Related Research Articles
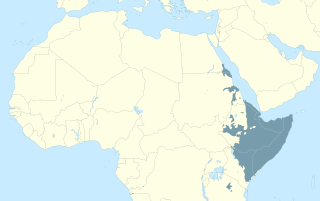
The Cushitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken primarily in the Horn of Africa, with minorities speaking Cushitic languages to the north in Egypt and Sudan, and to the south in Kenya and Tanzania. As of 2012, the Cushitic languages with over one million speakers were Oromo, Somali, Beja, Afar, Hadiyya, Kambaata, and Sidama.
Bench is a Northern Omotic language of the "Gimojan" subgroup, spoken by about 174,000 people in the Bench Maji Zone of the Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples Region, in southern Ethiopia, around the towns of Mizan Teferi and Shewa Gimira. In a 2006 dissertation, Christian Rapold described three varieties of Bench as "...mutually intelligible...varieties of one and the same language". Bench is the ancestral language of the Bench people.
Sidama or Sidaamu Afoo is an Afro-Asiatic language belonging to the Highland East Cushitic branch of the Cushitic family. It is spoken in parts of southern Ethiopia by the Sidama people, particularly in the densely populated Sidama National Regional State (SNRS). Sidaamu Afoo is the ethnic autonym for the language, while Sidaminya is its name in Amharic. It is not known to have any specific dialects. The word order is typically SOV. Sidaama has over 100,000 L2 speakers. The literacy rate for L1 speakers is 1%-5%, while for L2 speakers it is 20%. In terms of its writing, Sidaama used an Ethiopic script up until 1993, from which point forward it has used a Latin script.
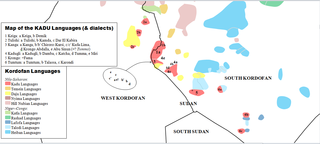
The Kadu languages, also known as Kadugli–Krongo or Tumtum, are a small language family of the Kordofanian geographic grouping, once included in Niger–Congo. However, since Thilo Schadeberg (1981), Kadu is widely seen as Nilo-Saharan. Evidence for a Niger-Congo affiliation is rejected, and a Nilo-Saharan relationship is controversial. A conservative classification would treat the Kadu languages as an independent family.
Libido is an Afroasiatic language of Ethiopia, which is spoken in the Mareko district Gurage Zone of the Southern Nations, Nationalities, and People's Region, directly south-east of Butajira. It has about 58,800 native speakers.

Kambaata is a Cushitic ethnic group in south-central Ethiopia, specifically in Kambaata Zone in Central Ethiopia Regional State. It is also known as Cambat, Kambata, Cambatta, Kambatta or Khambat by various historians and early explorers. The Kambaata people and Kambaatissa belongs to the East Highland Cushitic language family. Kambaata was first mentioned in the chronicles of Emperor Yeshaq I. Kambaata was "one of the southern kingdoms with well-established monarchical system...instituted in 16th century and operated without interruption until it ended at the last decade of ninetieth century" when it was incorporated by Emperor Menelik II. During this first period incorporation, Kambaata province was largely Christianized.
Hadiyya is the language of the Hadiya people of Ethiopia. It is a Highland East Cushitic language of the Afroasiatic family. Most speakers live in the Hadiya Zone of the Southern Nations, Nationalities, and People's Region (SNNPR).
The Awngi language, in older publications also called Awiya, is a endangered indigenous Central Cushitic language spoken by the Awi people, traditionally living in Central Gojjam in northwestern Ethiopia.
Southern Oromo, or Borana, is a variety of Oromo spoken in southern Ethiopia and northern Kenya by the Borana people. Günther Schlee also notes that it is the native language of a number of related peoples, such as the Sakuye.

The Majang language is spoken by the Majangir people of Ethiopia. Although it is a member of the Surmic language cluster, it is the most isolated one in the group. A language survey has shown that dialect variation from north to south is minor and does not seriously impede communication. The 2007 Ethiopian Census lists 6,433 speakers for Majang (Messengo), but also reports that the ethnic group consists of 32,822 individuals. According to the census, almost no speakers can be found in Mezhenger Zone of Gambela Region; a total of eleven speakers are listed for the zone, but almost 10,000 ethnic Mejenger or Messengo people.
Burji language is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken by the Burji people who reside in Ethiopia south of Lake Chamo. There are over 49,000 speakers in Ethiopia, and a further 36,900 speakers in Kenya. Burji belongs to the Highland East Cushitic group of the Cushitic branch of the Afro-Asiatic family.
