
The RWD 6 was a Polish sports plane of 1932, constructed by the RWD team. It was a winner of the Challenge 1932 international tourist aircraft contest.

The Hawker Duiker was an unusual and unsuccessful aircraft. It was the first design at Hawker under a new chief designer, Captain Thomson, in 1922. Much of the equipment and parts were proprietary and made by another aircraft company, Vickers, which shared the airfield at Brooklands with Hawker. The Duiker was a parasol wing monoplane in a period where the biplane held sway.

The VL Tuisku was a Finnish trainer aircraft designed in the 1930s. It was a two-seat, single-engined biplane with a welded steel framework, covered with fabric. 30 were produced for the Finnish Air Force and served from 1935 to 1949.

The Canadian Vickers Vedette was the first aircraft designed and built in Canada to meet a specification for Canadian conditions. It was a single-engine biplane flying boat purchased to meet a Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF) demand for a smaller aircraft than the Vickers Viking with a much greater rate of climb, to be suitable for forestry survey and fire protection work. The type went on to have a long and distinguished career in civil operations in Canada. Most of the topographical maps in use in Canada today are based on photos taken from these aircraft.

The Canadian Vickers Vancouver was a Canadian transport/patrol flying boat of the 1930s built by Canadian Vickers.

The Canadian Vickers Vanessa was a Canadian biplane transport seaplane of the 1920s. It was a single-engine, twin-float biplane of mixed construction, evaluated by the Royal Canadian Air Force and used for experimental air-mail services..

The Avro Type 584 Avocet was a British single-engined naval fighter prototype, designed and built by Avro. While the Avocet was not built in numbers, one of the prototypes was used as a seaplane trainer for the Royal Air Force's (RAF) High Speed Flight.

The BAT F.K.23 Bantam was a British single-seat fighter biplane produced by British Aerial Transport Company Limited of London during World War I.

The Avro 641 Commodore was a British single-engine five-seat cabin biplane built by Avro in the mid-1930s for private use. A total of only six were built, including the prototype.

The Edgar Percival E.P.9 was a 1950s British light utility aircraft designed by Edgar Percival and initially built by his company, Edgar Percival Aircraft Limited and later as the Lancashire Aircraft EP-9 Prospector by the Lancashire Aircraft Company.

The Cierva C.8 was an experimental autogyro built by Juan de la Cierva in England in 1926 in association with Avro. Like Cierva's earlier autogyros, the C.8s were based on existing fixed-wing aircraft fuselages – in this case, the Avro 552.
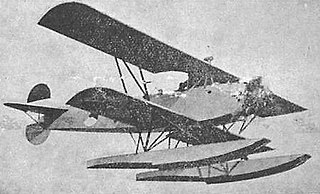
The Fokker C.VII-W was a reconnaissance seaplane built in the Netherlands in the late 1920s. Sharing elements of the highly successful C.V design, the C.VII-W was a conventional, single-bay biplane with wings of unequal span braced with N-struts. The undercarriage consisted of a standard twin-pontoon arrangement, and the fin and rudder continued through to the ventral side of the fuselage, creating a cruciform tail. The pilot and observer sat in tandem, open cockpits. The wing structure was wooden with fabric and plywood covering, and the fuselage was of steel tube construction with fabric covering.
The Nieuport-Delage NiD 640 was a French four-passenger transport monoplane built by Nieuport-Delage.

The Bayerische Flugzeugwerke M 18, was an airliner, produced in Germany in the late 1920s.
The Westland Wagtail was a prototype British fighter aircraft of the First World War. A single-engined tractor biplane, the Wagtail was a failure owing to the unreliability of its engine, only five being built.

The Canadian Vickers Vista was a Canadian-designed single-seat flying boat.

The de Havilland DH.56 Hyena was a prototype British army cooperation aircraft of the 1920s. A single-engined biplane, the Hyena was designed against an RAF requirement, but was unsuccessful with only two being built, the Armstrong Whitworth Atlas being preferred.

The Canadian Vickers Vigil was a single-seat patrol aircraft designed to meet a Royal Canadian Air Force requirement for a forest fire patrol aircraft.
The Ostrovia II or Moryson II was a 1930s Polish club trainer aircraft, a development of the Ostrovia I. Only one was built and was used by the Poznań flying club for five years.
The Stampe et Vertongen ST.26 was a 1930s Belgian military blind- and night-flying trainer aircraft.
















