Related Research Articles

Nephrology is a specialty of adult internal medicine and pediatric medicine that concerns the study of the kidneys, specifically normal kidney function and kidney disease, the preservation of kidney health, and the treatment of kidney disease, from diet and medication to renal replacement therapy. The word “renal” is an adjective meaning “relating to the kidneys”, and its roots are French or late Latin. Whereas according to some opinions, "renal" and "nephro" should be replaced with "kidney" in scientific writings such as "kidney medicine" or "kidney replacement therapy", other experts have advocated preserving the use of renal and nephro as appropriate including in "nephrology" and "renal replacement therapy", respectively.
Azotemia is a medical condition characterized by abnormally high levels of nitrogen-containing compounds in the blood. It is largely related to insufficient or dysfunctional filtering of blood by the kidneys. It can lead to uremia and acute kidney injury if not controlled.

Clinical chemistry is the area of chemistry that is generally concerned with analysis of bodily fluids for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. It is an applied form of biochemistry.
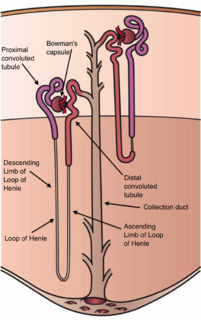
The nephron is the minute or microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney. It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and a cup-shaped structure called Bowman's capsule. The renal tubule extends from the capsule. The capsule and tubule are connected and are composed of epithelial cells with a lumen. A healthy adult has 1 to 1.5 million nephrons in each kidney. Blood is filtered as it passes through three layers: the endothelial cells of the capillary wall, its basement membrane, and between the foot processes of the podocytes of the lining of the capsule. The tubule has adjacent peritubular capillaries that run between the descending and ascending portions of the tubule. As the fluid from the capsule flows down into the tubule, it is processed by the epithelial cells lining the tubule: water is reabsorbed and substances are exchanged ; first with the interstitial fluid outside the tubules, and then into the plasma in the adjacent peritubular capillaries through the endothelial cells lining that capillary. This process regulates the volume of body fluid as well as levels of many body substances. At the end of the tubule, the remaining fluid—urine—exits: it is composed of water, metabolic waste, and toxins.

Kidney failure, also known as end-stage kidney disease, is a medical condition in which the kidneys are functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as either acute kidney failure, which develops rapidly and may resolve; and chronic kidney failure, which develops slowly and can often be irreversible. Symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vomiting, loss of appetite, and confusion. Complications of acute and chronic failure include uremia, high blood potassium, and volume overload. Complications of chronic failure also include heart disease, high blood pressure, and anemia.

A blood test is a laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose test or a cholesterol test, are often grouped together into one test panel called a blood panel or blood work. Blood tests are often used in health care to determine physiological and biochemical states, such as disease, mineral content, pharmaceutical drug effectiveness, and organ function. Typical clinical blood panels include a basic metabolic panel or a complete blood count. Blood tests are also used in drug tests to detect drug abuse.

Uremia is the term for high levels of urea in the blood. Urea is one of the primary components of urine. It can be defined as an excess of amino acid and protein metabolism end products, such as urea and creatinine, in the blood that would be normally excreted in the urine. Uremic syndrome can be defined as the terminal clinical manifestation of kidney failure. It is the signs, symptoms and results from laboratory tests which result from inadequate excretory, regulatory, and endocrine function of the kidneys. Both uremia and uremic syndrome have been used interchangeably to denote a very high plasma urea concentration that is the result of renal failure. The former denotation will be used for the rest of the article.

Renal functions include maintaining an acid–base balance; regulating fluid balance; regulating sodium, potassium, and other electrolytes; clearing toxins; absorption of glucose, amino acids, and other small molecules; regulation of blood pressure; production of various hormones, such as erythropoietin; and activation of vitamin D.
Acidosis is a process causing increased acidity in the blood and other body tissues. If not further qualified, it usually refers to acidity of the blood plasma.

Renal physiology is the study of the physiology of the kidney. This encompasses all functions of the kidney, including maintenance of acid-base balance; regulation of fluid balance; regulation of sodium, potassium, and other electrolytes; clearance of toxins; absorption of glucose, amino acids, and other small molecules; regulation of blood pressure; production of various hormones, such as erythropoietin; and activation of vitamin D.

