
Placental mammals are one of the three extant subdivisions of the class Mammalia, the other two being Monotremata and Marsupialia. Placentalia contains the vast majority of extant mammals, which are partly distinguished from monotremes and marsupials in that the fetus is carried in the uterus of its mother to a relatively late stage of development. The name is something of a misnomer, considering that marsupials also nourish their fetuses via a placenta, though for a relatively briefer period, giving birth to less-developed young, which are then nurtured for a period inside the mother's pouch. Placentalia represents the only living group within Eutheria, which contains all mammals that are more closely related to placentals than they are to marsupials.

Eutheria, also called Pan-Placentalia, is the clade consisting of placental mammals and all therian mammals that are more closely related to placentals than to marsupials.

Afrotheria is a superorder of placental mammals, the living members of which belong to groups that are either currently living in Africa or of African origin: golden moles, elephant shrews, otter shrews, tenrecs, aardvarks, hyraxes, elephants, sea cows, and several extinct clades. Most groups of afrotheres share little or no superficial resemblance, and their similarities have only become known in recent times because of genetics and molecular studies. Many afrothere groups are found mostly or exclusively in Africa, reflecting the fact that Africa was an island continent from the Cretaceous until the early Miocene around 20 million years ago, when Afro-Arabia collided with Eurasia.

Theria is a subclass of mammals amongst the Theriiformes. Theria includes the eutherians and the metatherians but excludes the egg-laying monotremes and various extinct mammals evolving prior to the common ancestor of placentals and marsupials.

Orycteropodidae is a family of afrotherian mammals. Although there are many fossil species, the only species surviving today is the aardvark, Orycteropus afer. Orycteropodidae is recognized as the only family within the order Tubulidentata, so the two are effectively synonyms.

Condylarthra is an informal group – previously considered an order – of extinct placental mammals, known primarily from the Paleocene and Eocene epochs. They are considered early, primitive ungulates. It is now largely considered to be a wastebasket taxon, having served as a dumping ground for classifying ungulates which had not been clearly established as part of either Perissodactyla or Artiodactyla, being composed thus of several unrelated lineages.

Ferae is a mirorder of placental mammals in grandorder Ferungulata, that groups together clades Pan-Carnivora and Pholidotamorpha.
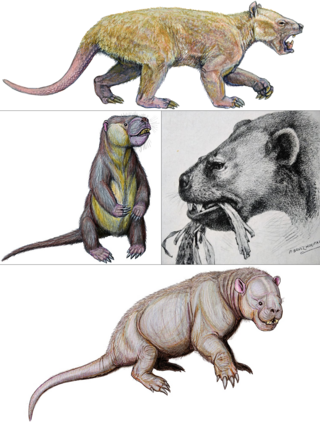
Taeniodonta is an extinct order of eutherian mammals, that lived in North America and Europe from the late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) to the middle Eocene.

The Afroinsectiphilia is a clade that has been proposed based on the results of recent molecular phylogenetic studies. Many of the taxa within it were once regarded as part of the order Insectivora, but Insectivora is now considered to be polyphyletic and obsolete. This proposed classification is based on molecular studies only, and there is no morphological evidence for it.

Ferungulata is a grandorder of placental mammals that groups together mirorder Ferae and clade Pan-Euungulata. It has existed in two guises, a traditional one based on morphological analysis and a revised one taking into account more recent molecular analyses. The Fereungulata is a sister group to the order Chiroptera (bats) and together they make clade Scrotifera.

Pegasoferae is a proposed clade of mammals based on genomic research in molecular systematics by Nishihara, Hasegawa and Okada (2006).

Cimolestes is a genus of early eutherians with a full complement of teeth adapted for eating insects and other small animals. Paleontologists have disagreed on its relationship to other mammals, in part because quite different animals were assigned to the genus, making Cimolestes a grade taxon of animals with similar features rather than a genus of closely related ones. Fossils have been found in North America, South America, Europe and Africa. Cimolestes first appeared during the Late Cretaceous of North America. According to some paleontologists, Cimolestes died out at the start of the Paleocene, while others report the genus from the early Eocene.

Ptolemaiida is a taxon of wolf-sized afrothere mammals that lived in northern and eastern Africa during the Paleogene. The oldest fossils are from the latest Eocene strata of the Jebel Qatrani Formation, near the Fayum oasis in Egypt. A tooth is known from an Oligocene-aged stratum in Angola, and Miocene specimens are known from Kenya and Uganda.
Deccanolestes is a scansorial, basal Euarchontan from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) and Paleocene Intertrappean Beds of Andhra Pradesh, India. It may be closely related to Sahnitherium. Deccanolestes has been referred to Palaeoryctidae in the past, but recent evidence has shown that it is either the most basal Euarchontan, as the earliest known Adapisoriculid, or as a stem-afrotherian.

Paratheria is an obsolete term for a taxonomic group including the xenarthran mammals and various groups thought to be related to them. It was proposed by Oldfield Thomas in 1887 to set apart the sloths, anteaters, armadillos, and pangolins, usually classified as placentals, from both marsupial and placental mammals, an arrangement that received little support from other workers. When teeth of the extinct gondwanathere mammals were first discovered in Argentina in the 1980s, they were thought to be related to xenarthrans, leading to renewed attention for the hypothesis that xenarthrans are not placentals. However, by the early 1990s, gondwanatheres were shown to be unrelated to xenarthrans, and xenarthrans are still considered to be placentals.

Scrotifera is a clade of placental mammals that groups together grandorder Ferungulata, Chiroptera (bats), other extinct members and their common ancestors. The clade Scrotifera is a sister group to the order Eulipotyphla based on evidence from molecular phylogenetics, and together they make superorder Laurasiatheria. The last common ancestor of Scrotifera is supposed to have diversified ca. 73.1 to 85.5 million years ago.
Kelba quadeemae is an extinct species of ptolemaiidan mammal, the sole species of the family Kelbidae, known from the Lower Miocene of East Africa. The genus name Kelba derives from the Arabic الكلب meaning "dog", and the specific name quadeemae from the Arabic quadeem, meaning "ancient". Kelba is only known from a partial skull and teeth, but estimated to have been, similar in size to a coyote but more heavily built. The teeth are rather unspecialized, suggesting a wide and varied diet, and show wear suggesting its diet included abrasive material.
Schowalteria is a genus of extinct mammal from the Cretaceous of Canada. It is the earliest known representative of order Taeniodonta, a specialised lineage of eutherian mammals otherwise found in Paleocene and Eocene deposits. It is notable for its large size, being among the largest of Mesozoic mammals, as well as its speciation towards herbivory, which in some respects exceeds that of its later relatives.
Altacreodus is an extinct genus of eutherian mammals. Fossils have been found in North America where they first appeared during the Late Cretaceous, and they died out prior to the start of the Paleocene. It is possibly one of the earliest known placental mammals in the fossil record.

Pholidotamorpha is a clade of placental mammals from mirorder Ferae that includes the order Pholidota and extinct order Palaeanodonta.



















