
The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), also known by its original name Rijndael, is a specification for the encryption of electronic data established by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in 2001.
The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), the symmetric block cipher ratified as a standard by National Institute of Standards and Technology of the United States (NIST), was chosen using a process lasting from 1997 to 2000 that was markedly more open and transparent than its predecessor, the Data Encryption Standard (DES). This process won praise from the open cryptographic community, and helped to increase confidence in the security of the winning algorithm from those who were suspicious of backdoors in the predecessor, DES.

In cryptography, a block cipher mode of operation is an algorithm that uses a block cipher to provide information security such as confidentiality or authenticity. A block cipher by itself is only suitable for the secure cryptographic transformation of one fixed-length group of bits called a block. A mode of operation describes how to repeatedly apply a cipher's single-block operation to securely transform amounts of data larger than a block.
In cryptography, Lucifer was the name given to several of the earliest civilian block ciphers, developed by Horst Feistel and his colleagues at IBM. Lucifer was a direct precursor to the Data Encryption Standard. One version, alternatively named DTD-1, saw commercial use in the 1970s for electronic banking.
In cryptography, Camellia is a symmetric key block cipher with a block size of 128 bits and key sizes of 128, 192 and 256 bits. It was jointly developed by Mitsubishi Electric and NTT of Japan. The cipher has been approved for use by the ISO/IEC, the European Union's NESSIE project and the Japanese CRYPTREC project. The cipher has security levels and processing abilities comparable to the Advanced Encryption Standard.
One-key MAC (OMAC) is a family of message authentication codes constructed from a block cipher much like the CBC-MAC algorithm. It may be used to provide assurance of the authenticity and, hence, the integrity of data. Two versions are defined:
In computer science and cryptography, Whirlpool is a cryptographic hash function. It was designed by Vincent Rijmen and Paulo S. L. M. Barreto, who first described it in 2000.
In cryptography, SAFER is the name of a family of block ciphers designed primarily by James Massey on behalf of Cylink Corporation. The early SAFER K and SAFER SK designs share the same encryption function, but differ in the number of rounds and the key schedule. More recent versions — SAFER+ and SAFER++ — were submitted as candidates to the AES process and the NESSIE project respectively. All of the algorithms in the SAFER family are unpatented and available for unrestricted use.
Phelix is a high-speed stream cipher with a built-in single-pass message authentication code (MAC) functionality, submitted in 2004 to the eSTREAM contest by Doug Whiting, Bruce Schneier, Stefan Lucks, and Frédéric Muller. The cipher uses only the operations of addition modulo 232, exclusive or, and rotation by a fixed number of bits. Phelix uses a 256-bit key and a 128-bit nonce, claiming a design strength of 128 bits. Concerns have been raised over the ability to recover the secret key if the cipher is used incorrectly.
In cryptography, FROG is a block cipher authored by Georgoudis, Leroux and Chaves. The algorithm can work with any block size between 8 and 128 bytes, and supports key sizes between 5 and 125 bytes. The algorithm consists of 8 rounds and has a very complicated key schedule.
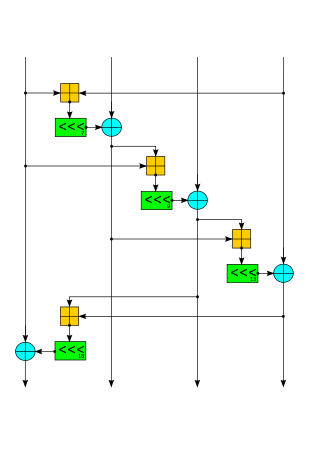
Salsa20 and the closely related ChaCha are stream ciphers developed by Daniel J. Bernstein. Salsa20, the original cipher, was designed in 2005, then later submitted to the eSTREAM European Union cryptographic validation process by Bernstein. ChaCha is a modification of Salsa20 published in 2008. It uses a new round function that increases diffusion and increases performance on some architectures.
In cryptography, Galois/Counter Mode (GCM) is a mode of operation for symmetric-key cryptographic block ciphers which is widely adopted for its performance. GCM throughput rates for state-of-the-art, high-speed communication channels can be achieved with inexpensive hardware resources.
An AES instruction set is a set of instructions that are specifically designed to perform AES encryption and decryption operations efficiently. These instructions are typically found in modern processors and can greatly accelerate AES operations compared to software implementations. An AES instruction set includes instructions for key expansion, encryption, and decryption using various key sizes.
In cryptography, format-preserving encryption (FPE), refers to encrypting in such a way that the output is in the same format as the input. The meaning of "format" varies. Typically only finite sets of characters are used; numeric, alphabetic or alphanumeric. For example:
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to cryptography:
There are various implementations of the Advanced Encryption Standard, also known as Rijndael.
A cipher suite is a set of algorithms that help secure a network connection. Suites typically use Transport Layer Security (TLS) or its deprecated predecessor Secure Socket Layer (SSL). The set of algorithms that cipher suites usually contain include: a key exchange algorithm, a bulk encryption algorithm, and a message authentication code (MAC) algorithm.

In cryptography, Twofish is a symmetric key block cipher with a block size of 128 bits and key sizes up to 256 bits. It was one of the five finalists of the Advanced Encryption Standard contest, but it was not selected for standardization. Twofish is related to the earlier block cipher Blowfish.

Speck is a family of lightweight block ciphers publicly released by the National Security Agency (NSA) in June 2013. Speck has been optimized for performance in software implementations, while its sister algorithm, Simon, has been optimized for hardware implementations. Speck is an add–rotate–xor (ARX) cipher.
In cryptography, a Key Checksum Value (KCV) is the checksum of a cryptographic key. It is used to validate the key integrity or compare keys without knowing their actual values. The KCV is computed by encrypting a block of bytes, each with value '00' or '01', with the cryptographic key and retaining the first 6 hexadecimal characters of the encrypted result. It is used in key management in different ciphering devices, like SIM-cards or Hardware Security Modules (HSM).




