
The Pacific Electric Railway Company, nicknamed the Red Cars, was a privately owned mass transit system in Southern California consisting of electrically powered streetcars, interurban cars, and buses and was the largest electric railway system in the world in the 1920s. Organized around the city centers of Los Angeles and San Bernardino, it connected cities in Los Angeles County, Orange County, San Bernardino County and Riverside County.

Santa Monica Boulevard is a major west–east thoroughfare in Los Angeles County, California, United States. It runs from Ocean Avenue in Santa Monica near the Pacific Ocean to Sunset Boulevard at Sunset Junction in Los Angeles. It passes through Beverly Hills and West Hollywood. A portion of it is designated as California State Route 2, while the full avenue was Historic Route 66.

The Hollywood Subway, as it is most commonly known, officially the Belmont Tunnel, was a subway tunnel used by the interurban streetcars of the Pacific Electric Railway. It ran from its northwest entrance in today's Westlake district to the Subway Terminal Building, in the Historic Core, the business and commercial center of Los Angeles from around the 1910s through the 1950s. The Subway Terminal was one of the Pacific Electric Railway’s two main hubs, the other being the Pacific Electric Building at 6th and Main. Numerous lines proceeded from the San Fernando Valley, Glendale, Santa Monica and Hollywood into the tunnel in Westlake and traveled southeast under Crown and Bunker Hill towards the Subway Terminal.

The Monrovia–Glendora Line was a route on the Pacific Electric Railway serving the San Gabriel Valley. It operated from 1902 to 1951, supporting nearby real estate development.

Glendale–Burbank is a defunct Pacific Electric railway line that was operational from 1904 to 1955 in Southern California, running from Downtown Los Angeles to Burbank via Glendale. Short lines terminated Downtown and in North Glendale, including the popular Edendale Local.

The Los Angeles and Independence Railroad, opened on October 17, 1875, was a steam-powered rail line which ran between the Santa Monica Long Wharf and 5th and San Pedro streets in downtown Los Angeles.

The Santa Monica Air Line was an interurban railroad operated by the Pacific Electric between Santa Monica and downtown Los Angeles. Electric passenger service operated over the line between 1908 and 1953. After abandonment as a freight railroad, most of the route was converted to light rail for use by the Metro E Line.

The Westgate Line was a suburban route operated by the Pacific Electric Railway from 1911 to 1940. This line was one of four lines connecting Downtown Los Angeles and Santa Monica that did not run through Hollywood. The line is notable for taking a circuitous route towards its end, along San Vicente Boulevard, mainly because it was built to encourage construction of new homes near Pacific Palisades.

The Sawtelle Line was an interurban railway route primarily operated by the Pacific Electric Railway that ran between Downtown Los Angeles and Santa Monica, California. The line was established by the Pasadena and Pacific Railway between 1896 and 1901, with passenger service running until 1940.

The South Hollywood–Sherman Line was a suburban route of the Pacific Electric Railway. The line ran between Downtown Los Angeles and the suburb of Sherman. The line was named after Moses Sherman, who built the line and the Sherman street car yard on the line in West LA. The large 5.56-acre (2.25 ha) rail facility was on Santa Monica Boulevard just west of La Cienega Boulevard. The yard had a steam power house, a car barn and a shop building.

The Hollywood Line was a local streetcar line of the Pacific Electric Railway. It primarily operated between Downtown Los Angeles and Hollywood, with some trips as far away as Beverly Hills and West Los Angeles. It was the company's busiest route prior to the opening of the Hollywood Subway. Designated as route 32, the line operated from 1909 until 1954.

The Venice Short Line was a Pacific Electric (PE) interurban railway line in Los Angeles which traveled from downtown Los Angeles to Venice, Ocean Park, and Santa Monica via Venice Boulevard. The route was especially busy on Sundays, as Venice was PE's most popular beachfront destination.

The Los Angeles Pacific Railroad (1896−1911) (LAP) was an electric public transit and freight railway system in Los Angeles County, California. At its peak it had 230 miles (370 km) of track extending from Downtown Los Angeles to the Westside, Santa Monica, and the South Bay towns along Santa Monica Bay.

The old Beverly Hills Main Post Office is a Renaissance Revival building at the Beverly Hills Civic Center in Beverly Hills, California. The building has carried the addresses 469 North Crescent Drive and 470 North Canon Drive. It was built as the main post office in the 1930s, remaining a post office until the 1990s, and in the 2010s became the Paula Kent Meehan Historic Building of the Wallis Annenberg Center for the Performing Arts.

The Western and Franklin Avenue Line was a Pacific Electric streetcar line which traveled from Los Angeles to Hollywood. It operated from 11th and Hill Streets via Hill, Sunset, Santa Monica Boulevard, Western Avenue, Franklin Avenue, Argyle Avenue, Yucca Street, and Vine Street to end at Hollywood and Vine Boulevards. It operated from 1908 to 1940. The Brush Canyon Line branched from this line at Bronson.

The San Bernardino–Riverside is a former Pacific Electric (PE) interurban railway line in the Inland Empire. Unlike most of the company's services, trains did not travel to Downtown Los Angeles and instead provided a suburban service between San Bernardino and Riverside.

The Venice–Inglewood Line is a former railway line in Los Angeles County, California. The route was established by the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway in 1887 before eventually being absorbed into the Pacific Electric interurban railway system. Service under electrification was very sparse, providing a suburban route between Venice and Inglewood.

The Venice Boulevard Line was a local streetcar line of the Pacific Electric. It operated between Downtown Los Angeles and Vineyard Junction, where riders could transfer to interurban cars. Nearly all Venice Short Line cars did not accept local passengers, leaving this as the primary streetcar service along its namesake boulevard.
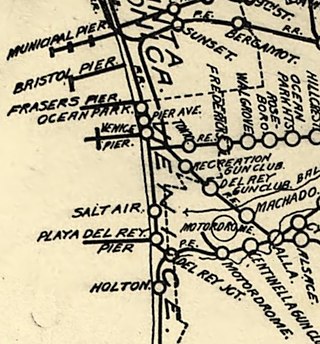
The Venice–Playa del Rey Line was a streetcar line of the Pacific Electric. It operated along the Pacific Ocean between Playa del Rey and Venice, California. It was also referred to as the Lagoon Line.


















