
Codeinone is an isoquinolone alkaloid found in the opium poppy. As an analgesic, it is one-third the potency of codeine. It is an important intermediate in the production of hydrocodone–a painkiller about three-quarters the potency of morphine–as well as of oxycodone, though the latter can also be synthesized from thebaine.
In enzymology, an aryl-alcohol dehydrogenase (NADP+) (EC 1.1.1.91) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a dihydrokaempferol 4-reductase (EC 1.1.1.219) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase (NADPH) (EC 1.1.1.34) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a mevaldate reductase (NADPH) (EC 1.1.1.33) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a salutaridine reductase (NADPH) (EC 1.1.1.248) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a tetrahydroxynaphthalene reductase (EC 1.1.1.252) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, divinyl chlorophyllide a 8-vinyl-reductase (EC 1.3.1.75) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a berbamunine synthase (EC 1.14.19.66, Formerly EC 1.1.3.34 and EC 1.14.21.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a protopine 6-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.55) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a salutaridine synthase (EC 1.14.21.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a (S)-cheilanthifoline synthase (EC 1.14.21.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a (S)-stylopine synthase (EC 1.14.21.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an aryl-aldehyde dehydrogenase (NADP+) (EC 1.2.1.30) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
A glutamyl-tRNA reductase (EC 1.2.1.70) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 1,2-dehydroreticulinium reductase (NADPH) (EC 1.5.1.27) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Berberine reductase (EC 1.5.1.31) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a salutaridinol 7-O-acetyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
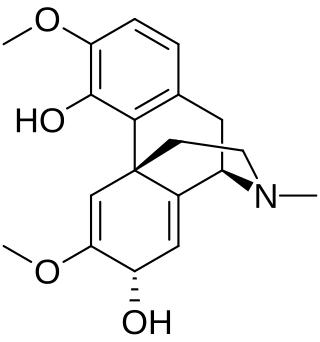
Salutaridinol is a modified benzyltetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloid with the formula C19H23NO4. It is produced in the secondary metabolism of the opium poppy Papaver somniferum (Papaveraceae) as an intermediate in the biosynthetic pathway that generates morphine. As an isoquinoline alkaloid, it is fundamentally derived from tyrosine as part of the shikimate pathway of secondary metabolism. Salutaridinol is a product of the enzyme salutaridine: NADPH 7-oxidoreductase and the substrate for the enzyme salutaridinol 7-O-acetyltransferase, which are two of the four enzymes in the morphine biosynthesis pathway that generates morphine from (R)-reticuline. Salutaridinol's unique position adjacent to two of the four enzymes in the morphine biosynthesis pathway gives it an important role in enzymatic, genetic, and synthetic biology studies of morphine biosynthesis. Salutaridinol levels are indicative of the flux through the morphine biosynthesis pathway and the efficacy of both salutaridine: NADPH 7-oxidoreductase and salutaridinol 7-O-acetyltransferase.
Morphinone reductase is an enzyme which catalyzes the NADH-dependent saturation of the carbon-carbon double bond of morphinone and codeinone, yielding hydromorphone and hydrocodone respectively. This saturation reaction is assisted by a FMN cofactor and the enzyme is a member of the α/β-barrel flavoprotein family. The sequence of the enzyme has been obtained from bacteria Pseudomonas putida M10 and has been successfully expressed in yeast and other bacterial species. The enzyme is reported to harbor high sequence and structural similarity to the Old Yellow Enzyme, a large group of flavin-dependent redox biocatalysts of yeast species, and an oestrogen-binding protein of Candida albicans. The enzyme has demonstrated value in biosynthesis of semi-opiate drugs in microorganisms, expanding the chemical diversity of BIA biosynthesis.




