
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire or the Dual Monarchy, was a constitutional monarchy in Central and Eastern Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed when the Austrian Empire adopted a new constitution; as a result Austria (Cisleithania) and Hungary (Transleithania) were placed on equal footing. It dissolved when its member states proclaimed sovereignty and independence following the First World War.

Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning 93,030 square kilometres (35,920 sq mi) in the Carpathian Basin, it borders Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Austria to the northwest, Romania to the east, Serbia to the south, Croatia to the southwest, and Slovenia to the west. With about 10 million inhabitants, Hungary is a medium-sized member state of the European Union. The official language is Hungarian, which is the most widely spoken Uralic language in the world, and among the few non-Indo-European languages to be widely spoken in Europe. Hungary's capital and largest city is Budapest; other major urban areas include Debrecen, Szeged, Miskolc, Pécs and Győr.

The House of Habsburg, also officially called the House of Austria, was one of the most influential and distinguished royal houses of Europe. The throne of the Holy Roman Empire was continuously occupied by the Habsburgs from 1438 until their extinction in the male line in 1740. The house also produced kings of Bohemia, Hungary, Croatia, Galicia, Portugal and Spain with their respective colonies, as well as rulers of several principalities in the Netherlands and Italy. From the 16th century, following the reign of Charles V, the dynasty was split between its Austrian and Spanish branches. Although they ruled distinct territories, they nevertheless maintained close relations and frequently intermarried.

Hungarian is a Uralic language, possibly of the Ugric branch, spoken in Hungary and parts of several neighbouring countries. It is the official language of Hungary and one of the 24 official languages of the European Union. Outside Hungary it is also spoken by communities of Hungarians in the countries that today make up Slovakia, western Ukraine (Subcarpathia), central and western Romania (Transylvania), northern Serbia (Vojvodina), northern Croatia and northern Slovenia.

Transylvania is a historical region which is located in central Romania. Bound on the east and south by its natural borders, the Carpathian mountain range, historical Transylvania extended westward to the Apuseni Mountains. The term sometimes encompasses not only Transylvania proper, but also parts of the historical regions of Crișana and Maramureș, and occasionally the Romanian part of Banat.

Budapest is the capital and the most populous city of Hungary, and the tenth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits. The city has an estimated population of 1,752,286 over a land area of about 525 square kilometres. Budapest is both a city and county, and forms the centre of the Budapest metropolitan area, which has an area of 7,626 square kilometres and a population of 3,303,786, comprising 33% of the population of Hungary.

The Treaty of Trianon was the peace agreement of 1920 that formally ended World War I between most of the Allies of World War I and the Kingdom of Hungary, the latter being one of the successor states to Austria-Hungary. The treaty regulated the status of an independent Hungarian state and defined its borders. It left Hungary as a landlocked state that covered 93,073 square kilometres (35,936 sq mi), only 28% of the 325,411 square kilometres (125,642 sq mi) that had constituted the pre-war Kingdom of Hungary. Its population was 7.6 million, only 36% of the pre-war kingdom's population of 20.9 million. The areas that were allocated to neighbouring countries in total had a majority of non-Hungarians but 31% of Hungarians were left outside of post-Trianon Hungary. Five of the pre-war kingdom's ten largest cities were drawn into other countries. The treaty limited Hungary's army to 35,000 officers and men, and the Austro-Hungarian Navy ceased to exist.

The Hungarian Revolution of 1956, or the Hungarian Uprising, was a nationwide revolution against the Hungarian People's Republic and its Soviet-imposed policies, lasting from 23 October until 10 November 1956. Leaderless at the beginning, it was the first major threat to Soviet control since the Red Army drove Nazi Germany from its territory at the End of World War II in Europe.
The Hungary national football team represents Hungary in international football and is controlled by the Hungarian Football Federation.

Pál Losonczi was a Hungarian Communist political figure. He was Chairman of the Hungarian Presidential Council from 1967 to 1987.

The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen I at Esztergom around the year 1000; his family led the monarchy for 300 years. By the 12th century, the kingdom became a European middle power within the Western world.

Habsburg Monarchy is an umbrella term used by historians for the lands and kingdoms of the House of Habsburg, especially for those of the Austrian branch. Although from 1438 until 1806 the head of the House of Habsburg was also Holy Roman Emperor, the Empire itself is not considered a part of the Habsburg Monarchy.

Cantanhede is a city and municipality in the Coimbra District, in the Centro Region, Portugal. The population in 2011 was 36,595, in an area of 390.88 km².

The Hungarian People's Republic was a one-party socialist republic from 20 August 1949 to 23 October 1989. It was governed by the Hungarian Socialist Workers' Party, which was under the influence of the Soviet Union. Pursuant to the 1944 Moscow Conference, Winston Churchill and Joseph Stalin had agreed that after the war Hungary was to be included in the Soviet sphere of influence.
Heresznye is a village in Somogy county, Hungary.

The Kingdom of Hungary, from 1945 to 1946 known as the Hungarian State, and sometimes referred to as the Regency or the Horthy era, existed as a country from 1920 to 1946 under the rule of Regent Miklós Horthy. Horthy officially represented the Hungarian monarchy of Charles IV, Apostolic King of Hungary. Attempts by Charles IV to return to the throne were prevented by threats of war from neighbouring countries and by the lack of support from Horthy. Charles died in 1922, leaving the throne empty for the remainder of the country's time as a kingdom.

Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary and historical Hungarian lands who share a common ancestry, culture, history and language. Hungarian belongs to the Uralic language family. There are an estimated 14.2–14.5 million ethnic Hungarians and their descendants worldwide, of whom 9.6 million live in today's Hungary. About 2.2 million Hungarians live in areas that were part of the Kingdom of Hungary before the Treaty of Trianon and are now parts of Hungary's seven neighbouring countries, Slovakia, Ukraine, Romania, Serbia, Croatia, Slovenia and Austria. Significant groups of people with Hungarian ancestry live in various other parts of the world, most of them in the United States, Canada, Germany, France, the United Kingdom, Brazil, Australia, and Argentina.
Hungary in its modern (post-1946) borders roughly corresponds to the Great Hungarian Plain . During the Iron Age, it was at the boundary of Celtic, Illyrian and Iranian (Scythian) cultural spheres.

Mazraat es-Siyad is a small town in the highlands of the Jbeil District in the Mount Lebanon Governorate, Lebanon. The town is 58 kilometres (36 mi) away from Beirut and stands at an elevation of 1,250 meters above sea level.
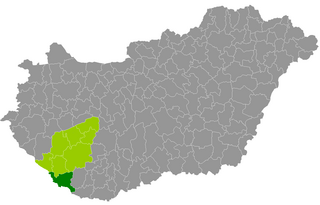
Barcs is a district in southern part of Somogy County. Barcs is also the name of the town where the district seat is found. The district is located in the Southern Transdanubia Statistical Region.




















