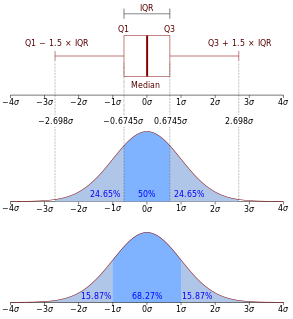
In descriptive statistics, the interquartile range (IQR), also called the midspread or middle 50%, or technically H-spread, is a measure of statistical dispersion, being equal to the difference between 75th and 25th percentiles, or between upper and lower quartiles, IQR = Q3 − Q1. In other words, the IQR is the first quartile subtracted from the third quartile; these quartiles can be clearly seen on a box plot on the data. It is a trimmed estimator, defined as the 25% trimmed range, and is a commonly used robust measure of scale.

Q is the 17th letter of the modern English alphabet and the ISO basic Latin alphabet. In nearly all languages using the Latin script it is a consonant, not a vowel.

In Euclidean plane geometry, a quadrilateral is a polygon with four edges and four vertices or corners. Sometimes, the term quadrangle is used, by analogy with triangle, and sometimes tetragon for consistency with pentagon (5-sided), hexagon (6-sided) and so on.
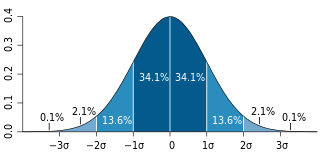
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure that is used to quantify the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of data values. A low standard deviation indicates that the data points tend to be close to the mean of the set, while a high standard deviation indicates that the data points are spread out over a wider range of values.
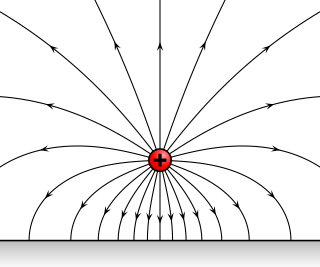
An electric field is a vector field surrounding an electric charge that exerts force on other charges, attracting or repelling them. Mathematically the electric field is a vector field that associates to each point in space the force, called the Coulomb force, that would be experienced per unit of charge by an infinitesimal test charge at that point. The units of the electric field in the SI system are newtons per coulomb (N/C), or volts per meter (V/m). Electric fields are created by electric charges, or by time-varying magnetic fields. Electric fields are important in many areas of physics, and are exploited practically in electrical technology. On an atomic scale, the electric field is responsible for the attractive force between the atomic nucleus and electrons that holds atoms together, and the forces between atoms that cause chemical bonding. Electric fields and magnetic fields are both manifestations of the electromagnetic force, one of the four fundamental forces of nature.

In mathematics, the quaternions are a number system that extends the complex numbers. They were first described by Irish mathematician William Rowan Hamilton in 1843 and applied to mechanics in three-dimensional space. A feature of quaternions is that multiplication of two quaternions is noncommutative. Hamilton defined a quaternion as the quotient of two directed lines in a three-dimensional space or equivalently as the quotient of two vectors.

In mathematics, the Euclidean distance or Euclidean metric is the "ordinary" straight-line distance between two points in Euclidean space. With this distance, Euclidean space becomes a metric space. The associated norm is called the Euclidean norm. Older literature refers to the metric as the Pythagorean metric. A generalized term for the Euclidean norm is the L2 norm or L2 distance.

The ideal gas law, also called the general gas equation, is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. It is a good approximation of the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. It was first stated by Émile Clapeyron in 1834 as a combination of the empirical Boyle's law, Charles's law, Avogadro's law, and Gay-Lussac's law. The ideal gas law is often written as
![Dead Sea Scrolls Ancient Jewish religious, mostly Hebrew, manuscripts found in the Qumran Caves in the West Bank] near the Dead Sea](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d4/Flag_of_Israel.svg/320px-Flag_of_Israel.svg.png)
The Dead Sea Scrolls are ancient Jewish religious, mostly Hebrew, manuscripts found in the Qumran Caves in the West Bank near the Dead Sea. Scholarly consensus dates these scrolls from the last three centuries BCE and the first century CE. The texts have great historical, religious, and linguistic significance because they include the second-oldest known surviving manuscripts of works later included in the Hebrew Bible canon, along with deuterocanonical and extra-biblical manuscripts which preserve evidence of the diversity of religious thought in late Second Temple Judaism. Almost all of the Dead Sea Scrolls collection is currently under the ownership of the Government of the state of Israel, and housed in the Shrine of the Book on the grounds of the Israel Museum.

