
The Congridae are the family of conger and garden eels. Congers are valuable and often large food fishes, while garden eels live in colonies, all protruding from the sea floor after the manner of plants in a garden. The family includes over 220 species in 32 genera.

The Carangidae are a family of ray-finned fish that includes the jacks, pompanos, jack mackerels, runners, trevallies, and scads. It is the largest of the six families included within the order Carangiformes. Some authorities classify it as the only family within that order but molecular and anatomical studies indicate that there is a close relationship between this family and the five former Perciform families which make up the Carangiformes.

The superorder Elopomorpha contains a variety of types of fishes that range from typical silvery-colored species, such as the tarpons and ladyfishes of the Elopiformes and the bonefishes of the Albuliformes, to the long and slender, smooth-bodied eels of the Anguilliformes. The one characteristic uniting this group of fishes is they all have leptocephalus larvae, which are unique to the Elopomorpha. No other fishes have this type of larvae.

Sawtooth eels are a family, Serrivomeridae, of eels found in temperate and tropical seas worldwide.

Trichogaster is a genus of gouramis native to South Asia from Pakistan to Myanmar. It is the only genus in the monotypic subfamily Trichogastrinae as set out in the 5th Edition of Fishes of the World, although that book states that there are two genera, the other being Colisa which is treated as a synonym of Trichogaster by Fishbase and the Catalog of Fishes. Fishbase also places the genus in the Luciocephalinae. Species of this genus are very popular in the aquarium trade.

The sea chubs, also known as rudderfish and pilot fish and in Hawaiian as enenue or nenue, are a family, Kyphosidae, of fishes in the order Perciformes native to the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans usually close to shore in marine waters.
Cyema is a monospecific genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the monotypic family Cyematidae. The only species in the genus is Cyema atrum, the arrow eel, bobtail eel, bobtail snipe eel or deepwater eel. This species has circumglobal distribution.
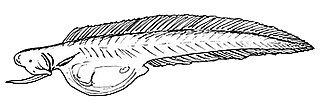
Monognathus, or onejaw, is the only genus of the family Monognathidae of deep-sea eels. The name comes from the Greek monos meaning “one” and gnathos meaning “jaw”, a reference to the large mouth in comparison with the rest of the fish, and also the absence of an upper jaw.
Polyacanthonotus is a genus of spiny eels, with these currently recognized species:
Chilorhinus is a small genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Chlopsidae, the false morays. These eels occur in tropical waters
Kaupichthys is a genus of eels in the family Chlopsidae.

Dysomma is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Synaphobranchidae, the cutthroat eels. These eels are found in the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans.

The Congrinae are a subfamily of eels in the family Congridae.

Uropterygiinae is a subfamily of moray eels.

Bathymyrinae is a subfamily of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Congridae, which includes the conger and garden eels. The eels of this subfamily are most diverse in the Indo-Pacific region but are also found in both the Eastern and Western Atlantic Oceans.

Myrophinae, the worm eels, is a subfamily of ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Ophichthidae, which also includes the snake eels in the subfamily Ophichthinae.

Congroidei is a suborder of ray-finned fishes belonging to the order Anguilliformes, the eels. These eels are mostly marine, although a few species of snake eel will enter freshwater, and they are found in tropical and tempareate waters throughout the world.

Naucratinae is a subfamily of ray-finned fish from the family Carangidae which consists of five genera and 13 species.

Centrarchinae is a subfamily of freshwater ray-finned fish, one of three subfamilies in the family Centrarchidae, the sunfishes.

Ilyophinae, the arrowtooth ells or mustard eels, is a subfamily of marine ray-finned fishes belongiing to the family Synaphobranchidae, the cutthroat eels. Within its family this subfamily shows greatest number of species and the greatest morphological diversity.
















