
Beryllium is a chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a steel-gray, strong, lightweight and brittle alkaline earth metal. It is a divalent element that occurs naturally only in combination with other elements to form minerals. Notable gemstones high in beryllium include beryl and chrysoberyl. It is a relatively rare element in the universe, usually occurring as a product of the spallation of larger atomic nuclei that have collided with cosmic rays. Within the cores of stars, beryllium is depleted as it is fused into heavier elements. Beryllium constitutes about 0.0004 percent by mass of Earth's crust. The world's annual beryllium production of 220 tons is usually manufactured by extraction from the mineral beryl, a difficult process because beryllium bonds strongly to oxygen.

Sulfur (in British English: sulphur) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature.

Sulfur dioxide or sulphur dioxide is the chemical compound with the formula SO
2. It is a toxic gas responsible for the smell of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic activity and is produced as a by-product of copper extraction and the burning of sulfur-bearing fossil fuels. Sulfur dioxide has a pungent smell like nitric acid.
A period 2 element is one of the chemical elements in the second row of the periodic table of the chemical elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behavior of the elements as their atomic number increases; a new row is started when chemical behavior begins to repeat, creating columns of elements with similar properties.
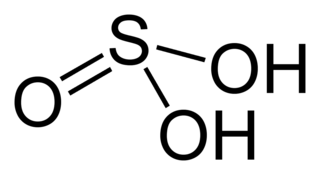
Sulfurous acid (also Sulfuric(IV) acid, Sulphuric acid (UK), Sulphuric(IV) acid (UK)) is the chemical compound with the formula H2SO3. There is no evidence that sulfurous acid exists in solution, but the molecule has been detected in the gas phase. The conjugate bases of this elusive acid are, however, common anions, bisulfite (or hydrogen sulfite) and sulfite. Sulfurous acid is an intermediate species in the formation of acid rain from sulfur dioxide.

Sulfites or sulphites are compounds that contain the sulfite ion, SO2−
3. The sulfite ion is the conjugate base of bisulfite. Although its acid is elusive, its salts are widely used.

A sulfonic acid (or sulphonic acid) refers to a member of the class of organosulfur compounds with the general formula R−S(=O)2−OH, where R is an organic alkyl or aryl group and the S(=O)2(OH) group a sulfonyl hydroxide. As a substituent, it is known as a sulfo group. A sulfonic acid can be thought of as sulfuric acid with one hydroxyl group replaced by an organic substituent. The parent compound (with the organic substituent replaced by hydrogen) is the parent sulfonic acid, HS(=O)2(OH), a tautomer of sulfurous acid, S(=O)(OH)2. Salts or esters of sulfonic acids are called sulfonates.

Thionyl chloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula SOCl
2. It is a moderately volatile colourless liquid with an unpleasant acrid odour. Thionyl chloride is primarily used as a chlorinating reagent, with approximately 45,000 tonnes per year being produced during the early 1990s, but is occasionally also used as a solvent. It is toxic, reacts with water, and is also listed under the Chemical Weapons Convention as it may be used for the production of chemical weapons.

Dimethyl sulfite is a sulfite ester with the chemical formula (CH3O)2SO.

Diethyl sulfite (C4H10O3S) is an ester of sulfurous acid. Among other properties, diethyl sulfite inhibits the growth of mold spores during grain storage.

The Schiff test is an early organic chemistry named reaction developed by Hugo Schiff, and is a relatively general chemical test for detection of many organic aldehydes that has also found use in the staining of biological tissues. The Schiff reagent is the reaction product of a dye formulation such as fuchsin and sodium bisulfite; pararosaniline and new fuchsin are not dye alternatives with comparable detection chemistry.

Beryllium hydroxide, Be(OH)2, is an amphoteric hydroxide, dissolving in both acids and alkalis. Industrially, it is produced as a by-product in the extraction of beryllium metal from the ores beryl and bertrandite. The natural pure beryllium hydroxide is rare (in form of the mineral behoite, orthorhombic) or very rare (clinobehoite, monoclinic). When alkali is added to beryllium salt solutions the α-form (a gel) is formed. If this left to stand or boiled, the rhombic β-form precipitates. This has the same structure as zinc hydroxide, Zn(OH)2, with tetrahedral beryllium centers.
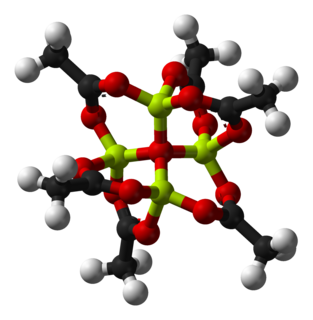
Basic beryllium acetate is the chemical compound with the formula Be4O(O2CCH3)6. This compound adopts a distinctive structure, but it has no applications and has been only lightly studied. It is a colourless solid that is soluble in organic solvents.
The sulfite process produces wood pulp that is almost pure cellulose fibers by treating wood chips with solutions of sulfite and bisulfite ions. These chemicals cleave the bonds between the cellulose and lignin components of the lignocellulose. A variety of sulfite/bisulfite salts are used, including sodium (Na+), calcium (Ca2+), potassium (K+), magnesium (Mg2+), and ammonium (NH4+). The lignin is converted to lignosulfonates, which are soluble and can be separated from the cellulose fibers. For the production of cellulose, the sulfite process competes with the Kraft process, which produces stronger fibers and is less environmentally costly.

Magnesium sulfite is the magnesium salt of sulfurous acid with the formula MgSO
3. Its most common hydrated form has 6 water molecules making it a hexahydrate, MgSO
3·6H
2O. When heated above 40 °C (104 °F), it is dehydrated to magnesium sulfite trihydrate, or MgSO
3·3H
2O. The anhydrous form is hygroscopic, meaning that it readily absorbs water from the air.

A disulfite, commonly known as metabisulfite or pyrosulfite, is a chemical compound containing the ion S
2O2−
5. It is a colorless dianion that is primarily marketed in the form of sodium metabisulfite or potassium metabisulfite. When dissolved in water, these salts release the bisulfite HSO−
3 ion. These salts act equivalently to sodium bisulfite or potassium bisulfite.

Ammonium sulfite is the ammonium salt of sulfurous acid with the chemical formula (NH4)2SO3.

Sodium bisulfite (or sodium bisulphite, sodium hydrogen sulfite) is a chemical mixture with the approximate chemical formula NaHSO3. Sodium bisulfite in fact is not a real compound, but a mixture of salts that dissolve in water to give solutions composed of sodium and bisulfite ions. It is a white solid with an odour of sulfur dioxide. Regardless of its ill-defined nature, "sodium bisulfite" is a food additive with E number E222.

Paper chemicals designate a group of chemicals that are used for paper manufacturing, or modify the properties of paper. These chemicals can be used to alter the paper in many ways, including changing its color and brightness, or by increasing its strength and resistance to water.

Thiosulfurous acid (HS−S(=O)−OH) is a hypothetical compound with the formula S2(OH)2. Attempted synthesis leads to polymers. It is a low oxidation state (+1) sulfur acid. It is the equivalent acid for disulfur monoxide. Salts derived from thiosulfurous acid, which are also unknown, are named "thiosulfites" or "sulfurothioites". The ion is S=SO2−
2.


















