
Gadiformes, also called the Anacanthini, are an order of ray-finned fish that include the cod, hakes, pollock, haddock, burbot, rocklings and moras, many of which are food fish of major commercial value. They are mostly marine fish found throughout the world and the vast majority are found in temperate or colder regions while a few species may enter brackish estuaries. Pacific tomcods, one of the two species that makes up the genus Microgadus, are able to enter freshwater, but there is no evidence that they breed there. Some populations of landlocked Atlantic tomcod on the other hand, complete their entire life cycle in freshwater. Yet only one species, the burbot, is a true freshwater fish.

The beardfishes consist of a single extant genus, Polymixia, of deep-sea marine ray-finned fish named for their pair of long hyoid barbels. They are classified in their own order Polymixiiformes. But as Nelson says, "few groups have been shifted back and forth as frequently as this one, and they were recently added to Paracanthoptergii". For instance, they have previously been classified as belonging to the Beryciformes, and are presently considered either paracanthopterygians or the sister group to acanthopterygians. They are of little economic importance.

The Congridae are the family of conger and garden eels. Congers are valuable and often large food fishes, while garden eels live in colonies, all protruding from the sea floor after the manner of plants in a garden. The family includes over 220 species in 32 genera.

The cusk-eel family, Ophidiidae, is a group of marine bony fishes in the Ophidiiformes order. The scientific name is from the Greek ophis meaning "snake", and refers to their eel-like appearance. True eels diverged from other ray-finned fish during the Jurassic, while cusk-eels are part of the Percomorpha clade, along with tuna, perch, seahorses and others.
The deep-sea smelts are any members of the family Bathylagidae, a distinct group of marine smelts.

The herring smelts or argentines are a family, Argentinidae, of marine smelts. They are similar in appearance to smelts but have much smaller mouths.

Paraulopus is the only genus in the family Paraulopidae, a family of grinners in the order Aulopiformes. They are commonly known as cucumberfishes, but locally some other Teleostei are also known by that name. They were considered in the Chlorophthalmidae or greeneye family until 2001.

Apateodus is a genus of prehistoric marine ray-finned fish which was described by Woodward in 1901. It was a relative of modern lizardfish and lancetfish in the order Aulopiformes, and one of a number of prominent nektonic aulopiforms of Cretaceous marine ecosystems.

The Maastricht Formation, named after the city of Maastricht in the Netherlands, is a geological formation in the Netherlands and Belgium whose strata date back to the Late Cretaceous, within 500,000 years of the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary, now dated at 66 million years ago. The formation is part of the Chalk Group and is between 30 and 90 metres thick. It crops out in southern parts of Dutch and Belgian Limburg and adjacent areas in Germany. It can be found in the subsurface of northern Belgium and southeastern Netherlands, especially in the Campine Basin and Roer Valley Graben. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.

Eels are ray-finned fish belonging to the order Anguilliformes, which consists of eight suborders, 20 families, 164 genera, and about 1000 species. Eels undergo considerable development from the early larval stage to the eventual adult stage and are usually predators.
Casierius is an extinct genus of marine ray-finned fish that lived during the Albian stage of the Early Cretaceous epoch. It was a relative of the modern bonefish in the extinct family Phyllodontidae, although some authorities consider it either a true albulid or a very early eel. It contains a single species, C. heckeli, known from the Glen Rose Formation near Hood County, Texas.
Ampheristus is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine ray-finned fish. It was a basal or stem member of the family Ophidiidae, which contains modern cusk-eels. Fossils are known from worldwide from the Late Cretaceous to the late Paleogene, making it a rather successful survivor of the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event.

The Argentiniformes is an order of marine ray-finned fish whose distinctness was recognized only fairly recently. In former times, they were included in the Osmeriformes as suborder Argentinoidei. That term refers only to the suborder of marine smelts and barreleyes in the classification used here, with the slickheads and allies being the Alepocephaloidei. These suborders were treated as superfamilies Argentinoidea and Alepocephaloidea, respectively, when the present group was still included in the Osmeriformes.
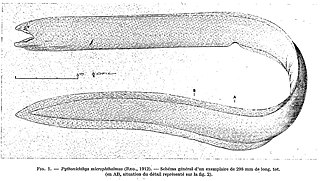
Pythonichthys is a genus of eels of the family Heterenchelyidae that occur in tropical waters of the eastern Pacific Ocean off of Panama and in the Atlantic Ocean near the Caribbean Sea and the west coast of Africa. It contains the following described species:

Argentina is a genus of fishes in the family Argentinidae.

Polymixia is the only extant genus of the order Polymixiiformes and family Polymixiidae. It contains 10 species, all of which live in deepwater marine environments. They are found in tropical and subtropical waters of the Atlantic, Indian and western Pacific Oceans. They are bottom-dwelling fish, found down to about 800 m (2,600 ft). Most are relatively small fish, although one species is over 40 cm (16 in) in length. They can be considered "living fossils" due to being the only surviving members of the once-diverse order Polymixiiformes.

The term Paleocene ammonites describes families or genera of Ammonoidea that may have survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, which occurred 66.043 million years ago. Although almost all evidence indicated that ammonites did not survive past the K–Pg boundary, there is some scattered evidence that some ammonites lived for a short period of time during the Paleocene epoch, although none survived the Danian ; they were likely extinct within 500,000 years of the K-Pg extinction event, which correlates to roughly 65.5 Ma. The evidence for Paleocene ammonoids is rare and remains controversial.
This list of fossil fish research presented in 2021 is a list of new taxa of jawless vertebrates, placoderms, acanthodians, fossil cartilaginous fishes, bony fishes, and other fishes that were described during the year, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleoichthyology that occurred in 2021.

The Dercetidae are an extinct family of aulopiform ray-finned fish that are known from the Late Cretaceous to the early Paleocene. They are among the many members of the diverse, extinct suborder Enchodontoidei, which were dominant during the Cretaceous.













