
Placodermi is a class of armoured prehistoric fish, known from fossils, which lived from the Silurian to the end of the Devonian period. Their head and thorax were covered by articulated armoured plates and the rest of the body was scaled or naked, depending on the species. Placoderms were among the first jawed fish; their jaws likely evolved from the first of their gill arches.

Arthrodira is an order of extinct armored, jawed fishes of the class Placodermi that flourished in the Devonian period before their sudden extinction, surviving for about 50 million years and penetrating most marine ecological niches. Arthrodires were the largest and most diverse of all groups of Placoderms.
Camuropiscidae is a family of mostly small, bullet or spindle-shaped extinct arthrodire placoderms from the Late Devonian. With the exception of the snub-nosed Simosteus, camuropiscid placoderms are characterized by an elongated, tubular snout. The entire family is restricted to the Frasnian Gogo Reef Formation of Australia.

Holonematidae is an extinct family of relatively large arthrodire placoderms from the Early to Late Devonian. Almost all fossil specimens are of armor fragments, though, all have distinctive ornamentation, often of unique arrangements and patterns of tubercles, that are diagnostic of the family. The trunkshield is very elongated, giving the armor an overall "barrel" like appearance.

Buchanosteus is an extinct genus of arthrodire placoderm. Its fossils have been found in Early Devonian-aged marine strata throughout Asia and Australia. It contains the following species:

Homostiidae is a family of flattened arthrodire placoderms from the Early to Middle Devonian. Fossils appear in various strata in Europe, Russia, Morocco, Australia, Canada and Greenland.

Buchanosteidae is a family of arthrodire placoderms that lived from the Early to Middle Devonian. Fossils appear in various strata in Russia, Central Asia, Australia, and China.

Jiuchengia longoccipita is a coccosteid arthrodire placoderm from the Late Emsian epoch of Wuding, Yunnan.

Arenipiscis westolli is an extinct buchanosteid arthrodire placoderm. Its fossils have been found in Emsian-aged marine strata of New South Wales, Australia.

Errolosteus goodradigbeensis is an extinct buchanosteid arthrodire placoderm. Its fossils have been found in Emsian-aged marine strata of New South Wales, Australia.

Parabuchanosteus murrumbidgeensis is an extinct buchanosteid arthrodire placoderm. Its fossils have been found in the Late Emsian-aged marine strata of New South Wales, Australia.

Taemasosteus is an extinct genus of arthrodire placoderm. Its fossils have been found in Emsian-aged marine strata in New South Wales, Australia. It contains two species, T. novaustrocambricus, and T. maclartiensis.

Goodradigbeeon is an extinct genus of buchanosteid arthrodire placoderm. Its fossils have been found in Emsian-aged marine strata from the Taemas-Wee Jasper reef of New South Wales, Australia and the type species is G. australianum.

Burrinjucosteus asymmetricus is an extinct buchanosteid arthrodire placoderm. Its fossils have been found in Emsian-aged marine strata of New South Wales, Australia.

Angarichthys hyperboreus is an extinct homostiid arthrodire placoderm from the Middle Devonian of Siberia. It is known from an infragnathal plate, an intero-lateral plate, and a marginal plate found from the Middle Devonian strata of the Tynep Series formation, in the Bakhta River basin, Tunguska Plateau. A. hyperboreus differs from Homosteus in that the former's marginal plate has a ridge where the central plate would have overlapped it, and in the infragnathal, which is curved sigmoidally, and bears at least seven tooth-like prongs nearer to the functional anterior end.

Tityosteus is an extinct genus of homostiid arthrodire from the Early Emsian of the Early Devonian, with fossils known from Germany, the Ibero-Armorican Trough, and southern Siberia.
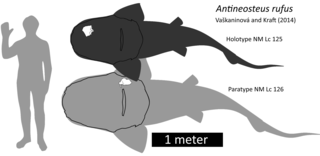
Antineosteus is an extinct genus of homostiid arthrodire from the Emsian, Early Devonian Kess-Kess Mounds, in the eastern Anti-Atlas Mountains, Morocco, and the Barrandian area of the Czech Republic.
Atlantidosteus is an extinct genus of homostiid arthrodire from the Early to Middle Devonian of Morocco and Queensland. It contains two known species, A. hollardi and A. pacifica.
Dhanguura is an extinct genus of homostiid arthrodire from the Early Devonian of Wee Jasper, NSW. It contains the single species D. johnstoni.
Cathlesichthys is an extinct genus of homostiid arthrodire from Wee Jasper, during the Early Devonian.






















