
NI Railways, also known as Northern Ireland Railways, is the railway operator in Northern Ireland. NIR is a subsidiary of Translink, whose parent company is the Northern Ireland Transport Holding Company (NITHCo), and is one of nine publicly owned train operators in the United Kingdom, the others being Direct Rail Services, Caledonian Sleeper, Northern Trains, Transport for Wales Rail, Southeastern, LNER, ScotRail, and TransPennine Express. It has a common Board of Management with the other two companies in the group, Ulsterbus and Metro.

The Dublin Area Rapid Transit system is an electrified commuter rail railway network serving the coastline and city of Dublin, Ireland. The service makes up the core of Dublin's suburban railway network, stretching from Greystones, County Wicklow, in the south to Howth and Malahide in north County Dublin. The DART serves 31 stations and consists of 53 route kilometres of electrified railway, and carries in the region of 20 million passengers per year. In a similar manner to the Berlin S-Bahn, the DART blends elements of a commuter rail service and a rapid transit system.
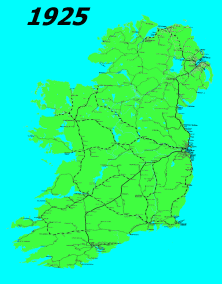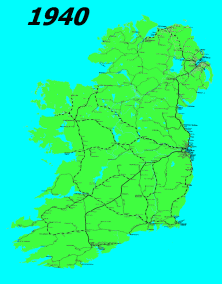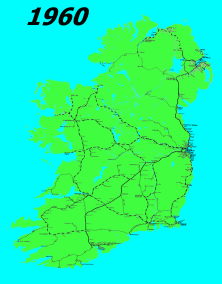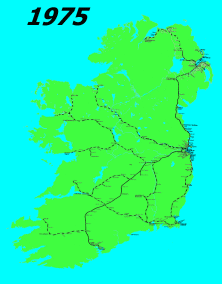
The history of rail transport in Ireland began only a decade later than that of Great Britain. By its peak in 1920, Ireland had 3,500 route miles (5,630 km). The current status is less than half that amount, with a large unserviced area around the border area between Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland.

Rail transport in Ireland is provided by Iarnród Éireann in the Republic of Ireland and by Northern Ireland Railways in Northern Ireland.

Iarnród Éireann, or Irish Rail, is the operator of the national railway network of Ireland. Established on 2 February 1987, it is a subsidiary of Córas Iompair Éireann (CIÉ). It operates all internal InterCity, Commuter, DART and freight railway services in the Republic of Ireland, and, jointly with Northern Ireland Railways, the Enterprise service between Dublin and Belfast. In 2019, IÉ carried a record peak of 50 million passengers, up from 48 million in 2018.

Connolly station or Dublin Connolly is the busiest railway station in Dublin and Ireland, and is a focal point in the Irish route network. On the North side of the River Liffey, it provides InterCity, Enterprise and commuter services to the north, north-west, south-east and south-west. The north–south Dublin Area Rapid Transit (DART) and Luas red line light rail services also pass through the station. The station offices are the headquarters of Irish Rail, Iarnród Éireann. Opened in 1844 as Dublin Station, the ornate facade has a distinctive Italianate tower at its centre.

Heuston Station, also known as Dublin Heuston, is one of Dublin's largest railway stations and links the capital with the south, southwest and west of Ireland. It is operated by Iarnród Éireann (IÉ), the national railway operator. It also houses the head office of its parent company, Córas Iompair Éireann (CIÉ). The station is named in honour of Seán Heuston, an executed leader of the 1916 Easter Rising, who had worked in the station's offices.

Pearse railway station or Dublin Pearse is a railway station on Westland Row on the Southside of Dublin, Ireland. It is Ireland's busiest commuter station and second busiest station overall with 9 million passenger journeys through the station in 2016.

Clondalkin is a southwestern outer suburb of Dublin, Ireland, 10 km (6 mi) west of Dublin city centre, Ireland, under the administrative jurisdiction of South Dublin. It features an 8th-century round tower that acts as a focal point for the area.

The Seaford line is a commuter railway line in the city of Adelaide, South Australia. It is the city's second longest metropolitan railway line at 35.9 kilometres (22.3 mi).

Transport 21 was an Irish infrastructure plan, announced in November 2005. Its aims were to greatly expand Ireland's transport network. A cost estimate of €34 billion was attached to the plan at the time.

The Green Line is one of the two lines of Dublin's Luas light rail system. The Green Line was formerly entirely in the south side of Dublin city. It mostly follows the route of the old Harcourt Street railway line, which was reserved for possible re-use when it closed in 1958. The Green Line allows for passengers to transfer at O’ Connell GPO and Marlborough to Luas Red Line services and also allows commuters to use Broombridge as an interchange station to reach outer suburbs such as Castleknock and Ongar as well as Iarnrod Éireann services.
MetroLink is a proposed metro line for the city of Dublin. It replaces an earlier proposal called Metro North which was first recommended in the then Irish Government's 2005 Transport 21 transport plan.

The Dublin Suburban Rail network, branded as Commuter, is a railway network that serves the city of Dublin, Ireland, most of the Greater Dublin Area and outlying towns. The system is made up of five lines:

The Cork Suburban Rail network serves areas in and around Cork city in Ireland.

Adamstown railway station is a station on the Dublin to Kildare Commuter service. It serves the new town of Adamstown and South Western Commuter services call to the station.

InterCity is the brand name given to rail services operated by Iarnród Éireann that run between Dublin and other major cities in Ireland. InterCity branding is also used in other European countries by unaffiliated organizations.

Commuter is a brand of suburban rail services operated by Iarnród Éireann in the Republic of Ireland, serving the cities of Dublin, Cork, Limerick and Galway. This brand is distinct from the longer distance InterCity brand, and Dublin's higher frequency DART brand. Most Commuter services share a track with InterCity services. During the first decade of the new millennium, Iarnród Éireann put a significant amount of effort into upgrading its network, with new tracks, signalling, station upgrades and trains. Commuter services are operated by diesel multiple unit train sets.

This article deals with transport in the Greater Dublin Area centred on the city of Dublin in Ireland.

The Dublin-Navan line is a partially-open commuter rail line between Dublin and the town of Navan in County Meath. Since September 2010, train services operate from Docklands Station to M3 Parkway, with an extension to Navan itself proposed.



















