
The Yangtze, Yangzi or Changjiang is the longest river in Eurasia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains of the Tibetan Plateau and flows 6,300 km (3,915 mi) in a generally easterly direction to the East China Sea. It is the fifth-largest primary river by discharge volume in the world. Its drainage basin comprises one-fifth of the land area of China, and is home to nearly one-third of the country's population.

Sichuan is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the Sichuan Basin and the easternmost part of the Tibetan Plateau between the Jinsha River on the west, the Daba Mountains in the north and the Yungui Plateau to the south. Sichuan's capital city is Chengdu. The population of Sichuan stands at 83 million. Sichuan neighbors are Qinghai to the northwest, Gansu to the north, Shaanxi to the northeast, Chongqing to the east, Guizhou to the southeast, Yunnan to the south, and the Tibet Autonomous Region to the west.

Chongqing is a major city in the People's Republic of China. Chongqing is a connection in the Yangtze River Economic Belt and a base for China's Belt and Road Initiative.

Yibin is a prefecture-level city in the southeastern part of Sichuan province, China, located at the junction of the Min and Yangtze Rivers. Its population was 4,588,804 inhabitants, according to the 2020 census, of whom 2,158,312 lived in the built-up area comprising three urban districts.

The Sichuan Basin, formerly transliterated as the Szechwan Basin, sometimes called the Red Basin, is a lowland region in southwestern China. It is surrounded by mountains on all sides and is drained by the upper Yangtze River and its tributaries. The basin is anchored by Chengdu, the capital of Sichuan province, in the west, and the direct-administered municipality of Chongqing in the east. Due to its relative flatness and fertile soils, it is able to support a population of more than 100 million. In addition to being a dominant geographical feature of the region, the Sichuan Basin also constitutes a cultural sphere that is distinguished by its own unique customs, cuisine and dialects. It is famous for its rice cultivation and is often considered the breadbasket of China. In the 21st century its industrial base is expanding with growth in the high-tech, aerospace, and petroleum industries.

Luzhou (simplified Chinese: 泸州; traditional Chinese: 瀘州; pinyin: Lúzhōu; Sichuanese Pinyin: Nu2zou1; Luzhou dialect: ), formerly transliterated as Lu-chou or Luchow, is a prefecture-level city located in the southeast of Sichuan Province, China. The city, named Jiangyang until the Southern and Northern Dynasties, is known as the "Liquor City" (酒城). Situated at the confluence of the Tuo River and the Yangtze River, Luzhou is the largest port in both size and output in Sichuan province since Chongqing was separated from Sichuan province in 1997. As of the 2020 Chinese census, its population was 4,254,149 inhabitants whom 1,241,273 lived in the built-up (or metro) area made of Jiangyang and Longmatan districts, as Naxi district is not conurbated yet. Luzhou, which borders Yunnan, Guizhou and Chongqing, is the only geographic junction of the four provinces, and was therefore the logical place for a port in ancient China. After the PRC was founded in 1949, Luzhou became the capital of southern Sichuan province. In 1983, Luzhou was approved as a prefecture-level city administratively.
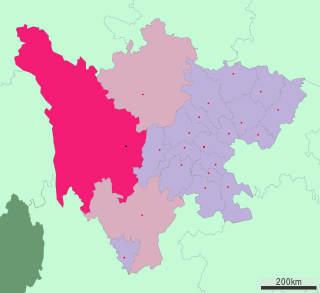
Garzê Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, often shortened to Ganzi Prefecture, is an autonomous prefecture in the western arm of Sichuan province, China bordering Yunnan to the south, the Tibet Autonomous Region to the west, and Gansu to the north and northwest.

Liangshan Yi Autonomous Prefecture is an autonomous prefecture occupying much of the southern extremity of Sichuan province, People's Republic of China. Its seat is Xichang. Liangshan has an area of 60,261 km2 (23,267 sq mi) and over 4.5 million inhabitants (2010). It has the largest population of ethnic Yi among China's prefectures. Liangshan contains a number of isolated villages high up on its cliffs, often known as "cliff villages".