Assessment of kidney function occurs in different ways, using the presence of symptoms and signs, as well as measurements using urine tests, blood tests, and medical imaging.
Hyperchloremia is an electrolyte disturbance in which there is an elevated level of chloride ions in the blood. The normal serum range for chloride is 96 to 106 mEq/L, therefore chloride levels at or above 110 mEq/L usually indicate kidney dysfunction as it is a regulator of chloride concentration. As of now there are no specific symptoms of hyperchloremia; however, it can be influenced by multiple abnormalities that cause a loss of electrolyte-free fluid, loss of hypotonic fluid, or increased administration of sodium chloride. These abnormalities are caused by diarrhea, vomiting, increased sodium chloride intake, renal dysfunction, diuretic use, and diabetes. Hyperchloremia should not be mistaken for hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis as hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis is characterized by two major changes: a decrease in blood pH and bicarbonate levels, as well as an increase in blood chloride levels. Instead those with hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis are usually predisposed to hyperchloremia.
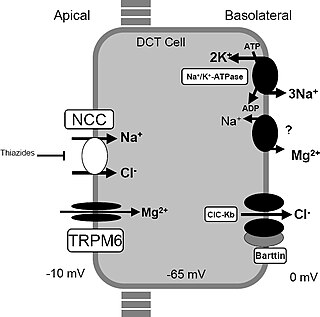
Gitelman syndrome (GS) is an autosomal recessive kidney tubule disorder characterized by low blood levels of potassium and magnesium, decreased excretion of calcium in the urine, and elevated blood pH. The disorder is caused by genetic mutations resulting in improper function of the thiazide-sensitive sodium-chloride symporter located in the distal convoluted tubule of the kidney. The distal convoluted tubule of the kidney plays an important homoestatic role in sodium and chloride absorption as well as of the reabsorption of magnesium and calcium.

Nephritic syndrome is a syndrome comprising signs of nephritis, which is kidney disease involving inflammation. It often occurs in the glomerulus, where it is called glomerulonephritis. Glomerulonephritis is characterized by inflammation and thinning of the glomerular basement membrane and the occurrence of small pores in the podocytes of the glomerulus. These pores become large enough to permit both proteins and red blood cells to pass into the urine. By contrast, nephrotic syndrome is characterized by proteinuria and a constellation of other symptoms that specifically do not include hematuria. Nephritic syndrome, like nephrotic syndrome, may involve low level of albumin in the blood due to the protein albumin moving from the blood to the urine.

Bartter syndrome (BS) is a rare inherited disease characterised by a defect in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle, which results in low potassium levels (hypokalemia), increased blood pH (alkalosis), and normal to low blood pressure. There are two types of Bartter syndrome: neonatal and classic. A closely associated disorder, Gitelman syndrome, is milder than both subtypes of Bartter syndrome.
In medicine, the BUN-to-creatinine ratio is the ratio of two serum laboratory values, the blood urea nitrogen (BUN) (mg/dL) and serum creatinine (Cr) (mg/dL). Outside the United States, particularly in Canada and Europe, the term urea is often used. BUN only reflects the nitrogen content of urea and urea measurement reflects the whole of the molecule, urea is approximately twice that of BUN. In Canada and Europe the units are also different (mmol/L). The units of creatinine are also different (μmol/L), and this value is termed the urea-to-creatinine ratio. The ratio may be used to determine the cause of acute kidney injury or dehydration.

Milk-alkali syndrome (MAS), also referred to as calcium-alkali syndrome, is the third most common cause of hypercalcemia. Milk-alkali syndrome is characterized by elevated blood calcium levels, metabolic alkalosis, and acute kidney injury.
The fractional excretion of sodium (FENa) is the percentage of the sodium filtered by the kidney which is excreted in the urine. It is measured in terms of plasma and urine sodium, rather than by the interpretation of urinary sodium concentration alone, as urinary sodium concentrations can vary with water reabsorption. Therefore, the urinary and plasma concentrations of sodium must be compared to get an accurate picture of kidney clearance. In clinical use, the fractional excretion of sodium can be calculated as part of the evaluation of acute kidney failure in order to determine if hypovolemia or decreased effective circulating plasma volume is a contributor to the kidney failure.

The comprehensive metabolic panel, or chemical screen, is a panel of 14 blood tests that serves as an initial broad medical screening tool. The CMP provides a rough check of kidney function, liver function, diabetic and parathyroid status, and electrolyte and fluid balance, but this type of screening has its limitations. Abnormal values from a CMP are often the result of false positives and thus the CMP may need to be repeated, requiring a second blood drawing procedure and possibly additional expense for the patient, even though no disease is present. This test is also known as SMA12+2 test.

Adrenal crisis is a potentially life-threatening medical condition requiring immediate emergency treatment. It is a constellation of symptoms that indicate severe adrenal insufficiency caused by insufficient levels of the hormone cortisol. This may be the result of either previously undiagnosed or untreated Addison's disease, a disease process suddenly affecting adrenal function, suddenly stopping intake of glucocorticoids or an intercurrent problem in someone known to have Addison's disease, congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH), or other form of primary adrenal insufficiency.
References
- ↑ MedlinePlus Encyclopedia : 003462
- ↑ MedlinePlus Encyclopedia : 003481
- ↑ MedlinePlus Encyclopedia : 003484
- ↑ MedlinePlus Encyclopedia : 003485
- ↑ MedlinePlus Encyclopedia : 003469
- ↑ MedlinePlus Encyclopedia : 003474
- ↑ MedlinePlus Encyclopedia : 003475
- ↑ MedlinePlus Encyclopedia : 003482
- ↑ "BASIC METABOLIC PANEL, SERUM". Archived from the original on March 13, 2005. Retrieved 2007-08-26.
- ↑ "Basic Metabolic Panel-Topic Overview" . Retrieved 2007-08-26.