Related Research Articles

The Nilo-Saharan languages are a proposed family of around 210 African languages spoken by somewhere around 70 million speakers, mainly in the upper parts of the Chari and Nile rivers, including historic Nubia, north of where the two tributaries of the Nile meet. The languages extend through 17 nations in the northern half of Africa: from Algeria to Benin in the west; from Libya to the Democratic Republic of the Congo in the centre; and from Egypt to Tanzania in the east.
Shabo is an endangered language and likely language isolate spoken by about 400 former hunter-gatherers in southwestern Ethiopia, in the eastern part of the South West Ethiopia Peoples' Region.
The Nuer language (Thok Naath) ("people's language") is a Nilotic language of the Western Nilotic group. It is spoken by the Nuer people of South Sudan and in western Ethiopia (region of Gambela). The language is very similar to Dinka and Atuot.

The Eastern Jebel languages are a small subfamily belonging to the Eastern Sudanic subgroup of Nilo-Saharan. They are spoken in the hills of An Nil al Azraq province in eastern Sudan
Turkana is the language of the Turkana people of Kenya and Ethiopia. It is spoken in northwestern Kenya, primarily in Turkana County, which lies west of Lake Turkana. It is one of the Eastern Nilotic languages, and is closely related to Karamojong, Jie and Teso of Uganda, to Toposa spoken in the extreme southeast of South Sudan, and to Nyangatom in the South Sudan/Ethiopia Omo valley borderland; these languages together form the cluster of Ateker Languages.
Dinka is a Nilotic dialect cluster spoken by the Dinka people, a major ethnic group of South Sudan. There are several main varieties, such as Padang, Rek, Agaar, Ciec, Malual, Apaak, Aliab, Bor, Hol, Nyarweng, Twic East and Twic Mayardit, which are distinct enough to require separate literary standards. Jaang, Jieng or Muonyjieng is used as a general term to cover all Dinka languages. Recently Akutmɛ̈t Latueŋ Thuɔŋjäŋ has proposed a unified written grammar of Dinka.

The languages of Ethiopia include the official languages of Ethiopia, its national and regional languages, and a large number of minority languages, as well as foreign languages.
The Gumuz are an ethnic group speaking a Nilo-Saharan language inhabiting the Benishangul-Gumuz Region in western Ethiopia, as well as the Fazogli region in Sudan. They speak the Gumuz language, which belongs to the Nilo-Saharan family. The Gumuz number around 250,000 individuals.

The Kunama language has been included in the proposed Nilo-Saharan language family, though it is distantly related to the other languages, if at all. Kunama is spoken by the Kunama people of the Gash-Barka Region in western Eritrea and just across the Ethiopian border. The language has several dialects including: Barka, Marda, Aimara, Odasa, Tika, Lakatakura, Sokodasa, Takazze-Setit and Tigray. Ilit and Bitama are not mutually intelligible and so may be considered distinct languages.
Mursi is a Southeast Surmic language spoken by the Mursi people who live in the South Omo Zone on the eastern side of the lower Omo valley in southwest Ethiopia. The language is similar to Suri, another Southeast Surmic language spoken to the west of the Mursi language area. It is spoken by approximately 7,400 people.

The Berta (Bertha) or Funj or Benishangul are an ethnic group living along the border of Sudan and Ethiopia. They speak a Nilo-Saharan language that is not related to those of their Nilo-Saharan neighbors. The total population of Ethiopian-Bertas in Ethiopia is 208,759 people. Sudanese-Bertas number around 180,000.