Enshi Tujia and Miao Autonomous Prefecture is located in the mountainous southwestern corner of Hubei province, People's Republic of China. It forms Hubei's southwestern "panhandle", bordering on Hunan in the south and Chongqing Municipality in the west and northwest. The Yangtze River crosses the prefecture's northeastern corner in Badong County.

Zhaotong is a prefecture-level city located in the northeast corner of Yunnan province, China, bordering the provinces of Guizhou to the south and southeast and Sichuan to the northeast, north, and west.

China National Highway 212 (G212) runs from Lanzhou in Gansu to Chongqing. It was originally 1302 kilometres in length. In the 2013 National Highway Network Planning it was extended to Longbang, Guangxi, on the border with Vietnam. After the extension, the length is circa 2,300 km (1,400 mi).

The Hengduan Mountains are a group of mountain ranges in southwest China that connect the southeast portions of the Tibetan Plateau with the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau. The Hengduan Mountains are primarily large north-south mountain ranges that effectively separate lowlands in northern Myanmar from the lowlands of the Sichuan Basin. These ranges are characterized by significant vertical relief originating from the Indian subcontinent's collision with the Eurasian Plate, and further carved out by the major rivers draining the eastern Tibetan Plateau. These rivers, the Yangtze, Mekong, and Salween, are recognized today as the Three Parallel Rivers UNESCO World Heritage Site.

The Dadu River, known in Tibetan as the Gyelmo Ngul Chu, is a major river located primarily in Sichuan province, southwestern China. The Dadu flows from the eastern Tibetan Plateau into the Sichuan Basin where it joins with the Min River, a tributary of the Yangtze River. Measured from its geographic source, the Dadu is actually longer than the Min and thus forms the main stem of the Min River system.

The 2008 South China floods began on 26 May 2008. Four rounds of torrential rains with landslides and flooding lasted for 20 days and affected fifteen provinces in Eastern and Southern China.

The bridges and tunnels across the Yangtze River carry rail and road traffic across China's longest and largest river and form a vital part of the country's transportation infrastructure. The river bisects China proper from west to east, and every major north–south bound highway and railway must cross the Yangtze. Large urban centers along the river such as Chongqing, Wuhan, and Nanjing also have urban mass transit rail lines crossing the Yangtze.

The Daba Mountains, also known by their Chinese name as the Dabashan, are a mountain range in Central China between the watersheds of the Yellow and Yangtze Rivers. Part of the larger Qinling mountain range, it cuts through four provinces: Sichuan, Chongqing, Shaanxi, and Hubei. It is about 1,000 kilometers (620 mi) long.

Shanghai–Wuhan–Chengdu passenger-dedicated railway, is a fully completed higher-speed railway corridor in China. It is operated by CR Shanghai Group, CR Wuhan Group and CR Chengdu Group. The Chinese name of the railway line, Huhanrong, is a combination of the abbreviations for Shanghai, Wuhan, and Chengdu, three major cities along the line.

The Shanghai–Chengdu Expressway, designated as G42 and commonly referred to as the Hurong Expressway is an east–west bound expressway that connects the eastern metropolis of Shanghai to Chengdu, the capital city of Sichuan. The expressway passes through six provinces and serves major cities such as Suzhou, Wuxi, Changzhou, Nanjing, Hefei, Wuhan, and Yichang. The eastern terminus of G42 is at the Wuning Road Interchange of Shanghai Middle Ring Road. At its western terminus, the expressway intersects the East 3rd Ring Road and connects East Erxianqiao Road in Chenghua District, Chengdu. The expressway spans 1,960 km (1,220 mi) in length.

The Kangbo Yangtze River Bridge, was called Second Hejiang Bridge, is a highway bridge over the Yangtze River in Hejiang County, Sichuan, China. The bridge is on the G93 Chengdu–Chongqing Ring Expressway just 10 kilometres west of the Bosideng Bridge. It was originally called Hejiang Bridge 2 since Bosideng Bridge was first called Hejiang Bridge 1. The bridge has a length of 1,715 metres (5,627 ft) and is 30 metres (98 ft) wide. Its two pylons are each 208 metres (682 ft) high, making the bridge to the one with the highest pylons in Sichuan.





















