
The Nilo-Saharan languages are a proposed family of African languages spoken by somewhere around 70 million speakers, mainly in the upper parts of the Chari and Nile rivers, including historic Nubia, north of where the two tributaries of the Nile meet. The languages extend through 17 nations in the northern half of Africa: from Algeria to Benin in the west; from Libya to the Democratic Republic of the Congo in the centre; and from Egypt to Tanzania in the east.
The Nubian languages are a group of related languages spoken by the Nubians. In the past, Nubian languages were spoken throughout much of Sudan, but as a result of Arabization they are today mostly limited to the Nile Valley between Aswan and Al Dabbah. In the 1956 Census of Sudan there were 167,831 speakers of Nubian languages. Nubian is not to be confused with the various Nuba languages spoken in villages in the Nuba mountains and Darfur.
Tama, or Tamongobo, is the primary language spoken by the Tama people in Ouaddai, eastern Chad and in Darfur, western Sudan. It is a Taman language which belongs to the Eastern Sudanic branch of the Nilo-Saharan language family. Miisiirii is often considered a dialect, though it is not particularly close.
The Kujargé language is spoken in seven villages in eastern Chad near Jebel Mirra, and in villages scattered along the lower Wadi Salih and Wadi Azum in Darfur, Sudan. It is estimated to have about 1,000 speakers.

In most classifications, the Eastern Sudanic languages are a group of nine families of languages that may constitute a branch of the Nilo-Saharan language family. Eastern Sudanic languages are spoken from southern Egypt to northern Tanzania.
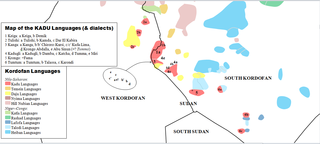
The Kadu languages, also known as Kadugli–Krongo or Tumtum, are a small language family of the Kordofanian geographic grouping, once included in Niger–Congo. However, since Thilo Schadeberg (1981), Kadu is widely seen as Nilo-Saharan. Evidence for a Niger-Congo affiliation is rejected, and a Nilo-Saharan relationship is controversial. A conservative classification would treat the Kadu languages as an independent family.
The Shatt language is a Daju language of the Eastern Daju family spoken by the Shatt people in the Shatt Hills southwest of Kaduqli in South Kordofan province in southern Sudan.
Dar Sila is the name of the wandering sultanate of the Dar Sila Daju, a multi-tribal ethnic group in Chad and Sudan. The number of the people in this group exceeds 50,000. They speak the Sila language, a Nilo-Saharan language. Most members of this ethnic group are Muslims.
The Daju people are a group of seven distinct ethnicities speaking related languages living on both sides of the Chad-Sudan border and in the Nuba Mountains. Separated by distance and speaking different languages, at present, they generally have little cultural affinity to each other.
Birgid is an extinct Nubian language that was spoken in western Sudan, north of the city of Nyala in South Darfur. Canadian linguist Thelwall mentions his last contact with elderly speakers of Birgid in 1972.
Nyala, also known as Dar Fur, Darfur Daju, Daju Darfur, Beke, Dagu, Daju Ferne and Fininga, is an Eastern Sudanic language of Sudan, one of three closely related languages in the area called "Daju". It is spoken near Nyala, the capital of South Darfur province by the Dar Fur Daju people. There are two divergent dialects: Nyala and Lagowa.
The Sila language, also known as Dar Sila, Dar Sila Daju, Bokor, Bokorike, Bokoruge, Dadjo, Dajou, Daju, and Sula, is an Eastern Sudanic language, one of three closely related languages in the area called "Daju". It is spoken in Chad near the Darfur border, with migration into Sudan. There are two dialects, Sila proper and Mongo, the latter not to be confused with Daju Mongo.
Daju Mongo, also Wadai Daju or Dar Daju Daju, is an Eastern Sudanic language, one of three closely related languages in the area called "Daju". It is spoken in Chad by the Dar Daju Daju people near the Darfur border. There are three dialects, Bardangal, Eref, and Gadjira.
Midob is a Nubian language spoken by the Midob people of North Darfur region of Sudan. As a Nubian language, it is part of the wider Nilo-Saharan language family.
Afitti is a language spoken on the eastern side of Jebel el-Dair, a solitary rock formation in the North Kordofan province of Sudan. Although the term ‘Dinik’ can be used to designate the language regardless of cultural affiliation, people in the villages of the region readily recognize the terms ‘Ditti’ and ‘Afitti.’ There are approximately 4,000 speakers of the Afitti language and its closest linguistic neighbor is the Nyimang language, spoken west of Jebel el-Dair in the Nuba Mountains of the South Kordofan province of Sudan.
Logorik, Subori, or Saburi is a (critically) endangered language spoken in Eastern Sudan and Western Chad.
The Logorik are an ethnic group in the southern part of Sudan. They are one of seven distinct ethnicities comprising the Daju people. They speak the Logorik language, a Nilo-Saharan language. They live in the north, central Nuba Mountains in the Jebel Liguri hills area northeast of Kadugli. The population of this ethnic group likely exceeds 2,000.
The Dar Fur Daju are an ethnic group in the Sudan. They are one of seven distinct ethnicities comprising the Daju people. They speak the Nyala language. They live in Southern Darfur in the Sudan in the Daju Hills 40 km northeast of Nyala - although most of this population has fled to Chad as a result of the Darfur Conflict. There is also a small population of Dar Fur Daju near the city of Lagowa in the Nuba Hills. Their total population numbers 98,000 (2017). They are mostly Muslim.

The Nuba Mountains, located in the West Kordofan and South Kordofan states in the south of Sudan, are inhabited by a diverse set of populations speaking various languages not closely related to one another.
The Kujarke people are a little-known ethnic group of the Ouaddaï Region in eastern Chad and South Darfur, Sudan. They speak Kujargé, a divergent, unclassified Afro-Asiatic language. Their current population and locations are unknown due to the war in Darfur. Furthermore, they have not been previously recorded as a separate ethnic group by any government or foreign aid organization.