Gedeo is a Highland East Cushitic language of the Afro-Asiatic family spoken in south central Ethiopia. Alternate names for the language include Derasa, Deresa, Darassa, Geddeo, Derasanya, Darasa. It is spoken by the Gedeo people, who live in the highland area, southwest of Dila and east of Lake Abaya.
Highland East Cushitic or Burji-Sidamo is a branch of the Afroasiatic language family spoken in south-central Ethiopia. They are often grouped with Lowland East Cushitic, Dullay, and Yaaku as East Cushitic, but that group is not well defined. The most populous language is Sidama, with close to two million speakers.
Alaba-Kʼabeena, also known as Wanbasana, is a Highland East Cushitic language spoken in Ethiopia by the Halaba and Kebena people in the Great Rift Valley southwest of Lake Shala, specifically in Alaba special district, the Kebena district of Gurage Zone, and the Goro district of Oromia Region. The literacy rate of native speakers in their language is below 1%, while their literacy rate in second languages is 8.6%; Alaba-Kʼabeena is taught in primary schools. It has an 81% lexical similarity with Kambaata. However, Fleming (1976) classifies Kʼabeena as a dialect of Kambaata, and Blench (2006) classifies both as dialects of Kambaata. The 2007 census in Ethiopia lists Alaba and Qebena as separate languages.
Dizin is an Omotic language of the Afro-Asiatic language family spoken by the Dizi people, primarily in the Maji woreda of the Southern Nations, Nationalities and Peoples Region, located in southwestern Ethiopia. The 2007 census listed 33,927 speakers. A population of 17,583 was identified as monolinguals in 1994.
The Ethiopian language area is a hypothesized linguistic area that was first proposed by Charles A. Ferguson, who posited a number of phonological and morphosyntactic features that were found widely across Ethiopia and Eritrea, including the Ethio-Semitic, Cushitic and Omotic languages but not the Nilo-Saharan languages.
David Appleyard is a British academic and an specialist in Ethiopian languages and linguistics.
Murle is a Surmic Language spoken by the Murle people in the southeast of South Sudan, near the Ethiopian border. A very small number of Murle live across the border in southwestern Ethiopia.
The Halaba people are an ethnic group inhabiting the central Ethiopian highlands. The Halaba claim to originate from the Arab cleric, Abadir who settled in Harar. In the middle ages, Halaba were part of the Hadiya state. In the 1400s, their Garad (chief) was in conflict with the Abyssinian monarch Zara Yaqob. They are mostly Muslims but there are also some Christians. A map of the region from 1628 shows a Kingdom of Halaba. They speak Halaba-Kʼabeena which is a member of the Highland East Cushitic languages within the Afroasiatic family. Sidi Mohammed the Garad of Hadiya is stated to be a forefather for the Halaba people.
Proto-Cushitic is the reconstructed proto-language common ancestor of the Cushitic language family. Its words and roots are not directly attested in any written works, but have been reconstructed through the comparative method, which finds regular similarities between languages not explained by coincidence or word-borrowing, and extrapolates ancient forms from these similarities.
References
- ALAMU BANTA ATAARA, Kookaata. Kambaatissa–Amaarsa–Ingiliizissa Laaga Doonnuta. ከምባትሳ–ኣማርኛ–እንግሊዝኛ መዝገበ ቃላት. Kambatissa–Amharic–English Dictionary (Addis Abäba: Bǝrhanǝnna sälam mattämiya dǝrǝǧǧǝt, 2009 EC = 2016/2017 CE); 1165 pp.
- Korhonen, Elsa, Mirja Saksa, and Ronald J. Sim. 1986. "A dialect study of Kambaata-Hadiyya (Ethiopia) [part 1]." Afrikanistische Arbeitspapiere 5: 5-41.
- Korhonen, Elsa, Mirja Saksa, and Ronald J. Sim. 1986. "A dialect study of Kambaata-Hadiyya (Ethiopia), part 2: Appendices." Afrikanistische Arbeitspapiere 6: 71-121.
- Sim, Margaret G. 1985. "Kambaata Verb Morphophonemics," The morphophonemics of five Highland East Cushitic languages including Burji. Afrikanistische Arbeitspapiere 2. Köln: Institut für Afrikanistik, Universität zu Köln. Pages 44–63.
- Sim, Margaret. 1988. "Palatalization and gemination in the Kambaata verb." Journal of Afroasiatic Languages 1.58-65.
- Treis, Yvonne (2008). A Grammar of Kambaata. Part 1: Phonology, Nominal Morphology and Non-verbal Predication. Cushitic Language Studies. Vol. 26. Köln: Rüdiger Köppe Verlag.