Exclusive or or exclusive disjunction is a logical operation that outputs true only when inputs differ.

Capacitance is the ratio of the change in an electric charge in a system to the corresponding change in its electric potential. There are two closely related notions of capacitance: self capacitance and mutual capacitance. Any object that can be electrically charged exhibits self capacitance. A material with a large self capacitance holds more electric charge at a given voltage than one with low capacitance. The notion of mutual capacitance is particularly important for understanding the operations of the capacitor, one of the three elementary linear electronic components.
Hamiltonian mechanics is a theory developed as a reformulation of classical mechanics and predicts the same outcomes as non-Hamiltonian classical mechanics. It uses a different mathematical formalism, providing a more abstract understanding of the theory. Historically, it was an important reformulation of classical mechanics, which later contributed to the formulation of statistical mechanics and quantum mechanics.
In probability theory and statistics, the Bernoulli distribution, named after Swiss mathematician Jacob Bernoulli, is the discrete probability distribution of a random variable which takes the value 1 with probability and the value 0 with probability that is, the probability distribution of any single experiment that asks a yes–no question; the question results in a boolean-valued outcome, a single bit of information whose value is success/yes/true/one with probability p and failure/no/false/zero with probability q. It can be used to represent a coin toss where 1 and 0 would represent "heads" and "tails", respectively, and p would be the probability of the coin landing on heads or tails, respectively. In particular, unfair coins would have
In algebra, the partial fraction decomposition or partial fraction expansion of a rational function is an operation that consists of expressing the fraction as a sum of a polynomial and one or several fractions with a simpler denominator.
In mathematical statistics, the Kullback–Leibler divergence is a measure of how one probability distribution is different from a second, reference probability distribution. Applications include characterizing the relative(Shannon) entropy in information systems, randomness in continuous time-series, and information gain when comparing statistical models of inference. In contrast to variation of information, it is a distribution-wise asymmetric measure and thus does not qualify as a statistical metric of spread. In the simple case, a Kullback–Leibler divergence of 0 indicates that the two distributions in question are identical. In simplified terms, it is a measure of surprise, with diverse applications such as applied statistics, fluid mechanics, neuroscience and machine learning.

The DHC-8 Dash 8 is a series of turboprop-powered regional airliners, introduced by de Havilland Canada (DHC) in 1984. DHC was later bought by Boeing in 1988, then by Bombardier in 1992; the program is to be resold to Viking Air parent Longview Aviation Capital by late 2019. Powered by two Pratt & Whitney Canada PW100s, it was developed from the Dash 7 with improved cruise performance, lowered operational costs but worse STOL performance. Three sizes were offered: initially the 37-40 seat -100 until 2005 and the more powerful -200 from 1995, the stretched 50-56 seats -300 from 1989, both until 2009, and the 68-90 seats -400 from 1999, still in production. The Q Series are post-1997 variants with quieter cabins.
In linear algebra, a rotation matrix is a matrix that is used to perform a rotation in Euclidean space. For example, using the convention below, the matrix
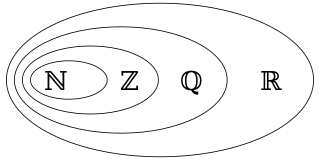
In mathematics, a rational number is any number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction p/q of two integers, a numerator p and a non-zero denominator q. Since q may be equal to 1, every integer is a rational number. The set of all rational numbers, often referred to as "the rationals", the field of rationals or the field of rational numbers is usually denoted by a boldface Q ; it was thus denoted in 1895 by Giuseppe Peano after quoziente, Italian for "quotient".

Coulomb's law, or Coulomb's inverse-square law, is a law of physics for quantifying Coulomb's force, or electrostatic force. Electrostatic force is the amount of force with which stationary, electrically charged particles either repel, or attract each other. This force and the law for quantifying it, represent one of the most basic forms of force used in the physical sciences, and were an essential basis to the study and development of the theory and field of classical electromagnetism. The law was first published in 1785 by French physicist Charles-Augustin de Coulomb.











![Dead Sea Scrolls Ancient Jewish religious, mostly Hebrew, manuscripts found in the Qumran Caves in the West Bank] near the Dead Sea](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d4/Flag_of_Israel.svg/320px-Flag_of_Israel.svg.png)



