
The Afroasiatic languages are a language family of about 400 languages spoken predominantly in West Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and parts of the Sahara and Sahel. Over 500 million people are native speakers of an Afroasiatic language, constituting the fourth-largest language family after Indo-European, Sino-Tibetan, and Niger–Congo. Most linguists divide the family into six branches: Berber, Chadic, Cushitic, Egyptian, Omotic, and Semitic. The vast majority of Afroasiatic languages are considered indigenous to the African continent, including all those not belonging to the Semitic branch.

The Berber languages, also known as the Amazigh languages or Tamazight, are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They comprise a group of closely related but mostly mutually unintelligible languages spoken by Berber communities, who are indigenous to North Africa. The languages are primarily spoken and not typically written. Historically, they have been written with the ancient Libyco-Berber script, which now exists in the form of Tifinagh. Today, they may also be written in the Berber Latin alphabet or the Arabic script, with Latin being the most pervasive.
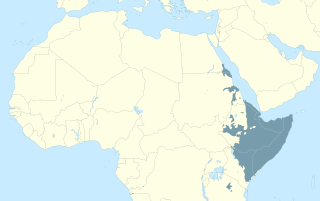
The Cushitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken primarily in the Horn of Africa, with minorities speaking Cushitic languages to the north in Egypt and Sudan, and to the south in Kenya and Tanzania. As of 2012, the Cushitic languages with over one million speakers were Oromo, Somali, Beja, Afar, Hadiyya, Kambaata, and Sidama.
Ongota is a moribund language of southwest Ethiopia. UNESCO reported in 2012 that out of a total ethnic population of 115, only 12 elderly native speakers remained, the rest of their small village on the west bank of the Weito River having adopted the Tsamai language instead. The default word order is subject–object–verb. The classification of the language is obscure.

Ogiek is a Southern Nilotic language of the Kalenjin family spoken or once spoken by the Ogiek peoples, scattered groups of hunter-gatherers in Southern Kenya and Northern Tanzania. Most Ogiek speakers have assimilated to cultures of surrounding peoples: the Akie in northern Tanzania now speak Maasai and the Ogiek of Kinare, Kenya now speak Gikuyu. Ndorobo is a term considered derogatory, occasionally used to refer to various groups of hunter-gatherers in this area, including the Ogiek.
Lowland East Cushitic is a group of roughly two dozen diverse languages of the Cushitic branch of the Afro-Asiatic family. Its largest representatives are Oromo and Somali.
The South Cushitic or Rift languages of Tanzania are a branch of the Cushitic languages. The most numerous is Iraqw, with one million speakers. Scholars believe that these languages were spoken by Southern Cushitic agro-pastoralists from Ethiopia, who began migrating southward into the Great Rift Valley in the third millennium BC.
The Maa languages are a group of closely related Eastern Nilotic languages spoken in parts of Kenya and Tanzania by more than a million speakers. They are subdivided into North and South Maa. The Maa languages are related to the Lotuko languages spoken in South Sudan.
Ongamo, or Ngas, is an extinct Eastern Nilotic language of Tanzania. It is closely related to the Maa languages, but more distantly than they are to each other. Ongamo has 60% of lexical similarity with Maasai, Samburu, and Camus. Speakers have shifted to Chagga, a dominant regional Bantu language.
The Yaaku are a people who are said to have lived in regions of southern Ethiopia and central Kenya, possibly through to the 18th century. The language they spoke is today called Yaakunte. The Yaaku assimilated a hunter-gathering population, whom they called Mukogodo, when they first settled in their place of origin and the Mukogodo adopted the Yaakunte language. However, the Yaaku were later assimilated by a food producing population and they lost their way of life. The Yaakunte language was kept alive for sometime by the Mukogodo who maintained their own hunter-gathering way of life, but they were later immersed in Maasai culture and adopted the Maa language and way of life. The Yaakunte language is today facing extinction but is undergoing a revival movement. In the present time, the terms Yaaku and Mukogodo, are used to refer to a population living in Mukogodo forest west of Mount Kenya.
The Asa (Aasá) language, commonly rendered Aasax, is an extinct Afroasiatic language formerly spoken by the Asa people of Tanzania. The language is extinct; ethnic Assa in northern Tanzania remember only a few words they overheard their elders use, and none ever used it themselves. Little is known of the language; what is recorded was probably Aasa lexical words used in a register of Maasai, similar to the mixed language Mbugu.

The languages of Ethiopia include the official languages of Ethiopia, its national and regional languages, and a large number of minority languages, as well as foreign languages.
Animere is a language spoken in Ghana, in the Kecheibe and Kunda villages of the Benimbere people. It is most closely related to Kebu or Akebu of Togo. Both are Ghana Togo Mountain languages (GTM), classified as members of the Ka-Togo group by Heine (1968). Like most other GTM languages, Animere is a noun-class language.
El Molo is a possibly extinct language belonging to the Cushitic branch of the Afro-Asiatic language family. It was spoken by the El Molo people on the southeastern shore of Lake Turkana, in northern Kenya. Alternate names to El Molo are Dehes, Elmolo, Fura-Pawa, and Ldes. It was thought to be extinct in the middle part of the 20th century, but a few speakers were found in the later 20th century. Most of the El Molo population have shifted to the neighboring Samburu language. El Molo also has no known dialects but it is similar to Daasanach.
Alagwa (Alaagwa’isa) is a Cushitic language spoken in Tanzania in the Dodoma region. Some Alagwa have shifted to other languages such as Sandawe.
Maʼa is a Bantu language of Tanzania.
Taita is a Bantu language spoken in the Taita Hills of Kenya. It is closely related to the Chaga languages of Kenya and Tanzania. The Saghala variety is distinct enough to be considered a language separate from the Daw'ida and Kasigau dialects.
The East Cushitic languages are a branch of Cushitic within the Afroasiatic phylum. Prominent East Cushitic languages include Oromo, Somali, and Sidama. The unity of East Cushitic has been contested: Robert Hetzron suggested combining the Highland East Cushitic languages with the Agaw languages into a "Highland Cushitic" branch, while most other scholars follow Martino Mario Moreno in seeing Highland and Lowland as two branches of East Cushitic.
The Mukogodo, are a people who are said to have lived in regions of central Kenya around Mt. Kenya, possibly through to the 18th century. A community known as the Yaaku later moved into their territory and the Mukogodo, adopted the Yaaku language, referred to as Yaakunte. The Yaaku community was later assimilated by a food producing population and they lost their way of life. Their language, Yaakunte, was kept alive for some time by the Mukogodo who had all along maintained their own hunter-gathering way of life. However, the Mukogodo were later assimilated by the Maasai and adopted the Maa language. The Yaakunte language is today facing extinction but is undergoing a revival movement. In the present time, the terms Yaaku and Mukogodo, are used to refer to a population living in Mukogodo forest west of Mount Kenya.

The boundaries of this corridor can be defined within the Maasai territory. The corridor stretches from the Arusha Region, through the Kilimanjaro Region of Tanzania to the Taita-Taveta County of Kenya. To varying degrees, the people in this corridor are essentially a mixture of similar Bantu, Nilotic and Cushitic branches of the African people. The groups were dynamic, fluid and flexible. They shared a common history characterised by constant movement between the different areas for trade, battles, migration as well as social reasons. They were categorised arbitrarily by Europeans into the following culturally, linguistically and/or genetically related groups:





