
The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), also known by its original name Rijndael, is a specification for the encryption of electronic data established by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in 2001.
In cryptography, a block cipher is a deterministic algorithm that operates on fixed-length groups of bits, called blocks. Block ciphers are the elementary building blocks of many cryptographic protocols. They are ubiquitous in the storage and exchange of data, where such data is secured and authenticated via encryption.

The Data Encryption Standard is a symmetric-key algorithm for the encryption of digital data. Although its short key length of 56 bits makes it too insecure for modern applications, it has been highly influential in the advancement of cryptography.
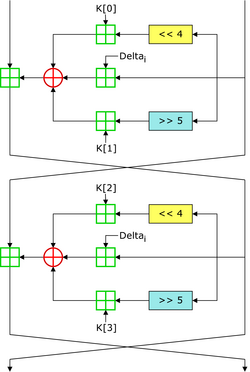
In cryptography, the Tiny Encryption Algorithm (TEA) is a block cipher notable for its simplicity of description and implementation, typically a few lines of code. It was designed by David Wheeler and Roger Needham of the Cambridge Computer Laboratory; it was first presented at the Fast Software Encryption workshop in Leuven in 1994, and first published in the proceedings of that workshop.
MARS is a block cipher that was IBM's submission to the Advanced Encryption Standard process. MARS was selected as an AES finalist in August 1999, after the AES2 conference in March 1999, where it was voted as the fifth and last finalist algorithm.

In cryptography, RC2 is a symmetric-key block cipher designed by Ron Rivest in 1987. "RC" stands for "Ron's Code" or "Rivest Cipher"; other ciphers designed by Rivest include RC4, RC5, and RC6.
In cryptography, Khufu and Khafre are two block ciphers designed by Ralph Merkle in 1989 while working at Xerox's Palo Alto Research Center. Along with Snefru, a cryptographic hash function, the ciphers were named after the Egyptian Pharaohs Khufu, Khafre and Sneferu.
In cryptography, the Cellular Message Encryption Algorithm (CMEA) is a block cipher which was used for securing mobile phones in the United States. CMEA is one of four cryptographic primitives specified in a Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) standard, and is designed to encrypt the control channel, rather than the voice data. In 1997, a group of cryptographers published attacks on the cipher showing it had several weaknesses which give it a trivial effective strength of a 24-bit to 32-bit cipher. Some accusations were made that the NSA had pressured the original designers into crippling CMEA, but the NSA has denied any role in the design or selection of the algorithm. The ECMEA and SCEMA ciphers are derived from CMEA.

In cryptography, DEAL is a symmetric block cipher derived from the Data Encryption Standard (DES). Its design was presented by Lars Knudsen at the SAC conference in 1997, and submitted as a proposal to the AES contest in 1998 by Richard Outerbridge.
In cryptography, mod n cryptanalysis is an attack applicable to block and stream ciphers. It is a form of partitioning cryptanalysis that exploits unevenness in how the cipher operates over equivalence classes modulo n. The method was first suggested in 1999 by John Kelsey, Bruce Schneier, and David Wagner and applied to RC5P and M6. These attacks used the properties of binary addition and bit rotation modulo a Fermat prime.

In cryptography, MacGuffin is a block cipher created in 1994 by Bruce Schneier and Matt Blaze at a Fast Software Encryption workshop. It was intended as a catalyst for analysis of a new cipher structure, known as Generalized Unbalanced Feistel Networks (GUFNs). The cryptanalysis proceeded very quickly, so quickly that the cipher was broken at the same workshop by Vincent Rijmen and Bart Preneel.
In cryptography, NewDES is a symmetric key block cipher. It was created in 1984–1985 by Robert Scott as a potential DES replacement.
In cryptography, a related-key attack is any form of cryptanalysis where the attacker can observe the operation of a cipher under several different keys whose values are initially unknown, but where some mathematical relationship connecting the keys is known to the attacker. For example, the attacker might know that the last 80 bits of the keys are always the same, even though they don't know, at first, what the bits are.
In cryptography, integral cryptanalysis is a cryptanalytic attack that is particularly applicable to block ciphers based on substitution–permutation networks. It was originally designed by Lars Knudsen as a dedicated attack against Square, so it is commonly known as the Square attack. It was also extended to a few other ciphers related to Square: CRYPTON, Rijndael, and SHARK. Stefan Lucks generalized the attack to what he called a saturation attack and used it to attack Twofish, which is not at all similar to Square, having a radically different Feistel network structure. Forms of integral cryptanalysis have since been applied to a variety of ciphers, including Hierocrypt, IDEA, Camellia, Skipjack, MISTY1, MISTY2, SAFER++, KHAZAD, and FOX.
In cryptography, BaseKing is a block cipher designed in 1994 by Joan Daemen. It is very closely related to 3-Way, as the two are variants of the same general cipher technique.
In cryptography, M6 is a block cipher proposed by Hitachi in 1997 for use in the IEEE 1394 FireWire standard. The design allows some freedom in choosing a few of the cipher's operations, so M6 is considered a family of ciphers. Due to export controls, M6 has not been fully published; nevertheless, a partial description of the algorithm based on a draft standard is given by Kelsey, et al. in their cryptanalysis of this family of ciphers.
ORYX is an encryption algorithm used in cellular communications in order to protect data traffic. It is a stream cipher designed to have a very strong 96-bit key strength with a way to reduce the strength to 32-bits for export. However, due to mistakes the actual strength is a trivial 16-bits and any signal can be cracked after the first 25–27 bytes.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to cryptography:

In cryptography, Twofish is a symmetric key block cipher with a block size of 128 bits and key sizes up to 256 bits. It was one of the five finalists of the Advanced Encryption Standard contest, but it was not selected for standardization. Twofish is related to the earlier block cipher Blowfish.
This article summarizes publicly known attacks against block ciphers and stream ciphers. Note that there are perhaps attacks that are not publicly known, and not all entries may be up to date.







