A dual carriageway (BrE) or a divided highway (AmE) is a class of highway with carriageways for traffic travelling in opposite directions separated by a central reservation (BrE) or median (AmE). Roads with two or more carriageways which are designed to higher standards with controlled access are generally classed as motorways, freeways, etc., rather than dual carriageways.
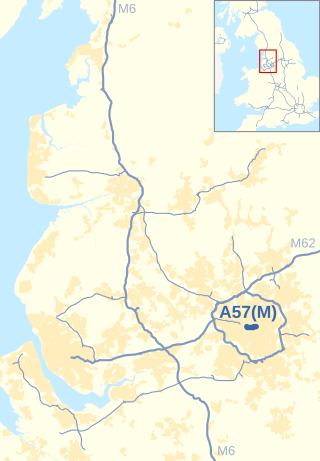
The Mancunian Way is a two mile long grade separated elevated motorway in Manchester, England. It is officially made up of the A57(M) and A635(M) motorways, although the latter does not appear on road signs for practical reasons. It is also part of two other roads: the A57 to the west, which runs east–west through Greater Manchester linking the M602 and M67 motorways, and a short section of non-motorway A635 to the east. Part of this non-motorway section collapsed on 14 August 2015 due to a sinkhole.
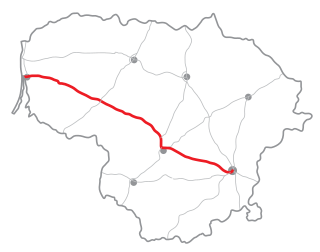
The A1 highway is a highway in Lithuania, connecting the three largest cities in the country: Vilnius, Kaunas, and Klaipėda. The highway is 311.4 kilometres (193.5 mi) long, making it the longest highway route in Lithuania.
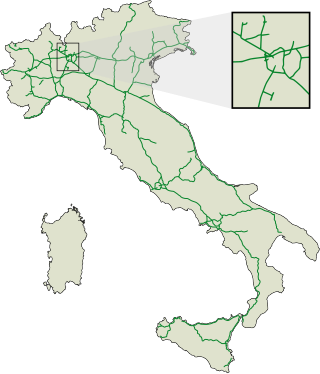
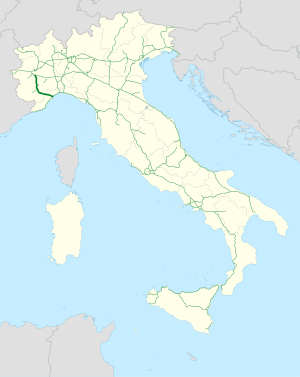
The autostrade are roads forming the Italian national system of motorways. The total length of the system is about 7,016 kilometres (4,360 mi), as of 30 July 2022. To these data are added 13 motorway spur routes, which extend for 355 kilometres (221 mi).

A controlled-access highway is a type of highway that has been designed for high-speed vehicular traffic, with all traffic flow—ingress and egress—regulated. Common English terms are freeway, motorway, and expressway. Other similar terms include throughway or thruway and parkway. Some of these may be limited-access highways, although this term can also refer to a class of highways with somewhat less isolation from other traffic.

Bundesautobahn 10 is an orbital motorway around the German capital city of Berlin. Colloquially called Berliner Ring , it is predominantly located in the state of Brandenburg, with a short stretch of 5 km in Berlin itself. It should not be confused with the Berliner Stadtring around Berlin's inner city.

The autostrada A2 in Poland, officially named the Motorway of Freedom, is a motorway which runs from the Polish-German border, through Poznań and Łódź to Warsaw and, in the future, to the Polish-Belarusian border. It is a part of European route E30.

The autostrada A1, officially named Amber Highway in Poland is a north–south motorway that runs through central Poland, from Gdańsk through Łódź and the Upper Silesian Industry Area to the Polish-Czech border in Gorzyczki/Věřňovice, where it is connected with the Czech motorway D1. Its total length is 566.6 km (352.1 mi). Except for its southernmost section, A1 is a part of European route E75.

The autostrada A6 in Poland is a short motorway that starts at the Polish/German border at Kołbaskowo/Pomellen connecting to the German A11 autobahn. It forms a southern bypass of the Szczecin metropolitan area and terminates at Rzęśnica interchange to the east of the city, from where it continues in an expressway standard as S3 towards Świnoujście and S6 towards Gdańsk. Its length is 29.2 km (18.1 mi). The motorway is part of the European route E28.
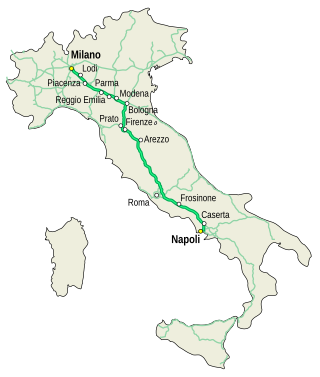
The Autostrada A1, nicknamed Autostrada del Sole, is the longest autostrada in Italy, linking some of the largest cities of the country: Milan, Bologna, Florence, Rome and Naples. It is a part of the E35 and E45 European routes.

The Autostrada A10, also known as the Autostrada dei Fiori or the AutoFiori, is an Italian motorway, passing through Liguria and connecting Genoa with Ventimiglia. It connects to the French A8 autoroute, which finishes in Aix-en-Provence, and forms part of European route E80. It is 158.7 kilometres (98.6 mi) long.

Autostrada A13 is an Italian motorway which connects Bologna to Padua, passing through Ferrara and Rovigo. It is 116.7 kilometres (72.5 mi) long. Near the two extremities of the track are situated two of the biggest Italian freight villages, in Bologna and Padua. Snow tyres are compulsory from 15 November to 15 April on the whole highway track, according to the Italian directives.

The Autostrada A91, also called Autostrada Roma-Fiumicino, is an Italian motorway which connects Rome to the Fiumicino Airport.

Expressway S3 or express road S3 is a Polish highway, which is planned to run from Świnoujście on the Baltic Sea through Szczecin, Gorzów Wielkopolski, Zielona Góra and Legnica, to the border with the Czech Republic, where it will connect to the planned D11 motorway. The total intended length is 470.6 km (292.4 mi), of which 404.7 km (251.5 mi) is open to traffic and 65.9 km (40.9 mi) is under construction as of March 2024.

Adriatic–Ionian motorway or Trieste-Kalamata Highway or the Blue Corridor, is a future motorway that will stretch along the entire eastern shore of the Adriatic and Ionian seas, spanning the western coast of the Balkan peninsula from Italy in the north through Slovenia, Croatia, Montenegro, Albania to Greece in the south.

Torino Lingotto railway station is one of the main stations serving the city and comune of Turin, capital of the region of Piedmont, northwestern Italy. The Torino Lingotto metro station is located nearby, and opened on March 6, 2011.

Roads in Italy are an important mode of transport in Italy. The classification of the roads of Italy is regulated by the Italian traffic code, both from a technical and administrative point of view. The street nomenclature largely reflects the administrative classification. Italy is one of the countries with the most vehicles per capita, with 690 per 1000 people in 2010.

Controlled-access highways in Romania are dual carriageways, grade separated with controlled-access, designed for high speeds. There are two types of highways, motorways and expressways, with the main difference being that motorways have emergency lanes and slightly wider lanes. The maximum allowed speed limit for motorways is 130 km/h (81 mph), while for expressways the limit is 120 km/h (75 mph). There are no toll roads, but a road vignette is required.

Mondovì railway station is the railway station serving the comune of Mondovì, in the Piedmont region of northwestern Italy. It is the junction of the Turin–Savona and Cuneo–Mondovì railways.