The Bathydraconidae, or the Antarctic dragonfishes, are a family of marine ray-finned fishes, notothenioids belonging to the Perciform suborder Notothenioidei. The family comprises four genera. These fishes are endemic to deep waters off Antarctica.

Bovichtidae, the temperate icefishes or thornfishes, is a family of marine ray-finned fishes, classified in the suborder Notothenioidei of the order Perciformes. They are native to coastal waters off Australia, New Zealand, and South America.

Bovichtus variegatus, the thornfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Bovichtidae, the temperate icefishes or thornfishes. It is endemic to New Zealand.

Notothenia is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes with the species in this genus often having the common name of rockcod. They are native to the Southern Ocean and other waters around Antarctica.

The Artedidraconidae, barbeled plunderfishes, are a family of marine ray-finned fishes, notothenioids belonging to the Perciform suborder Notothenioidei. The family comprises four genera. These fishes are endemic to deep waters off Antarctica.

Harpagifer, the spiny plunderfishes is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes, belonging to the family Harpagiferidae, it is the only genus in this monotypic family. They are found in the Southern Ocean.

Chionodraco hamatus is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Channichthyidae, the crocodile icefishes. It is found in the Southern Ocean.

Zanclorhynchus spinifer, also known as the Antarctic horsefish or spiny horsefish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Congiopodidae, the horsefishes or pigfishes. This fish is found in the Southern Ocean where it occurs at depths of from 5 to 400 metres. This species grows to a length of 40 centimetres (16 in) TL and is of minor importance to the commercial fishery industry.

Mawson's dragonfish is a species of Antarctic dragonfish native to the Southern Ocean around Antarctica. It is found at depths of from 110 to 300 metres over the continental shelf. This species is the only known member of its genus.
Gerlachea is a monotypic genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Bathydraconidae, the Antarctic dragonfishes, its only species is Gerlachea australis. It is found at depths of from 200 to 670 metres over the Antarctic continental shelf. This species is the only known member of its genus.

Prionodraco is a monotypic genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Bathydraconidae, the Antarctic dragonfishes, its only species is Prionodraco evansii. These fishes are native to the Southern Ocean.
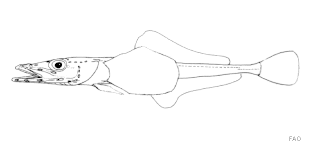
Vomeridens is a monotypic genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Bathydraconidae, the Antarctic dragonfishes, its only species is Vomeridens infuscipinnis. These fishes are native to the Southern Ocean.

Cottoperca is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Bovichtidae, the temperate icefishes or thornfishes. They are found in the southeastern Pacific, southwestern Atlantic and northern Southern Oceans off southern South America.

Chionobathyscus dewitti is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Channichthyidae, the crocodile icefishes. This species is found in the Southern Ocean.
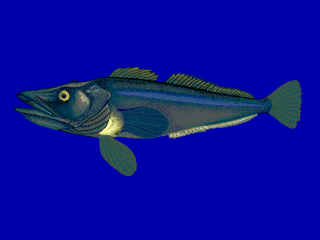
Pseudochaenichthys is a monotypic genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Channichthyidae, the crocodile icefishes. Its only member is Pseudochaenichthys georgianus, the South Georgia icefish, which is found in the Southern Ocean.
Nototheniops is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. The species in this genus are native to the Southern Ocean.
Gobionotothen acuta, the triangular rockcod or the triangular notothen, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. It is native to the French Southern and Antarctic Lands, the Heard Islands and the Kerguelen Plateau in the Southern Ocean.

Bovictus diacanthus, the Tristan klipfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a temperate icefish or thornfish, belonging to the family Bovichtidae. It is endemic to two isolated, small island groups in the South Atlantic.

Bovichtus angustifrons, the dragonet, horny, horny thornfish, marblefish, thornfish or variegated marblefish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a temperate icefish or thornfish, belonging to the family Bovichtidae. It is endemic to southeastern Australia and Tasmania on rocky reefs in shallow waters.

Notothenia trigramma is a species of marine ray-finned fish, belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. It occurs in the southwestern Atlantic Ocean.
















