
Italy has a well developed transport infrastructure. The Italian rail network is extensive, especially in the north, and it includes a high-speed rail network that joins the major cities of Italy from Naples through northern cities such as Milan and Turin. The Florence–Rome high-speed railway was the first high-speed line opened in Europe when more than half of it opened in 1977. Italy has 2,507 people and 12.46 km2 per kilometer of rail track, giving Italy the world's 13th largest rail network. The Italian rail network is operated by state-owned Ferrovie dello Stato, while the rail tracks and infrastructure are managed by Rete Ferroviaria Italiana.

Arona is a town and comune on Lake Maggiore, in the province of Novara. Its main economic activity is tourism, especially from Milan, France and Germany.

The Autostrade are roads forming the Italian national system of motorways. The total length of the system is about 7,016 kilometres (4,360 mi), as of 30 July 2022. In North and Central Italy, the Autostrade mainly consists of tollways managed by Autostrade per l'Italia, a holding company controlled by Cassa Depositi e Prestiti. Other operators include ASTM, ATP, and Autostrade Lombarde in the north-west; Autostrada del Brennero, A4 Holding, Concessioni Autostradali Venete, and Autovie Venete in the north-east; Strada dei Parchi, SALT, SAT, and Autocisa in the center; and CAS in the south.

The autoroute system in France consists largely of toll roads. It is a network of 11,882 km (7,383 mi) of motorways as of 2014. On road signs, autoroute destinations are shown in blue, while destinations reached through a combination of autoroutes are shown with an added autoroute logo. Toll autoroutes are signalled with the word péage.
Switzerland has a two-class highway system: motorways with separated roads for oncoming traffic and a standard maximal speed limit of 120 kilometres per hour (75 mph), and expressways often with oncoming traffic and a standard maximal speed limit of 100 kilometres per hour (62 mph).

The Autostrada A56, more commonly known as the Tangenziale di Napoli, is a controlled access toll road bypassing the urban center and suburban developments of Naples, Italy — connecting the SS7 near Arco Felice/Pozzuoli at the west to the A1 Autostrade at the east, with a total length of 20.2 km. The most eastward section, from Junction 3 at Doganella to the A1, is toll-free.

The Autostrada A9 or Autostrada dei Laghi is a motorway in northern Italy. Built in 1924, it was the first motorway in Italy and in the world.

High-speed rail in Italy consists of two lines connecting most of the country's major cities. The first line connects Turin to Salerno via Milan, Bologna, Florence, Rome and Naples, the second runs from Turin to Venice via Milan and Verona, and is under construction in parts. Trains are operated with a top speed of 300 km/h (190 mph).

European route E 62 is a road in Europe, part of the United Nations International E-road network. Approximately 1,307 kilometers (812 mi) long, it connects the French Atlantic port city of Nantes to Genoa, largest of Italy's port cities. Between France and Italy it also passes through Switzerland, via Geneva and Lausanne. After crossing into Italy, the E 62 passes Milan, Italy's largest commercial and industrial centre, before descending to Genoa on the Mediterranean coast.

The Autostrada A6 is an Italian motorway opened in 1960 which connects Turin, the southernmost area of Piedmont, especially the Cuneo province, to the west coast of Liguria and the city of Savona. Its construction finished in 2001, when it was completely overhauled into a two-road motorway

The Autostrada A10, also known as the Autostrada dei Fiori or the AutoFiori, is an Italian motorway, passing through Liguria and connecting Genoa with Ventimiglia. It connects to the French A8 autoroute, which finishes in Aix-en-Provence, and forms part of European route E80. It is 158.7 kilometres (98.6 mi) long.

Autostrada A13 is an Italian motorway which connects Bologna to Padua, passing through Ferrara and Rovigo. It is 116.7 kilometres (72.5 mi) long. Near the two extremities of the track are situated two of the biggest Italian freight villages, in Bologna and Padua. Snow tyres are compulsory from 15 November to 15 April on the whole highway track, according to the Italian directives.

Motorways in Serbia are called auto-put, a name which simply means car-road. Roads that are motorways are categorized as state roads of IA category and are marked with one-digit numbers. Motorways in Serbia have three lanes in each direction, signs are white-on-green, and the normal speed limit is 130 km/h (81 mph). They are maintained and operated by the national road operator company JP "Putevi Srbije".
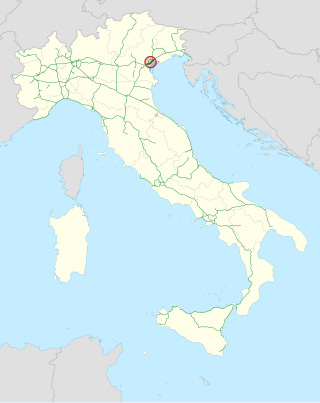
The Tangenziale di Mestre, or Autostrada A57, was opened to traffic on 3 September 1972 in northern Italy.

Adriatic–Ionian motorway or Trieste-Kalamata Highway or the Blue Corridor, is a future motorway that will stretch along the entire eastern shore of the Adriatic and Ionian seas, spanning the western coast of the Balkan peninsula from Italy in the north through Slovenia, Croatia, Montenegro, Albania to Greece in the south.
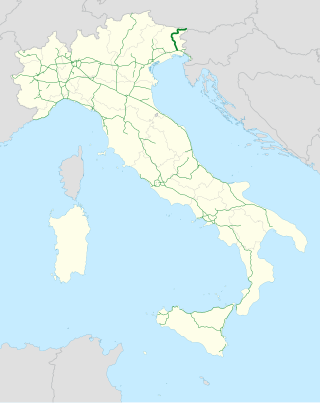
The Autostrada A23 is an Italian motorway, which connects the A4 motorway (Turin–Trieste) near Palmanova via Udine to Tarvisio and the Austrian Süd Autobahn (A2).

Controlled-access highways in Romania are dual carriageways, grade separated with controlled-access, designed for high speeds. There two types of highways, motorways and expressways, with the main difference being that motorways have emergency lanes and slightly wider lanes. The maximum allowed speed limit is 130 km/h (81 mph) and only 80 km/h (50 mph) during poor conditions, while for expressways the limit is 120 km/h (75 mph). There are no toll roads, but a road vignette is required.
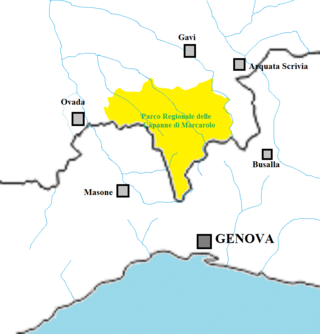
The Capanne di Marcarolo Natural Regional Park is a natural park in the province of Alessandria. It gets the name from a small village in the protected area, Capanne di Marcarolo.






