The Majang language is spoken by the Majangir people of Ethiopia. Although it is a member of the Surmic language cluster, it is the most isolated one in the group. A language survey has shown that dialect variation from north to south is minor and does not seriously impede communication. The 2007 Ethiopian Census lists 6,433 speakers for Majang (Messengo), but also reports that the ethnic group consists of 32,822 individuals. According to the census, almost no speakers can be found in Mezhenger Zone of Gambela Region; a total of eleven speakers are listed for the zone, but almost 10,000 ethnic Mejenger or Messengo people.
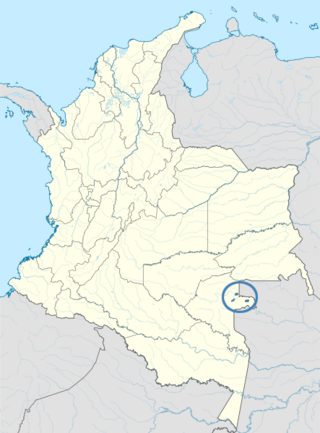
The Cacua language, also known as Kakua or Kakwa, is an indigenous language spoken by a few hundred people in Colombia and Brazil. There are many monolinguals, especially children. Apart from being close to or a dialect of Nukak, its classification is uncertain.
Komo is a Nilo-Saharan language spoken by the Kwama (Komo) people of Ethiopia, Sudan and South Sudan. It is a member of the Koman languages. The language is also referred to as Madiin, Koma, South Koma, Central Koma, Gokwom and Hayahaya. Many individuals from Komo are multilingual because they are in close proximity to Mao, Kwama and Oromo speakers. Komo is closely related to Kwama, a language spoken by a group who live in the same region of Ethiopia and who also identify themselves as ethnically Komo. Some Komo and Kwama speakers recognize the distinction between the two languages and culture, whereas some people see it as one "ethnolinguistic" community. The 2007 Ethiopian census makes no mention of Kwama, and for this reason its estimate of 8,000 Komo speakers may be inaccurate. An older estimate from 1971 places the number of Komo speakers in Ethiopia at 1,500. The Komo language is greatly understudied; more information is being revealed as researchers are discovering more data about other languages within the Koman family.

The Berta languages, or Funj, traditionally considered dialects of a single language, are Gebeto, Fadashi, and Undu. They are either a small family of their own, or a primary branch of the Nilo-Saharan language family.
Maba is a Nilo-Saharan language of the Maban branch spoken in Chad and Sudan. It is divided into several dialects, and serves as a local trade language. Maba is closely related to the Masalit language. Most speakers of Maba reside in Chad with 542,000 speakers as of 2019. In 2022 there were 28,000 speakers in Sudan where the language is known as Sulaihab.
Afitti is a language spoken on the eastern side of Jebel el-Dair, a solitary rock formation in the North Kordofan province of Sudan. Although the term ‘Dinik’ can be used to designate the language regardless of cultural affiliation, people in the villages of the region readily recognize the terms ‘Ditti’ and ‘Afitti.’ There are approximately 4,000 speakers of the Afitti language and its closest linguistic neighbor is the Nyimang language, spoken west of Jebel el-Dair in the Nuba Mountains of the North Kordofan province of Sudan.
Barawana (Baré) is an Arawakan language of Venezuela and Brazil, where it is nearly extinct. It was spoken by the Baré people. Aikhenvald (1999) reports "just a few old speakers left" of Baré proper, and that the Guinau variety was extinct. Kaufman (1994) considers Baré proper, Guinau, and Marawá to be distinct languages; Aikhenvald, dialects of a single languages.
Päri, or Lokoro, is a Luo language of South Sudan. Päri has been claimed to have ergative alignment, which is rare-to-nonexistent in African languages, although recent descriptions of the language have instead described the case system as marked nominative (nominative–absolutive).
Gumuz is a dialect cluster spoken along the border of Ethiopia and Sudan. It has been tentatively classified within the Nilo-Saharan family. Most Ethiopian speakers live in Kamashi Zone and Metekel Zone of the Benishangul-Gumuz Region, although a group of 1,000 reportedly live outside the town of Welkite. The Sudanese speakers live in the area east of Er Roseires, around Famaka and Fazoglo on the Blue Nile, extending north along the border. Dimmendaal et al. (2019) suspect that the poorly attested varieties spoken along the river constitute a distinct language, Kadallu.
References
- 1 2 Berta at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022)

- ↑ "Berta". Ethnologue. Retrieved 23 September 2023.
- ↑ Bremer, Nate D. 2016. A Sociolinguistic Survey of Six Berta Speech Varieties in Ethiopia . SIL Electronic Survey Report 2016-007. Addis Ababa: SIL International.
- ↑ Neudorf, Susanne (2016). Phonology of Berta. Dallas, Texas: SIL International.