation, known as citizenship. Beninese nationality is typically obtained under the principle of jus sanguinis, i.e. by birth in Benin or abroad to parents with Beninese nationality. It can be granted to persons with an affiliation to the country, or to a permanent resident who has lived in the country for a given period of time through naturalisation.














