Italy has a well developed transport infrastructure. The Italian rail network is extensive, especially in the north, and it includes a high-speed rail network that joins the major cities of Italy from Naples through northern cities such as Milan and Turin. The Florence–Rome high-speed railway was the first high-speed line opened in Europe when more than half of it opened in 1977. Italy has 2,507 people and 12.46 km2 per kilometer of rail track, giving Italy the world's 13th largest rail network. The Italian rail network is operated by state-owned Ferrovie dello Stato, while the rail tracks and infrastructure are managed by Rete Ferroviaria Italiana.
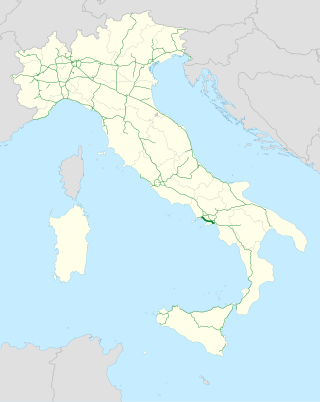
The Autostrada A3 is a motorway in Southern Italy, which runs from Naples to Salerno, in the region Campania.
Until 2017 the route was much longer, going after Salerno further south until Reggio Calabria; on this year, this section became part of the new A2 motorway and of its two spur routes.

The road hierarchy categorizes roads according to their functions and capacities. While sources differ on the exact nomenclature, the basic hierarchy comprises freeways, arterials, collectors, and local roads. Generally, the functional hierarchy can more or less correspond to the hierarchy of roads by their owner or administrator.

The province of La Spezia is a province in the Liguria region of Italy. Its capital is the city of La Spezia.
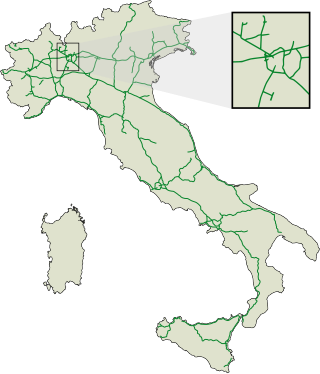
The autostrade are roads forming the Italian national system of motorways. The total length of the system is about 7,016 kilometres (4,360 mi), as of 30 July 2022. To these data are added 13 motorway spur routes, which extend for 355 kilometres (221 mi).

A controlled-access highway is a type of highway that has been designed for high-speed vehicular traffic, with all traffic flow—ingress and egress—regulated. Common English terms are freeway, motorway, and expressway. Other similar terms include throughway or thruway and parkway. Some of these may be limited-access highways, although this term can also refer to a class of highways with somewhat less isolation from other traffic.

The Autostrada A56, more commonly known as the Tangenziale di Napoli, is a controlled access toll road bypassing the urban center and suburban developments of Naples, Italy — connecting the SS7 near Arco Felice/Pozzuoli at the west to the A1 Autostrade at the east, with a total length of 20.2 km. The most eastward section, from Junction 3 at Doganella to the A1, is toll-free.

The Autostrada A26 is a motorway in the northwestern Italian regions of Liguria and Piedmont. It is named the Autostrada dei Trafori after the numerous tunnels through which it passes, both Apennine and Subalpine. It runs northwards from Genoa on the Ligurian coast, over the Apennines, and across the wide plain of the Po valley to the environs of Lake Maggiore and the mouth of the Val d’Ossola. In addition to this ‘main trunk’ of the road, there are three side branches, also of motorway class which function as link roads between the A26 and the A7, the A4 and the A8. The A26, together with these link roads, is managed by Autostrade per l'Italia S.p.A.

The Autostrada A6 is an Italian motorway opened in 1960 which connects Turin, the southernmost area of Piedmont, especially the Cuneo province, to the west coast of Liguria and the city of Savona. Its construction finished in 2001, when it was completely overhauled into a two-road motorway

The Autostrada A10, also known as the Autostrada dei Fiori or the AutoFiori, is an Italian motorway, passing through Liguria and connecting Genoa with Ventimiglia. It connects to the French A8 autoroute, which finishes in Aix-en-Provence, and forms part of European route E80. It is 158.7 kilometres (98.6 mi) long.

The Autostrada A91, also called Autostrada Roma-Fiumicino, is an Italian motorway which connects Rome to the Fiumicino Airport.

The Milan–Bologna high-speed railway is a railway line that links the cities of Milan and Bologna, part of the Italian high-speed rail network. It runs parallel to the historical north–south railway between Milan and Bologna, which itself follows the ancient Roman Road, the Via Aemilia. The new railway follows the Autostrada A1 closely for much of its length. The new line allows faster traffic to run separated and increase the overall railway capacity between the two cities.
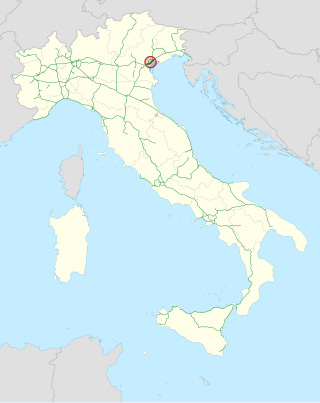
The Tangenziale di Mestre, or Autostrada A57, was opened to traffic on 3 September 1972 in northern Italy.

The A1, also commonly Rruga e Kombit or SH10, is the longest and only toll motorway in Albania, stretching 114 kilometres (71 mi) in the counties of Lezhë and Kukës. It consists for the most part of two traffic lanes and an emergency lane in each driving direction separated by a central reservation.
This article describes the highway systems available in selected countries.

The Autostrada A22 is one of the most important motorways in Italy, as it connects Pianura padana, the city of Modena and the A1 motorway to Austria through the Brenner Pass, located in the municipality of Brenner.

Roads in Italy are an important mode of transport in Italy. The classification of the roads of Italy is regulated by the Italian traffic code, both from a technical and administrative point of view. The street nomenclature largely reflects the administrative classification. Italy is one of the countries with the most vehicles per capita, with 690 per 1000 people in 2010.

The Highways in Albania are the central state and main transport network in Albania. The motorways and expressways are both part of the national road network. The motorways are primary roads with a speed limit of 110 kilometres per hour (68 mph). They have white on green road signs such as in Italy and other countries nearby. The expressways are the secondary roads, also dual carriageways, but without an emergency lane. They have a speed limit of 90 kilometres per hour (56 mph). They have white on blue road signs.

Strada statale 4 Via Salaria is an Italian state highway, linking Rome to the Adriatic sea passing through Rieti and Ascoli Piceno. Its route retraces that of the ancient Via Salaria Roman road. It is a single carriageway highway for most of its route.
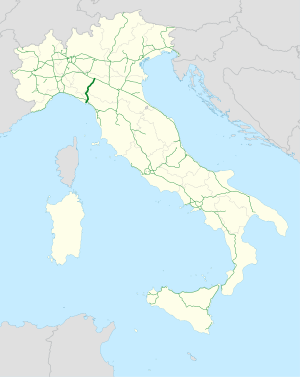
The Parma–La Spezia railway is the railway line that connects Parma, Italy with the Genoa–Pisa railway near La Spezia over the Cisa Pass through the Apennines. The route is approximately 120 kilometres long. Its Italian name derives from the town of Pontremoli, one of the main towns it passes through.